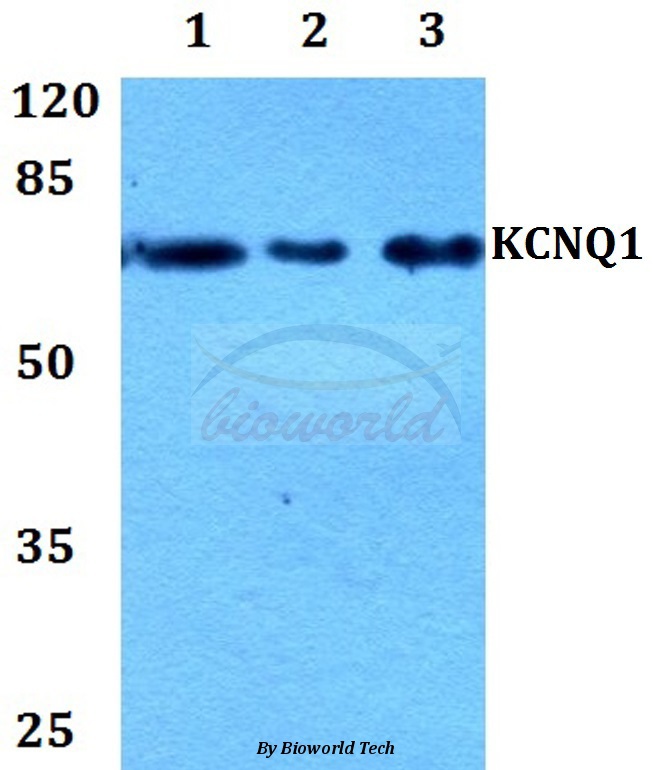
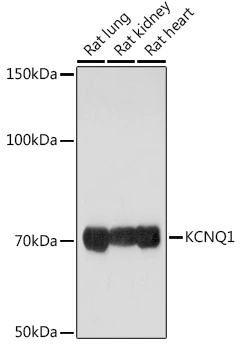
WB analysis of human heart lysate using GTX88458 KCNQ1 antibody, C-term. Dilution : 1μg/ml Loading : 35μg protein in RIPA buffer
KCNQ1 antibody, C-term
GTX88458
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetKCNQ1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameKCNQ1 antibody, C-term
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1-3microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.50 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3784
- Target nameKCNQ1
- Target descriptionpotassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1
- Target synonymsATFB1, ATFB3, JLNS1, KCNA8, KCNA9, KVLQT1, Kv1.9, Kv7.1, LQT, LQT1, RWS, SQT2, WRS, potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1, IKs producing slow voltage-gated potassium channel subunit alpha KvLQT1, kidney and cardiac voltage dependend K+ channel, potassium channel, voltage gated KQT-like subfamily Q, member 1, potassium voltage-gated channel, KQT-like subfamily, member 1, slow delayed rectifier channel subunit, voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.1
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP51787
- Protein NamePotassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a voltage-gated potassium channel required for repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. This protein can form heteromultimers with two other potassium channel proteins, KCNE1 and KCNE3. Mutations in this gene are associated with hereditary long QT syndrome 1 (also known as Romano-Ward syndrome), Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, and familial atrial fibrillation. This gene exhibits tissue-specific imprinting, with preferential expression from the maternal allele in some tissues, and biallelic expression in others. This gene is located in a region of chromosome 11 amongst other imprinted genes that are associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), and itself has been shown to be disrupted by chromosomal rearrangements in patients with BWS. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161