Chemical Structure
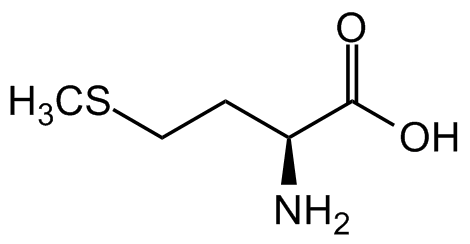
L-Methionine [63-68-3] [63-68-3]
CDX-M0524
CAS Number63-68-3
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight149.21
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameL-Methionine [63-68-3] [63-68-3]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number63-68-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC5H11NO2S
- Molecular Weight149.21
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 63-68-3. Formula: C5H11NO2S. MW: 149.21. Essential amino acid involved in various biochemical processes in humans and mammals. Important in angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels and supplementation may be beneficial in diseases such as Parkinsons, schizophrenia, asthma or allergies, as well as in radiation, copper poisoning, alcoholism or depressions. Through transmethylation it can be converted to S-adenosylmethionine, a primary methyl donor that methylates compounds to form such products as creatine and phosphatidylcholine. Methionine can be converted to cysteine, a precursor of glutathione and taurine. These molecules may regulate intestinal epithelial oxidative status, and may contribute to intestinal mucosal integrity and gut function. Overconsumption of methionine has been associated to cancer growth. Restriction of methionine can increase lifespans and inhibit cancer growth. Used in livestock nutrition. Apart from its nutritional function, also important for the metabolism and gut health of animals. L-Methionine serves as precursor for transmethylation and transsulphuration. Methionine adenosylation results in the formation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM). SAM serves as a methyl donor to a number of substances. This methylation is significantly associated with the immune system functioning. Thus, SAM deficiency causes severe combined immunodeficiencies. L-Methionines metabolic product, glutathione, is known to regulate immune response and has antiviral action. - Essential amino acid involved in various biochemical processes in humans and mammals. Important in angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels and supplementation may be beneficial in diseases such as Parkinsons, schizophrenia, asthma or allergies, as well as in radiation, copper poisoning, alcoholism or depressions. Through transmethylation it can be converted to S-adenosylmethionine, a primary methyl donor that methylates compounds to form such products as creatine and phosphatidylcholine. Methionine can be converted to cysteine, a precursor of glutathione and taurine. These molecules may regulate intestinal epithelial oxidative status, and may contribute to intestinal mucosal integrity and gut function. Overconsumption of methionine has been associated to cancer growth. Restriction of methionine can increase lifespans and inhibit cancer growth. Used in livestock nutrition. Apart from its nutritional function, also important for the metabolism and gut health of animals. L-Methionine serves as precursor for transmethylation and transsulphuration. Methionine adenosylation results in the formation of S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM). SAM serves as a methyl donor to a number of substances. This methylation is significantly associated with the immune system functioning. Thus, SAM deficiency causes severe combined immunodeficiencies. L-Methionines metabolic product, glutathione, is known to regulate immune response and has antiviral action.
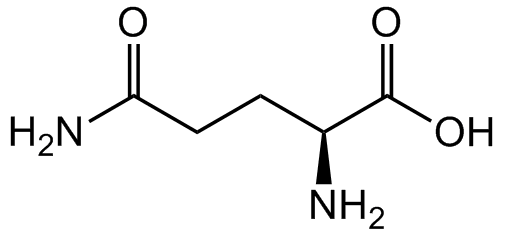
- SMILESN[C@H](C(O)=O)CCSC
- Storage InstructionRT
- UNSPSC12352200