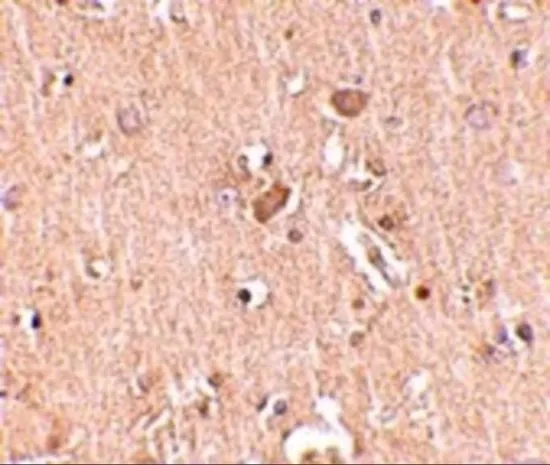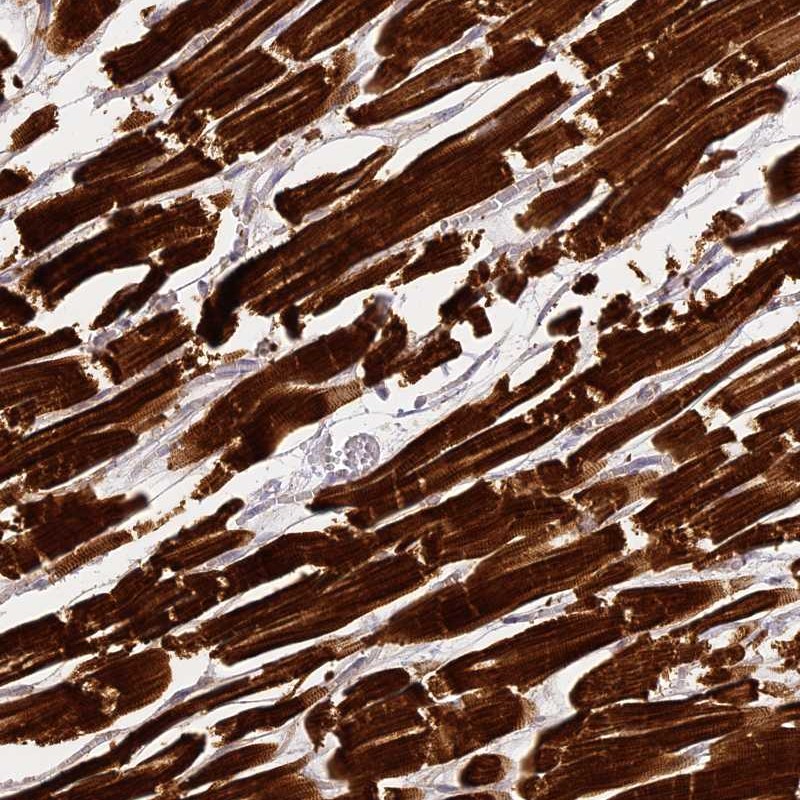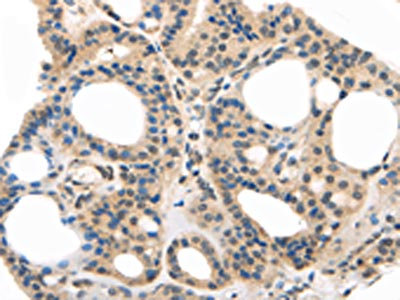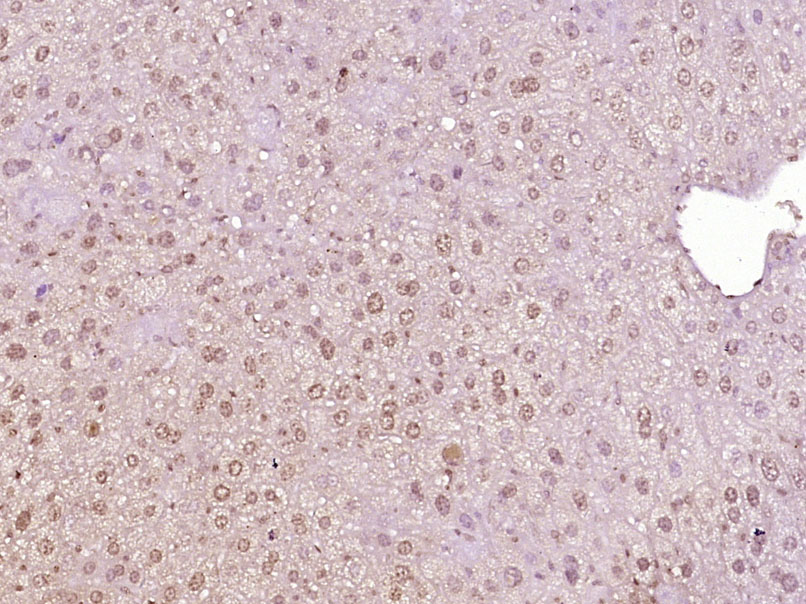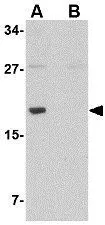
WB analysis of human brain tissue lysate in (A) the absence and (B) the presence of blocking peptide using GTX85388 MED28 antibody. Working concentration : 1 μg/ml
MED28 antibody
GTX85388
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetMED28
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMED28 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1 microg/mL. IHC-P: 2.5 microg/mL. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID80306
- Target nameMED28
- Target descriptionmediator complex subunit 28
- Target synonyms1500003D12Rik, EG1, magicin, mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 28, endothelial-derived gene 1, endothelial-derived protein 1, mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription, subunit 28 homolog, merlin and Grb2-interacting cytoskeletal protein, tumor angiogenesis marker EG-1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9H204
- Protein NameMediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 28
- Scientific DescriptionThe mediator complex is a multi-protein transcriptional co-activator that is expressed ubiquitously in eukaryotes from yeast to mammals and is required for induction of RNA polymerase II (pol II) transcription by DNA binding transcription factor. One of the proteins in this complex is MED28, also known as Magicin. MED28 is expressed in many cell lines and tissues. It has been shown that a down-regulation of MED28 expression in NIH3T3 cells results in a significant induction of several genes associated with smooth muscle cell differentiation and conversely its over-expression represses expression of SMC genes. MED28 can also form a ternary complex with Grb2 and Merlin, the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein, indicating that MED28 may play a role in Merlins tumor suppressive activity. MED28 has also been recently identified as an HIV dependency factor (HDF), suggesting that MED28 may be an important drug target in HIV treatment. At least two isoforms of MED28 are known to exist.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- MED28 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Through NFkappaB in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Huang CY et al., 2017 Jun, J Cell PhysiolRead this paper