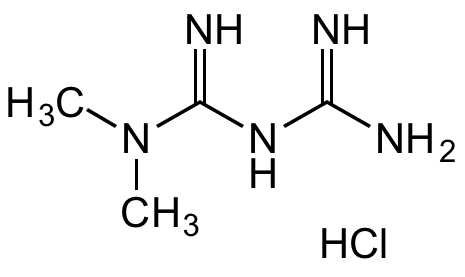
Chemical Structure
Metformin . HCl [1115-70-4] [1115-70-4]
AG-CR1-3689
CAS Number1115-70-4
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight129.2 . 36.5
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameMetformin . HCl [1115-70-4] [1115-70-4]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number1115-70-4
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC4H11N5 . HCl
- Molecular Weight129.2 . 36.5
- Scientific DescriptionAMPK activator. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Reported to stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), leading to the reduction in acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity and induction of fatty acid oxidation. Mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I inhibitor, reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). Antidiabetic and anti-hyperglycemic agent that reduces blood glucose levels, improves insulin sensitivity and decreases insulin resistance. Its metabolic effects, including the inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis, are mediated in part by activation of the LKB1-AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) pathway. Used as weight-loss agent in obesity and as insulin sensitizer in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Leptin sensitizer to mediate the weight-loss effect in the brain. Increases plasma concentrations of the glucose-lowering gut incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which may contribute to metformins glucose-lowering effect. Anticancer agent with antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity in cancer cell lines. Autophagy activator. Activates the aPKC-CBP pathway in neural precursors to promote neurogenesis. Targets brown adipose tissue (BAT) in vivo and reduces oxygen consumption. Anti-inflammatory agent. Described to suppress inflammatory responses by inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) via AMPK-dependent and independent pathways. Also described to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation, subsequent caspase-1 cleavage and interleukin-1beta secretion. - Chemical. CAS: 1115-70-4. Formula: C4H11N5 . HCl. MW: 129.2 . 36.5. . AMPK activator. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. Reported to stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), leading to the reduction in acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) activity and induction of fatty acid oxidation. Mitochondrial electron transport chin complex I inhibitor, reducing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). Antidiabetic and anti-hyperglycemic agent that reduces blood glucose levels, improves insulin sensitivity and decreases insulin resistance. Its metabolic effects, including the inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis, are mediated in part by activation of the LKB1-AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) pathway. Used as weight-loss agent in obesity and as insulin sensitizer in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Leptin sensitizer to mediate the weight-loss effect in the brain. Increase plasma concentrations of the glucose-lowering gut incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which may contribute to metformins glucose-lowering effect. Anticancer agent, with antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity in cancer cell lines. Autophagy activator. Activates the aPKC-CBP pathway in neural precursors to promote neurogenesis. Targets brown adipose tissue (BAT) in vivo and reduces oxygen consumption.
- SMILESCN(C(NC(N)=N)=N)C.Cl
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200



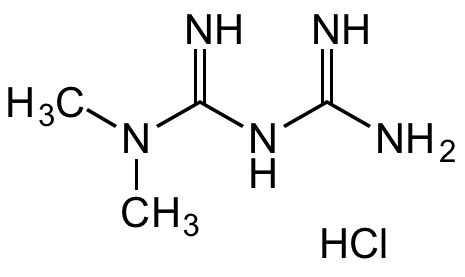
![Metformin hydrochloride [1115-70-4] [1115-70-4]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/C9/CgoaEGY7PfCEJAk7AAAAAL6wI4s089.png)