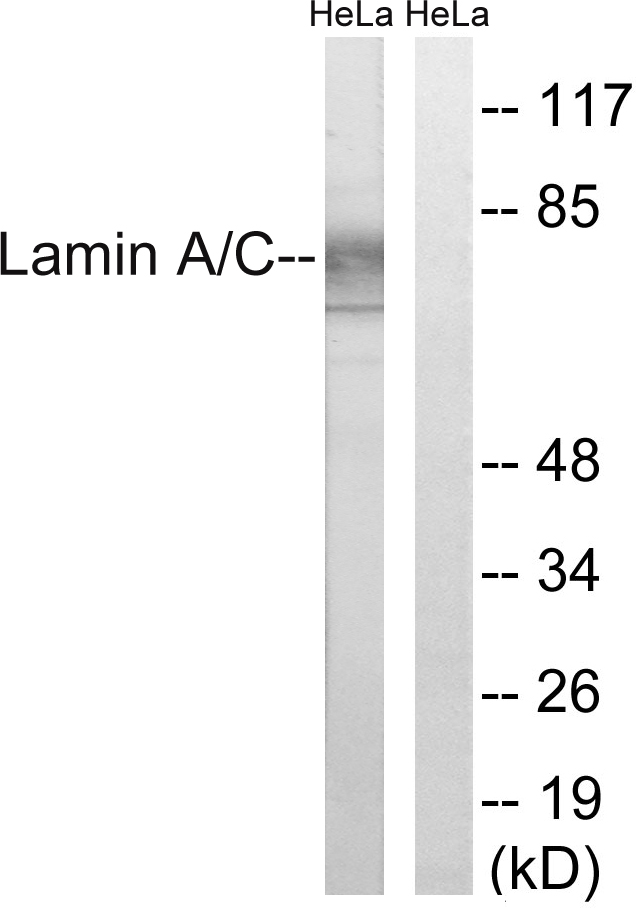
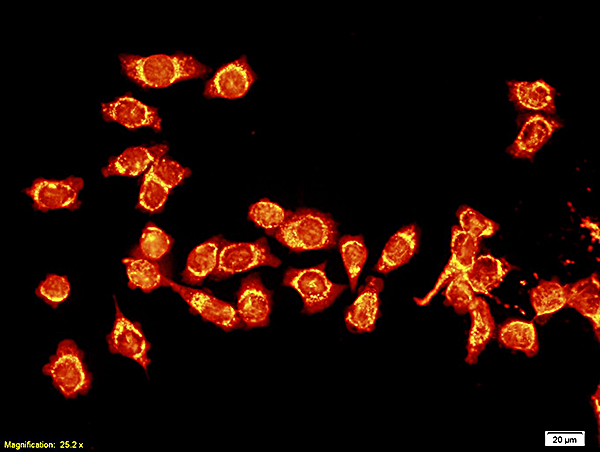
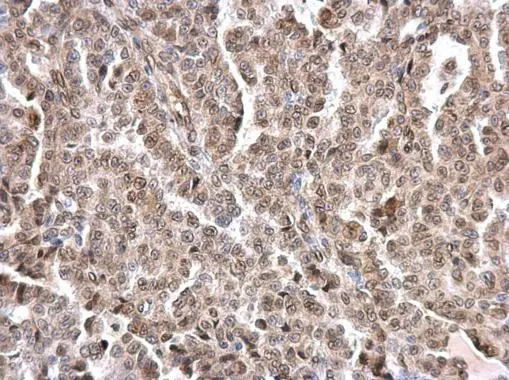
Mouse anti Lamin A
MUB1101P-CE/IVD
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Canine, Human, Mouse, Rat
TargetLMNA
Overview
- SupplierNordic-MUbio
- Product NameMouse anti Lamin A
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier Note133A2 is suitable for immunoblotting, immunocytochemistry on permeabilized cells, immunohistochemistry on frozen sections and paraffin embedded tissues, and flow cytometry. Optimal antibody dilution should be determined by titration; recommended range is 1:100 - 1:200 for immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry with fluorescent secondary antibodies or avidin-biotinylated horseradish peroxidase complex (ABC) as detection reagent, and 1:100 - 1:1000 for immunoblotting applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- Applications SupplierFlow Cytometry;Immunocytochemistry;Immunohistochemistry (frozen);Immunohistochemistry (paraffin);Western Blotting
- CertificationCE-IVD
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID133A2
- Gene ID4000
- Target nameLMNA
- Target descriptionlamin A/C
- Target synonymsCDCD1, CDDC, CMD1A, CMT2B1, EMD2, FPL, FPLD, FPLD2, HGPS, IDC, LDP1, LFP, LGMD1B, LMN1, LMNC, LMNL1, MADA, PRO1, lamin, 70 kDa lamin, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, lamin A/C-like 1, lamin C, mandibuloacral dysplasia type A, prelamin-A/C, progerin, renal carcinoma antigen NY-REN-32
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG3
- Protein IDP02545
- Protein NamePrelamin-A/C
- Source133A2 is a mouse monoclonal IgG3/kappa antibody obtained from fusion of P3/X63.Ag8.653 mouse myeloma cells with spleen cells from a BALB/c mouse immunized with partially purified recombinant human lamin A.
- ReactivityBovine, Canine, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Reactivity SupplierBovine;Canine;Human;Mouse;Rat
- UNSPSC12352203