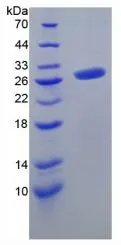
SDS-PAGE analysis of GTX00295-pro Mouse FGF23 protein (active).
Mouse FGF23 protein, His tag (active)
GTX00295-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDQ9EPC2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMouse FGF23 protein, His tag (active)
- Delivery Days Customer9
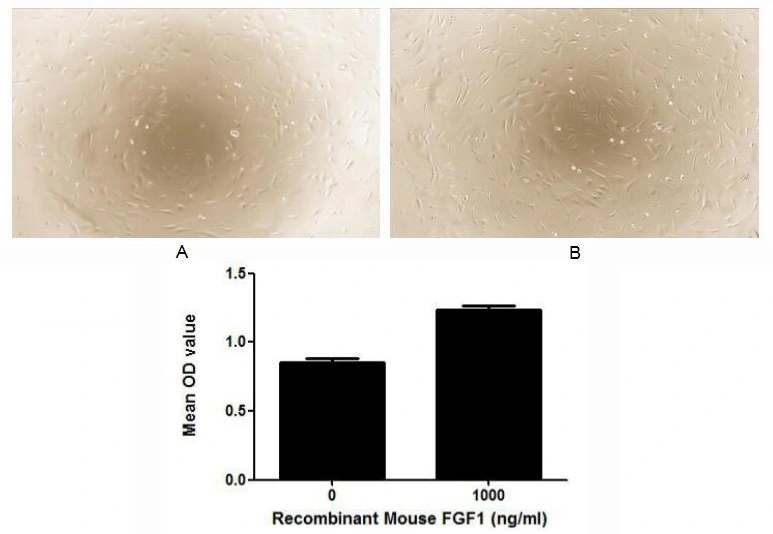
- Application Supplier NoteFGF23 (Fibroblast growth factor 23) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family, which possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities and are involved in a variety of biological processes. A proliferation assay was conducted to detect the bioactivity of recombinant mouse FGF23 using 3T3 cells. Briefly, 3T3 cells were seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates at a density of 2000 cells/well and allowed to attach overnight, then the medium was replaced with serum-free standard DMEM prior to the addition of various concentrations of FGF23. After incubated for 48h, cells were observed by inverted microscope and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, 10 microl of CCK-8 solution was added to each well of the plate, then the absorbance at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader after incubating the plate for 1-4 hours at 37C. Proliferation of 3T3 cells after incubation with FGF23 for 48h observed by inverted microscope. Cell viability was assessed by CCK-8 (Cell Counting Kit-8 ) assay after incubation with recombinant FGF23 for 48h. And FGF23 significantly increased cell viability of 3T3 cells.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID64654
- Target nameFgf23
- Target descriptionfibroblast growth factor 23
- Target synonymsFgf8b, fibroblast growth factor 23, FGF-23, fibroblast growth factor 8b
- Protein IDQ9EPC2
- Protein NameFibroblast growth factor 23
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the fibroblast growth factor family. The encoded protein regulates phosphate homeostasis and vitamin D metabolism. Mutation of the related gene in humans causes autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic rickets (ADHR). The secreted protein is further cleaved into N- and C-terminal chains, which results in loss of function. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2013]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116120
- SpeciesMouse