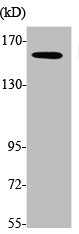![WB analysis of various tissue lysates using GTX11095 MYO6 antibody [MUD-19]. Dilution : 0.5 microg/mL Lane 1: A431 Lane 2: MCF-7 Lane 3: MDA-MB-231 WB analysis of various tissue lysates using GTX11095 MYO6 antibody [MUD-19]. Dilution : 0.5 microg/mL Lane 1: A431 Lane 2: MCF-7 Lane 3: MDA-MB-231](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX11095/GTX11095_20230502_WB_23050118_406.webp)
WB analysis of various tissue lysates using GTX11095 MYO6 antibody [MUD-19]. Dilution : 0.5 microg/mL Lane 1: A431 Lane 2: MCF-7 Lane 3: MDA-MB-231
MYO6 antibody [MUD-19]
GTX11095
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetMYO6
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMYO6 antibody [MUD-19]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 2 microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDMUD-19
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4646
- Target nameMYO6
- Target descriptionmyosin VI
- Target synonymsDFNA22, DFNB37, unconventional myosin-VI, unconventional myosin-6
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDQ9UM54
- Protein NameUnconventional myosin-VI
- Scientific DescriptionMyosins belong to a superfamily of actin based motor proteins comprising at least 15 or more classes. There are two main groups of myosins: the conventional (class II) and the unconventional myosins. Myosin VI is a relatively abundant widespread unconventional myosin composed of an N-terminal motor domain, a light chain binding neck region, a coil-coiled region, and a highly conserved C-terminal domain. At the converter region between the catalytic head and the neck region of myosin VI, there is a characteristic linker of approximately 50 amino acids. Native myosin VI is apparently a two-headed dimer of the heavy chains with each heavy chain bound to calmodulin light chain. Myosin VI is a unique reverse actin motor in vitro i.e. to display motility towards the pointed (minus) ends of actin filaments, a direction opposite to all other currently known myosins.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Hennlein L, Ghanawi H, Gerstner F, et al. Plastin 3 rescues cell surface translocation and activation of TrkB in spinal muscular atrophy. J Cell Biol. 2023,222(3). doi: 10.1083/jcb.202204113Read this paper