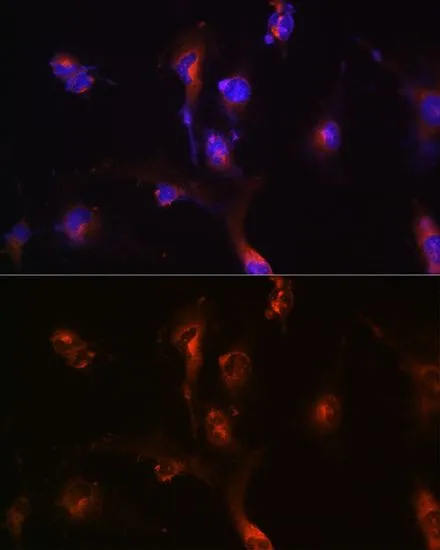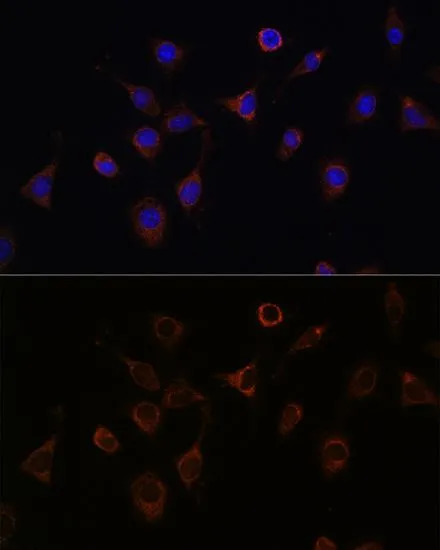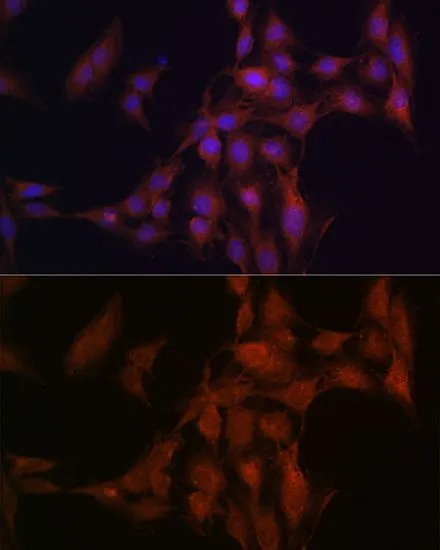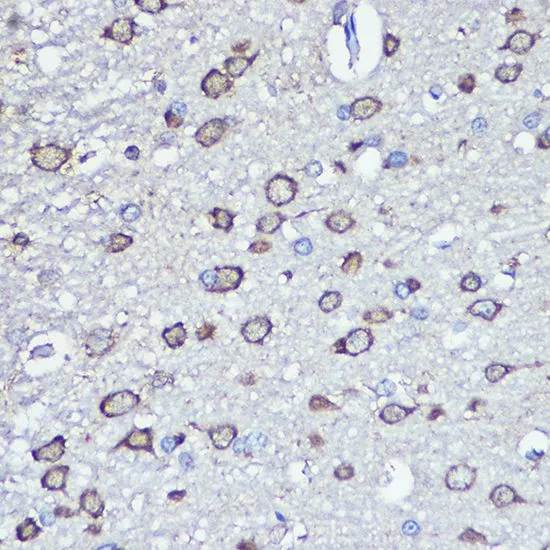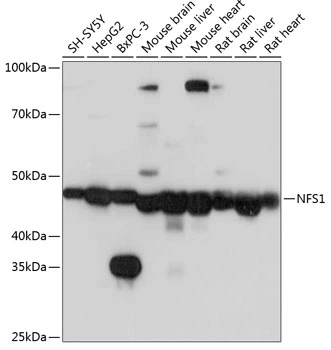
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX33356 NFS1 antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane
NFS1 antibody
GTX33356
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetNFS1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNFS1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:200. IHC-P: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9054
- Target nameNFS1
- Target descriptionNFS1 cysteine desulfurase
- Target synonymsCOXPD52, HUSSY-08, IscS, NIFS, cysteine desulfurase, NFS1 nitrogen fixation 1 homolog, cysteine desulfurase, mitochondrial, nitrogen fixation 1 (S. cerevisiae, homolog), nitrogen-fixing bacteria S-like protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9Y697
- Protein NameCysteine desulfurase
- Scientific DescriptionIron-sulfur clusters are required for the function of many cellular enzymes. The proteins encoded by this gene supply inorganic sulfur to these clusters by removing the sulfur from cysteine, creating alanine in the process. This gene uses alternate in-frame translation initiation sites to generate mitochondrial forms and cytoplasmic/nuclear forms. Selection of the alternative initiation sites is determined by the cytosolic pH. The encoded proteins belong to the class-V family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent aminotransferases. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- The one-carbon pool controls mitochondrial energy metabolism via complex I and iron-sulfur clusters. Rosenberger FA et al., 2021 Feb, Sci AdvRead this paper