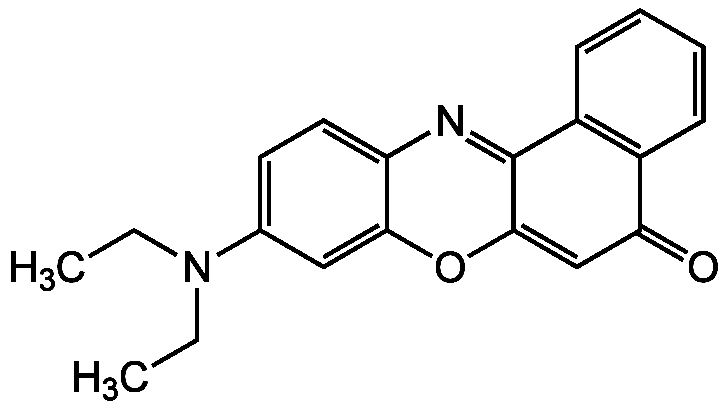
Chemical Structure
Nile Red [7385-67-3]
CDX-N0107
CAS Number7385-67-3
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight318.4
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameNile Red [7385-67-3]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number7385-67-3
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC20H18N2O2
- Molecular Weight318.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 7385-67-3. Formula: C20H18N2O2. MW: 318.4. Synthetic. Uncharged, hydrophobic, photostable fluorescent probe that strongly fluoresces bright red in hydrophobic (lipid-rich) environments, but is almost nonfluorescent in water. This lipophilic stain is commonly used for the detection of intracellular lipid droplets in cells such as adipocytes by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. It has been shown to detect the exposure or formation of new hydrophobic surfaces induced by ligand binding to calmodulin, oligomerization of melittin, or unfolding of ovalbumin during early thermal denaturation. This product has been employed to stain cell structures, as well as to visualize and localize colloidal drug carriers. Has been used to stain lipophilic proteins that have been separated by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis or to detect sphingolipids on thin-layer chromatograms. The fluorescence is unaffected between pH 4.5 and 8.5 and may be used in dilute concentrations to investigate hydrophobic protein sites. Spectral properties: Intracellular fat vacuoles, filled with neutral lipids such as cholesterol, lipoproteins and triglycerides will fluoresce green (Abs/Em =485/525) while polar lipids, such as phospholipids, will fluoresce red (Abs/Em = 552/636 nm). - Uncharged, hydrophobic, photostable fluorescent probe that strongly fluoresces bright red in hydrophobic (lipid-rich) environments, but is almost nonfluorescent in water. This lipophilic stain is commonly used for the detection of intracellular lipid droplets in cells such as adipocytes by fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. It has been shown to detect the exposure or formation of new hydrophobic surfaces induced by ligand binding to calmodulin, oligomerization of melittin, or unfolding of ovalbumin during early thermal denaturation. This product has been employed to stain cell structures, as well as to visualize and localize colloidal drug carriers. Has been used to stain lipophilic proteins that have been separated by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis or to detect sphingolipids on thin-layer chromatograms. The fluorescence is unaffected between pH 4.5 and 8.5 and may be used in dilute concentrations to investigate hydrophobic protein sites. Spectral properties: Intracellular fat vacuoles, filled with neutral lipids such as cholesterol, lipoproteins and triglycerides will fluoresce green (Abs/Em =485/525) while polar lipids, such as phospholipids, will fluoresce red (Abs/Em = 552/636 nm). Extinction coeff. 0.60 +/- 0.05 (0.01g/l; 0,5cm).
- SMILESCCN(CC)C1=CC=C2N=C3C(OC2=C1)=CC(=O)C1=C3C=CC=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12162000