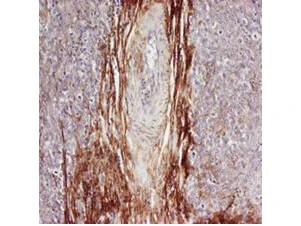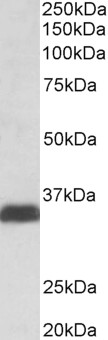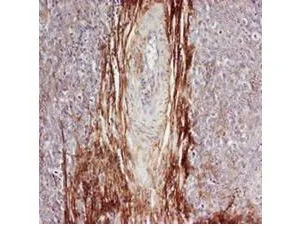
Rabbit anti-Osteopontin (GTX28448) was used at a 1:100-1:300 dilution to detect osteopontin by immunohistochemistry. Osteopontin is a normal component of elastic fibers in the breast (shown heavily stained in this section of human breast tumor cells). There is also weak staining of the extracellular matrix. Osteopontin is not expressed in breast tumor cells, and there is no staining of the breast cells in this section. No antigen retrieval is required
Osteopontin antibody
GTX28448
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
TargetSPP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameOsteopontin antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:2000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:300. IHC-Fr: 1:100-1:300. IP: 1:100. ELISA: 1:5000-1:20000. IHC: 1:100 - 1:300. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration95 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6696
- Target nameSPP1
- Target descriptionsecreted phosphoprotein 1
- Target synonymsBNSP, BSPI, ETA-1, OPN, osteopontin, SPP1/CALPHA1 fusion, early T-lymphocyte activation 1, lnc-PKD2-2-3, nephropontin, osteopontin/immunoglobulin alpha 1 heavy chain constant region fusion protein, secreted phosphoprotein 1 (osteopontin, bone sialoprotein I, early T-lymphocyte activation 1), urinary stone protein, uropontin
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP10451
- Protein NameOsteopontin
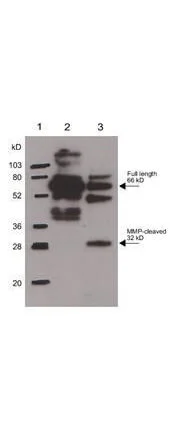
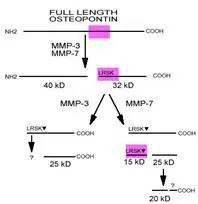
- Scientific DescriptionOsteopontin (OPN) is an arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD)-containing glycoprotein that interacts with integrins and CD44 as major receptors (ref 1). OPN is multifunctional, with activities in cell migration, cell survival, inhibition of calcification, regulation of immune cell function, and control of tumor cell phenotype (ref 1-4). Targeting of the gene encoding OPN, spp1 , has revealed that while OPN is not necessary for normal embryonic development, fertility, and health under pathogen-free conditions (ref 5, 6), loss of the protein has significant consequences in several models of injury/disease as diverse as renal injury, viral and bacterial infection, bone remodeling, and tumor growth (ref 7-12). The fact that no other proteins seem to share a redundant activity with OPN under these conditions suggests that OPN has a unique functional role during tissue injury and stress. Interestingly, several members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are also induced during injury/disease processes in patterns overlapping that of OPN (ref 13). OPN has recently been shown to be a novel substrate for two MMPs, MMP-3 (stromelysin-1) and MMP-7 (matrilysin) (ref 14). There are three cleavage sites for MMP-3 in human OPN, two of which are also cleaved by MMP-7 (see cleavage diagram). Biological assays demonstrate that the MMP-cleaved OPN has increased activity in promoting both cell adhesion and migration compared with full-length OPN. In addition, using inhibitory reagents, it was shown that the same receptors that interact with OPN also mediate interaction of MMP-cleaved OPN with tumor cells, suggesting that active forms of OPN at sites of tissue injury may be regulated by the activity of proteases including MMPs and that the differences in activity of modified OPN may be explained by differences in binding affinity of integrins or distinct downstream signaling events (ref 14).
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Malta FS, Garcia RP, Azarias JS, et al. Impact of hyperglycemia and treatment with metformin on ligature-induced bone loss, bone repair and expression of bone metabolism transcription factors. PLoS One. 2020,15(8):e0237660. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237660Read this paper
- Goriainov V, Cook RB, Murray JW, et al. Human Skeletal Stem Cell Response to Multiscale Topography Induced by Large Area Electron Beam Irradiation Surface Treatment. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2018,6:91. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00091Read this paper
- Pore SK, Hahm ER, Latoche JD, et al. Prevention of breast cancer-induced osteolytic bone resorption by benzyl isothiocyanate. Carcinogenesis. 2018,39(2):134-145. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx114Read this paper
- Wang JY, Chen WM, Wen CS, et al. Du-Huo-Ji-Sheng-Tang and its active component Ligusticum chuanxiong promote osteogenic differentiation and decrease the aging process of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017,198:64-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.011Read this paper
- Ghanaati S, Unger RE, Webber MJ, et al. Scaffold vascularization in vivo driven by primary human osteoblasts in concert with host inflammatory cells. Biomaterials. 2011,32(32):8150-60. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.07.041Read this paper