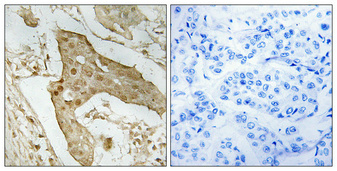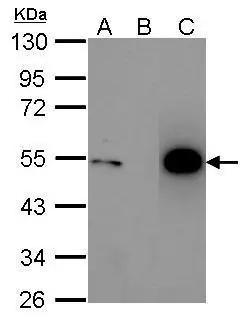
Immunoprecipitation of p53 protein. HCT116 lysates with 30uM cisplatin treatment for 24 hours were subjected to immunoprecipitation using (B) normal rabbit IgG or (C) 2.5 ug of anti-p53 antibody (GTX100629). (A) Input, 20ug of HCT116 lysates. The precipitated protein was detected by GTX100629 diluted at 1:10000. EasyBlot anti-Rabbit IgG Kit (GTX225856-01) was used in Western blot.
p53 antibody [N1], N-term
GTX100629
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetTP53
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namep53 antibody [N1], N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7157
- Target nameTP53
- Target descriptiontumor protein p53
- Target synonymsBCC7, BMFS5, LFS1, P53, TRP53, cellular tumor antigen p53, antigen NY-CO-13, mutant tumor protein 53, phosphoprotein p53, transformation-related protein 53, tumor protein 53, tumor supressor p53
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP04637
- Protein NameCellular tumor antigen p53
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes tumor protein p53, which responds to diverse cellular stresses to regulate target genes that induce cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, senescence, DNA repair, or changes in metabolism. p53 protein is expressed at low level in normal cells and at a high level in a variety of transformed cell lines, where its believed to contribute to transformation and malignancy. p53 is a DNA-binding protein containing transcription activation, DNA-binding, and oligomerization domains. It is postulated to bind to a p53-binding site and activate expression of downstream genes that inhibit growth and/or invasion, and thus function as a tumor suppressor. Mutants of p53 that frequently occur in a number of different human cancers fail to bind the consensus DNA binding site, and hence cause the loss of tumor suppressor activity. Alterations of this gene occur not only as somatic mutations in human malignancies, but also as germline mutations in some cancer-prone families with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Multiple p53 variants due to alternative promoters and multiple alternative splicing have been found. These variants encode distinct isoforms, which can regulate p53 transcriptional activity. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Whole cell extract (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with p53 antibody [N1], N-term (GTX100629) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Whole cell extract (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with p53 antibody [N1], N-term (GTX100629) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100629/GTX100629_39988_20200918_WB_w_23060100_774.webp)
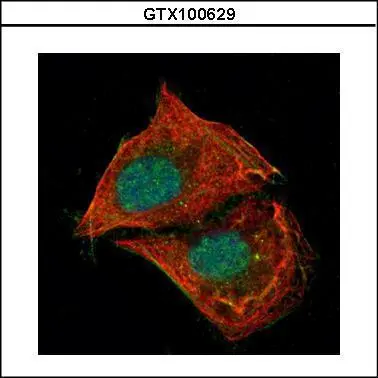
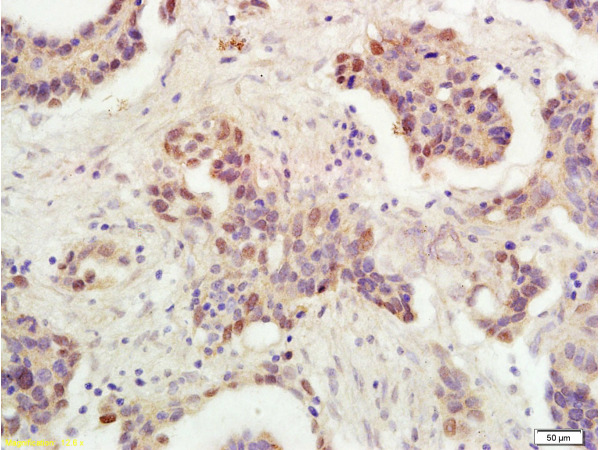
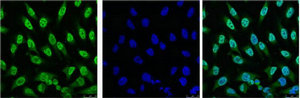
![p53 antibody [N1], N-term detects p53 protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Samples: HCT 116 cells mock (left) and treated with 30 μM Cisplatin for 24 hrs (right) were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: p53 protein stained by p53 antibody [N1], N-term (GTX100629) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. Scale bar = 10 μm. p53 antibody [N1], N-term detects p53 protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Samples: HCT 116 cells mock (left) and treated with 30 μM Cisplatin for 24 hrs (right) were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: p53 protein stained by p53 antibody [N1], N-term (GTX100629) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. Scale bar = 10 μm.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100629/GTX100629_39988_IFA_2_w_23060100_311.webp)