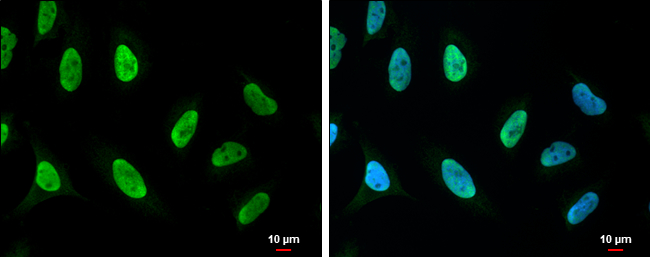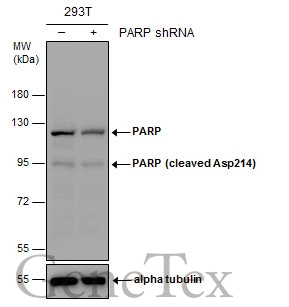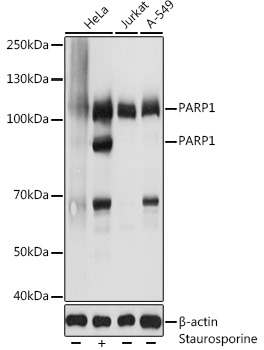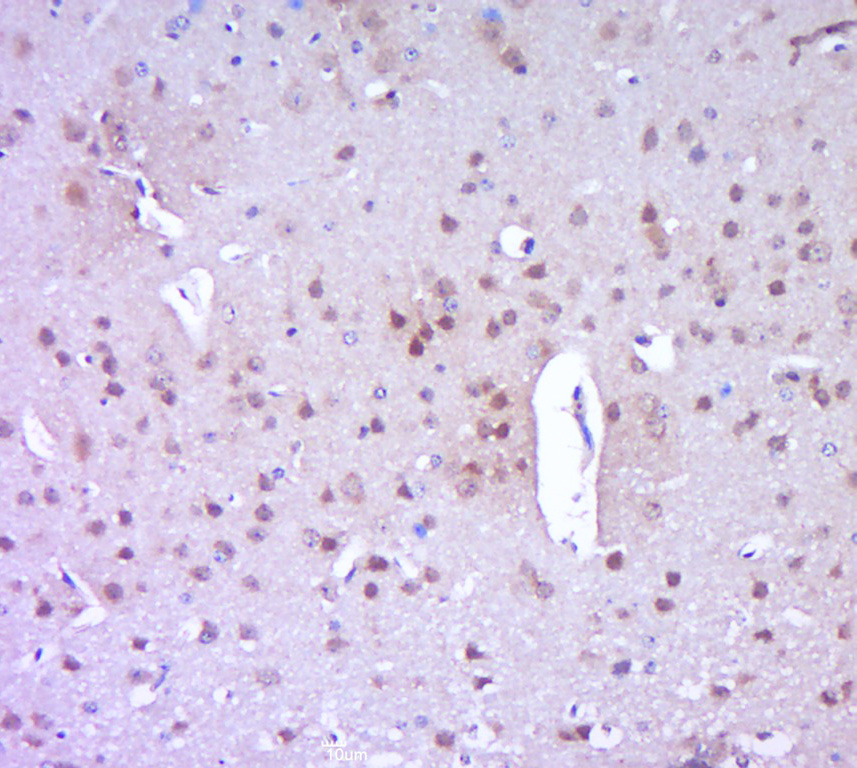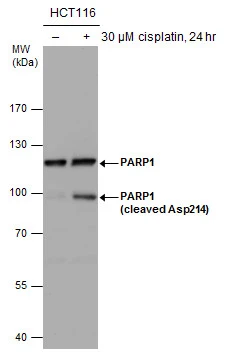
Untreated (–) and treated (+) HCT116 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with PARP antibody (GTX132329) diluted at 1:1000.
PARP antibody
GTX132329
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPARP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NamePARP antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.33 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID142
- Target namePARP1
- Target descriptionpoly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1
- Target synonymsADPRT, ADPRT 1, ADPRT1, ARTD1, PARP, PARP-1, PARS, PPOL, Poly-PARP, pADPRT-1, poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1, ADP-ribosyltransferase (NAD+; poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase), ADP-ribosyltransferase NAD(+), ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 1, DNA ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP1, NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase 1, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase family, member 1, poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase, poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase, poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 1, protein poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase PARP1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP09874
- Protein NamePoly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a chromatin-associated enzyme, poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase, which modifies various nuclear proteins by poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. The modification is dependent on DNA and is involved in the regulation of various important cellular processes such as differentiation, proliferation, and tumor transformation and also in the regulation of the molecular events involved in the recovery of cell from DNA damage. In addition, this enzyme may be the site of mutation in Fanconi anemia, and may participate in the pathophysiology of type I diabetes. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161