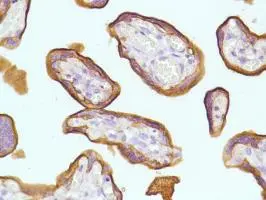
Human Placenta stained with anti-PLAP antibody
Placental Alkaline Phosphatase antibody [SP15] (ready-to-use)
GTX79434
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetALPP
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NamePlacental Alkaline Phosphatase antibody [SP15] (ready-to-use)
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDSP15
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID250
- Target nameALPP
- Target descriptionalkaline phosphatase, placental
- Target synonymsALP, ALPI, IAP, PALP, PLAP, PLAP-1, alkaline phosphatase, placental type, Intestinal alkaline phosphatase, Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase Regan isozyme, alkaline phosphomonoesterase, glycerophosphatase, placental alkaline phosphatase 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP05187
- Protein NameAlkaline phosphatase, placental type
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is an alkaline phosphatase, a metalloenzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphoric acid monoesters. It belongs to a multigene family composed of four alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. The enzyme functions as a homodimer and has a catalytic site containing one magnesium and two zinc ions, which are required for its enzymatic function. The protein is primarily expressed in placental and endometrial tissue; however, strong ectopic expression has been detected in ovarian adenocarcinoma, serous cystadenocarcinoma, and other ovarian cancer cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2015]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Zhu P, Verma A, Prasad T, et al. Expression and Function of Mas-Related G Protein-Coupled Receptor D and Its Ligand Alamandine in Retina. Mol Neurobiol. 2020,57(1):513-527. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01716-4Read this paper




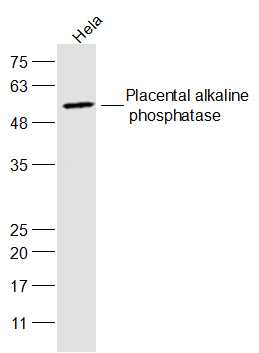

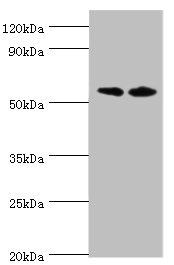
![IHC-P analysis of human seminoma tissue using GTX01925 Placental Alkaline Phosphatase antibody [8A9]. Note the strong membrane and cytoplasmic staining of malignant cells.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX01925/GTX01925_20200811_IHC-P_72_w_23053121_545.webp)