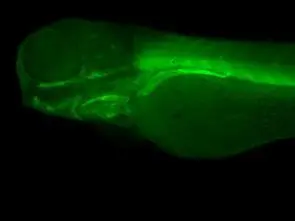
![PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse testis. PUF60 stained by PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse testis. PUF60 stained by PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX629887/GTX629887_41477_20180622_IHC-P_M_1_w_23061202_696.webp)
PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse testis. PUF60 stained by PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
PUF60 antibody [GT917]
GTX629887
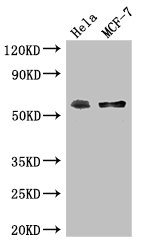
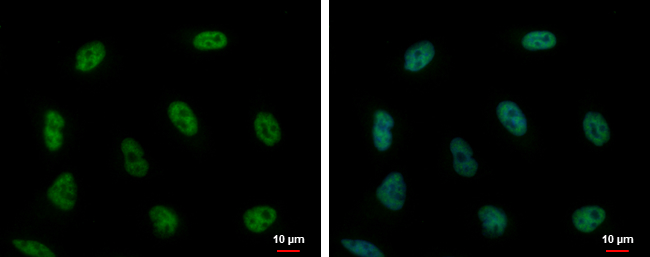
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetPUF60
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NamePUF60 antibody [GT917]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDGT917
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID22827
- Target namePUF60
- Target descriptionpoly(U) binding splicing factor 60
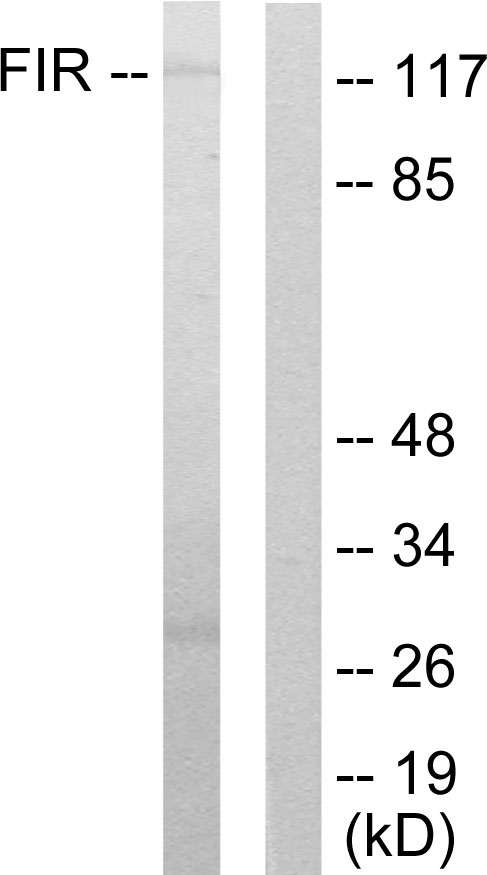
- Target synonymsFIR, RoBPI, SIAHBP1, VRJS, poly(U)-binding-splicing factor PUF60, FBP interacting repressor, FUSE-binding protein-interacting repressor, Ro ribonucleoprotein-binding protein 1, Siah binding protein 1, poly(U) binding splicing factor 60KDa, pyrimidine tract binding splicing factor
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDQ9UHX1
- Protein NamePoly(U)-binding-splicing factor PUF60
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a Ro RNP-binding protein. It interacts with Ro RNPs and their interaction is thought to represent a gain of function for Ro RNPs. This protein also forms a ternary complex with far upstream element (FUSE) and FUSE-binding protein. It can repress a c-myc reporter via the FUSE. It is also known to target transcription factor IIH and inhibit activated transcription. This gene is implicated in the xeroderma pigmentosum disorder. There are two alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding different isoforms. There seems to be evidence of multiple polyadenylation sites for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat colon. PUF60 stained by PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat colon. PUF60 stained by PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX629887/GTX629887_41477_20180622_IHC-P_R_w_23061202_944.webp)
![PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein by Western blot analysis. A. 50 μg rat brain lysate/extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGE PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) dilution: 1:1000 PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein by Western blot analysis. A. 50 μg rat brain lysate/extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGE PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) dilution: 1:1000](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX629887/GTX629887_41477_WB_R_brain_w_23061202_276.webp)
![PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse kidney. PUF60 stained by PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse kidney. PUF60 stained by PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX629887/GTX629887_41477_20180622_IHC-P_M_w_23061202_856.webp)
![PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein by Western blot analysis. A. 50 μg mouse brain lysate/extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGE PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) dilution: 1:1000 PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein by Western blot analysis. A. 50 μg mouse brain lysate/extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGE PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) dilution: 1:1000](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX629887/GTX629887_41477_WB_M_brain_w_23061202_167.webp)
![PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein by Western blot analysis. A. 30 μg 293T whole cell lysate/extract B. 30 μg A431 whole cell lysate/extract C. 30 μg HeLa whole cell lysate/extract D. 30 μg HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGE PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) dilution: 1:1000 PUF60 antibody [GT917] detects PUF60 protein by Western blot analysis. A. 30 μg 293T whole cell lysate/extract B. 30 μg A431 whole cell lysate/extract C. 30 μg HeLa whole cell lysate/extract D. 30 μg HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGE PUF60 antibody [GT917] (GTX629887) dilution: 1:1000](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX629887/GTX629887_41477_WB_w_23061202_475.webp)