Chemical Structure
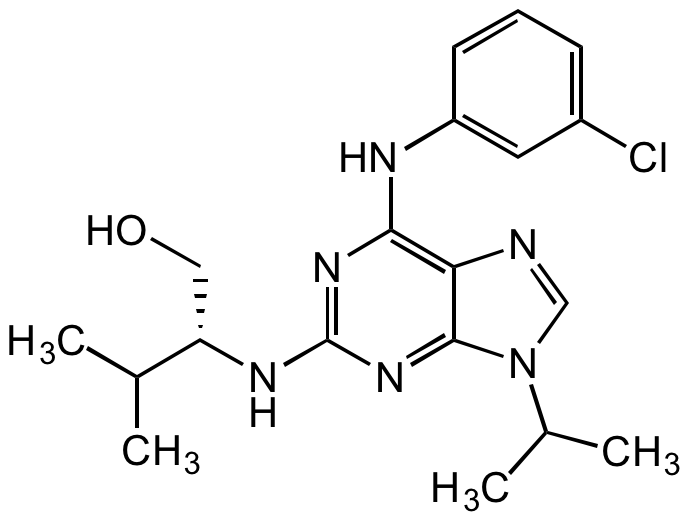
Purvalanol A [212844-53-6]
AG-CR1-2903
CAS Number212844-53-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight388.9
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NamePurvalanol A [212844-53-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number212844-53-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC19H25ClN6O
- Molecular Weight388.9
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 212844-53-6. Formula: C19H25ClN6O. MW: 388.9. Synthetic. Potent, cell permeable cyclin-dependent protein kinase (cdk) inhibitor. Inhibits human CDK1 (IC50=4nM), CDK2/cyclin A (IC50=70nM), Cdc2/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin E (IC50=35nM), CDK4/cyclin D1 (IC50=850nM) as well as CDK5/p35 (IC50=75nM). DYRK1A inhibitor (IC50=300nM). Anticancer agent. Strong apoptotic and autophagy inducer which causes cell cycle arrest in the G1 and G2 phase in various cancer cell lines. More membrane permeable than purvalanol B. Shown to inhibit ABCB1 and ABCB2 transporters and useful in co-treatment with selected anticancer drugs. - Potent, cell permeable cyclin-dependent protein kinase (cdk) inhibitor. Inhibits human CDK1 (IC50=4nM), CDK2/cyclin A (IC50=70nM), Cdc2/cyclin B, CDK2/cyclin E (IC50=35nM), CDK4/cyclin D1 (IC50=850nM) as well as CDK5/p35 (IC50=75nM). DYRK1A inhibitor (IC50=300nM). Anticancer agent. Strong apoptotic and autophagy inducer which causes cell cycle arrest in the G1 and G2 phase in various cancer cell lines. More membrane permeable than purvalanol B. Shown to inhibit ABCB1 and ABCB2 transporters and useful in co-treatment with selected anticancer drugs.
- SMILESClC1=CC=CC(NC2=C3C(N(C(C)C)C=N3)=NC(N[C@@H](CO)C(C)C)=N2)=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12161509