Rabbit anti Human PH Domain-containing family E member 1
X2736P
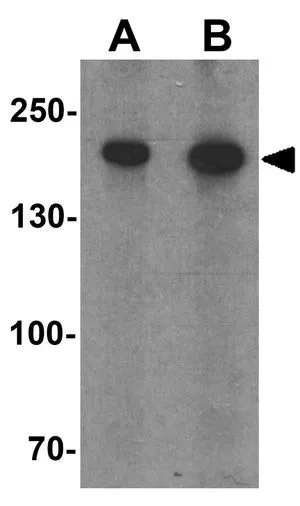
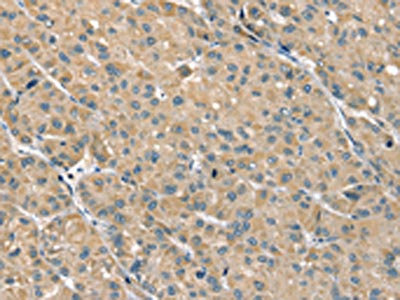
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPHLPP1
Overview
- SupplierNordic-MUbio
- Product NameRabbit anti Human PH Domain-containing family E member 1
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteOptimal concentration should be evaluated by serial dilutions.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- Applications SupplierWestern Blotting;Immunohistochemistry;Western Blotting;ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Gene ID23239
- Target namePHLPP1
- Target descriptionPH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 1
- Target synonymsPHLPP, PLEKHE1, PPM3A, SCOP, PH domain leucine-rich repeat-containing protein phosphatase 1, PH domain-containing family E member 1, SCN circadian oscillatory protein, pleckstrin homology domain containing, family E (with leucine rich repeats) member 1, protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent 3A, suprachiasmatic nucleus circadian oscillatory protein
- HostRabbit
- Protein IDO60346
- Protein NamePH domain leucine-rich repeat-containing protein phosphatase 1
- Scientific DescriptionKIAA0606, PHLPP, PLEKHE1, SCOP, PHLPP1, PH domain leucine-rich repeat-containing protein phosphatase 1; Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family E member 1; Suprachiasmatic nucleus circadian oscillatory protein
- Shelf life instructionSee expiration date on vial
- ReactivityHuman
- Reactivity SupplierHuman
- Reactivity Supplier NoteSynthetic peptide derived from the human PHLPP1 protein
- UNSPSC12352203