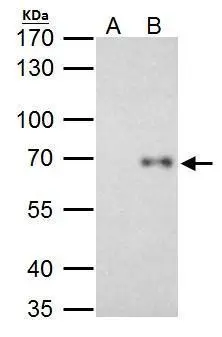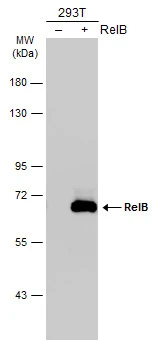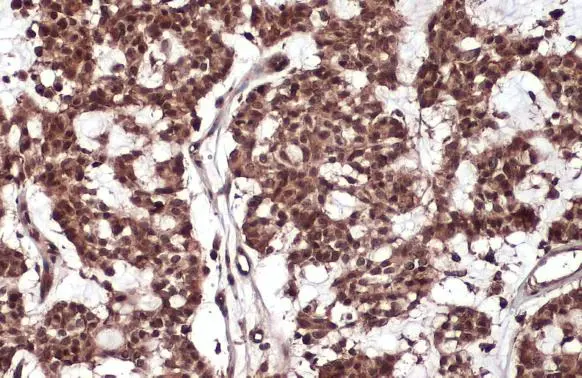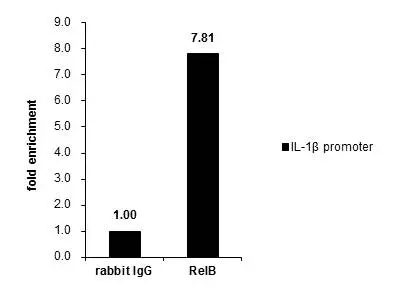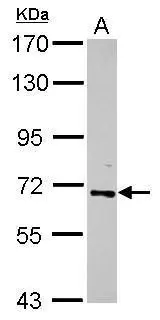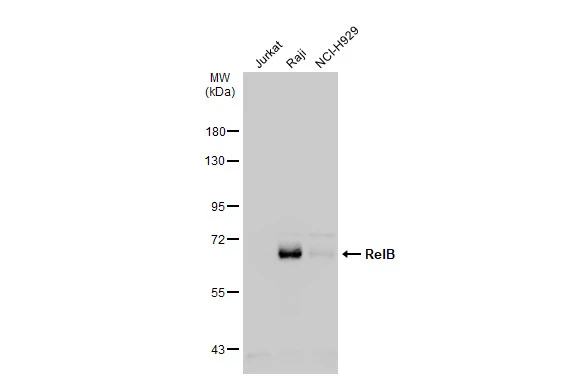
Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with RelB antibody (GTX102333) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
RelB antibody
GTX102333
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetRELB
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameRelB antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.42 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID5971
- Target nameRELB
- Target descriptionRELB proto-oncogene, NF-kB subunit
- Target synonymsI-REL, IMD53, IREL, REL-B, transcription factor RelB, v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B (nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3), v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog B, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ01201
- Protein NameTranscription factor RelB
- Scientific DescriptionNF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric RelB-p50 and RelB-p52 complexes are transcriptional activators. RELB neither associates with DNA nor with RELA/p65 or REL. Stimulates promoter activity in the presence of NFKB2/p49.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161