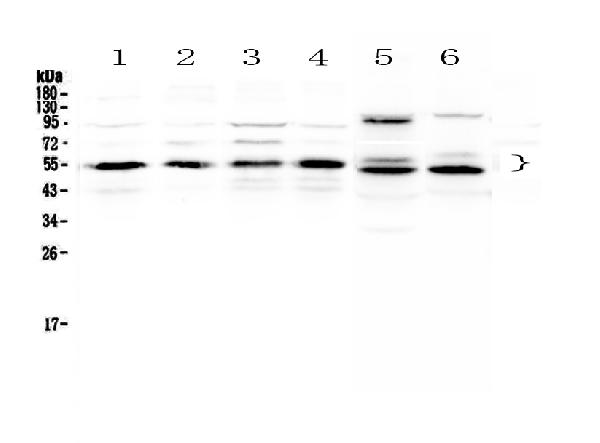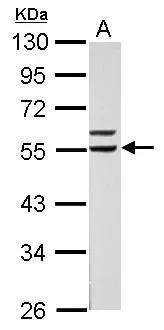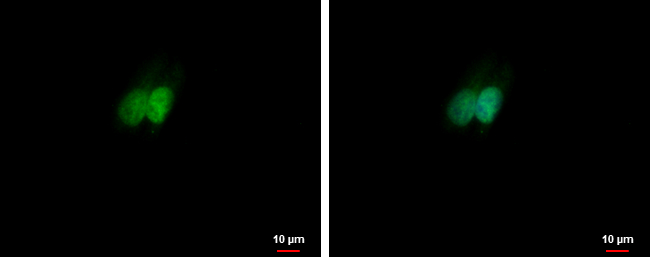
Retinoid X Receptor alpha antibody detects Retinoid X Receptor alpha protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HepG2 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Retinoid X Receptor alpha protein stained by Retinoid X Receptor alpha antibody (GTX113829) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.
Retinoid X Receptor alpha antibody
GTX113829
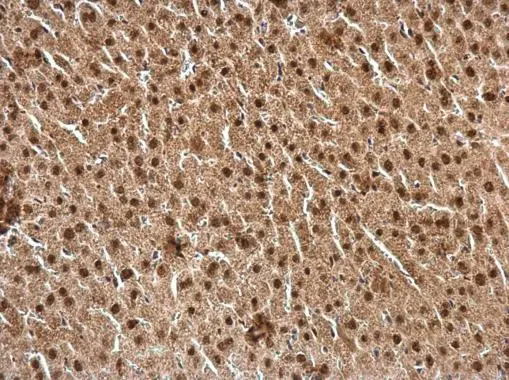
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetRXRA
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameRetinoid X Receptor alpha antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6256
- Target nameRXRA
- Target descriptionretinoid X receptor alpha
- Target synonymsNR2B1, RXR-alpha, RXRalpha, retinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha, nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group B member 1, retinoid X nuclear receptor alpha
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP19793
- Protein NameRetinoic acid receptor RXR-alpha
- Scientific DescriptionRetinoid X receptors (RXRs) and retinoic acid receptors (RARs) are nuclear receptors that mediate the biological effects of retinoids by their involvement in retinoic acid-mediated gene activation. These receptors function as transcription factors by binding as homodimers or heterodimers to specific sequences in the promoters of target genes. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily of transcriptional regulators. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161