SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.617.2.1 Variant, Delta Plus)
AG-40B-0212
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameSARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.617.2.1 Variant, Delta Plus)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
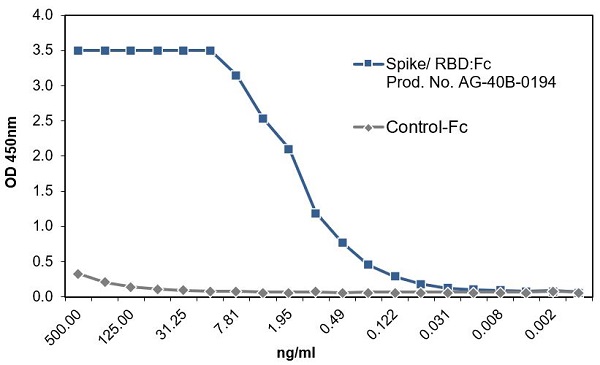
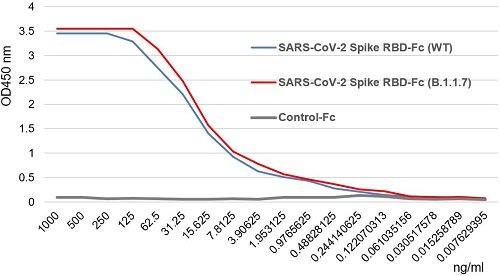
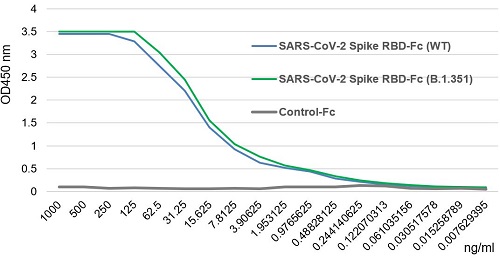
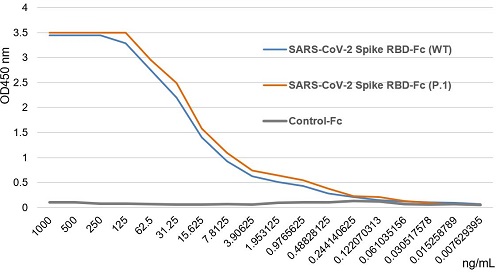
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Protein. Receptor-binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein S1 (aa 319-541) containing the mutations K417N, L452R & T478K is fused to the N-terminus of the Fc region of human IgG1. Binds to anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike (RBD) antibodies in serum or plasma. Binds to human ACE2. Lyophilized. Contains PBS. SARS-CoV-2 shares 79.5% sequence identity with SARS-CoV and is 96.2% identical at the genome level to the bat coronavirus BatCoV RaTG133, suggesting it had originated in bats. The coronaviral genome encodes four major structural proteins: the Spike (S) protein, Nucleocapsid (N) protein, Membrane/Matrix (M) protein and the Envelope (E) protein. The SARS Envelope (E) protein contains a short palindromic transmembrane helical hairpin that seems to deform lipid bilayers, which may explain its role in viral budding and virion envelope morphogenesis. The SARS Membrane/Matrix (M) protein is one of the major structural viral proteins. It is an integral membrane protein involved in the budding of the viral particles and interacts with SARS Spike (S) protein and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N protein contains two domains, both of them bind the virus RNA genome via different mechanisms. The CoV Spike (S) protein assembles as trimer and plays the most important role in viral attachment, fusion and entry. It is composed of a short intracellular tail, a transmembrane anchor and a large ectodomain that consists of a receptor binding S1 subunit (RBD domain) and a membrane-fusing S2 subunit. The S1 subunit contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which binds to the cell surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) present at the surface of epithelial cells. Recently, a new variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.617 was detected in India. Three sublineages have been found, B.1.617.1 (variant Kappa) and B.1.617.3 containing 4 mutations in the Spike protein with a double mutations in the Receptor Binding Region (L452R, E484Q) and B.1.617.2 (variant Delta) that is different since it contains the mutation T478K instead of E484Q. These variants (especially the B.1.617.1 & B.1.617.2) of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus have evolved as fast-growing variants outspacing other variants. Recently, a new variant derived from Delta (called Delta Plus and containing the mutations K417N, L452R & T478K) was detected in India and in several other countries. While studies are still underway, scientists say Delta Plus does not seem to be more transmissible than Delta. - SARS-CoV-2 shares 79.5% sequence identity with SARS-CoV and is 96.2% identical at the genome level to the bat coronavirus BatCoV RaTG133, suggesting it had originated in bats. The coronaviral genome encodes four major structural proteins: the Spike (S) protein, Nucleocapsid (N) protein, Membrane/Matrix (M) protein and the Envelope (E) protein. The SARS Envelope (E) protein contains a short palindromic transmembrane helical hairpin that seems to deform lipid bilayers, which may explain its role in viral budding and virion envelope morphogenesis. The SARS Membrane/Matrix (M) protein is one of the major structural viral proteins. It is an integral membrane protein involved in the budding of the viral particles and interacts with SARS Spike (S) protein and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N protein contains two domains, both of them bind the virus RNA genome via different mechanisms. The CoV Spike (S) protein assembles as trimer and plays the most important role in viral attachment, fusion and entry. It is composed of a short intracellular tail, a transmembrane anchor and a large ectodomain that consists of a receptor binding S1 subunit (RBD domain) and a membrane-fusing S2 subunit. The S1 subunit contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which binds to the cell surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) present at the surface of epithelial cells. Recently, a new variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.617 was detected in India. Three sublineages have been found, B.1.617.1 (variant Kappa) and B.1.617.3 containing 4 mutations in the Spike protein with a double mutations in the Receptor Binding Region (L452R, E484Q) and B.1.617.2 (variant Delta) that is different since it contains the mutation T478K instead of E484Q. These variants (especially the B.1.617.1 & B.1.617.2) of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus have evolved as fast-growing variants outspacing other variants. Recently, a new variant derived from Delta (called Delta Plus and containing the mutations K417N, L452R & T478K) was detected in India and in several other countries. While studies are still underway, scientists say Delta Plus does not seem to be more transmissible than Delta.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100