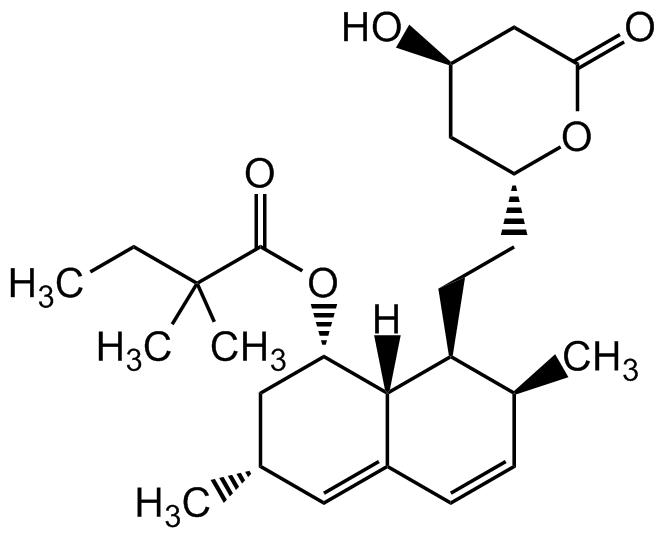
Chemical Structure
Simvastatin [79902-63-9]
AG-CN2-0052
CAS Number79902-63-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight418.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameSimvastatin [79902-63-9]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number79902-63-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC25H38O5
- Molecular Weight418.6
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 79902-63-9. Formula: C25H38O5. MW: 418.6. Synthetic. Synthetic analog of Lovastatin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0051 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0051/lovastatin.html ). Potent competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Anti-hypercholesterolemic agent. Cholesterol/isoprenoid biosynthesis inhibitor. Blocks the production of mevalonate, a critical compound in the production of cholesterol and isoprenoids. Inhibits the isoprenylation of Ras and Rho family GTPases. Smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibitor. Anti-adhesive, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory compound. Proteasome modulator. Stimulates bone formation. Apoptosis inducer. Anticancer compound. Increases cellular resistance to anticancer agents such as doxorubicin and etoposides (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3572 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cr1-3572/etoposide.html ). Suppresses ICAM-1-LFA-1 interactions, which blocks virus replication and infection. Anti-hypertensive agent. Suppresses TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation. - Synthetic analog of Lovastatin (Prod. No. AG-CN2-0051 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0051/lovastatin.html ). Potent competitive HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Anti-hypercholesterolemic agent. Cholesterol/isoprenoid biosynthesis inhibitor. Blocks the production of mevalonate, a critical compound in the production of cholesterol and isoprenoids. Inhibits the isoprenylation of Ras and Rho family GTPases . Anticancer compound that causes cell cycle arrest in G1 and G2/M phases through modulation of proteasome in cancer cell lines. SKP2 E3 ligase inhibitor. Decreases the expression of Skp2 and results in the inhibition of Skp2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p27 and p21, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibitor. Anti-adhesive, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory compound that stimulates bone formation. Suppresses TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation. Increases cellular resistance to anticancer agents such as doxorubicin and etoposides (Prod. No. AG-CR1-3572 http://www.adipogen.com/ag-cr1-3572/etoposide.html ). Suppresses ICAM-1-LFA-1 interactions, which blocks virus replication and infection. Anti-hypertensive agent.
- SMILES[H][C@]12[C@H](C[C@@H](C)C=C1C=C[C@H](C)[C@@H]2CC[C@@H]1C[C@@H](O)CC(=O)O1)OC(=O)C(C)(C)CC
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Simvastatin [79902-63-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/34/7A/CgoaEWarfs2EJF3pAAAAAD6i0Y0447.png)