Thyroid Hormone Receptor beta antibody [N1N3]
GTX113278
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetTHRB
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameThyroid Hormone Receptor beta antibody [N1N3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.76 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7068
- Target nameTHRB
- Target descriptionthyroid hormone receptor beta
- Target synonymsC-ERBA-2, C-ERBA-BETA, ERBA2, GRTH, NR1A2, PRTH, THR1, THRB1, THRB2, THRbeta, THRbeta1, TRb, TRbeta, TRbeta1, Thrbeta2, thyroid hormone receptor beta, nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group A member 2, oncogene ERBA2, thyroid hormone receptor, beta (erythroblastic leukemia viral (v-erb-a) oncogene homolog 2, avian)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP10828
- Protein NameThyroid hormone receptor beta
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear hormone receptor for triiodothyronine. It is one of the several receptors for thyroid hormone, and has been shown to mediate the biological activities of thyroid hormone. Knockout studies in mice suggest that the different receptors, while having certain extent of redundancy, may mediate different functions of thyroid hormone. Mutations in this gene are known to be a cause of generalized thyroid hormone resistance (GTHR), a syndrome characterized by goiter and high levels of circulating thyroid hormone (T3-T4), with normal or slightly elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Moreno M, Silvestri E, Coppola M, et al. 3,5,3'-Triiodo-L-Thyronine- and 3,5-Diiodo-L-Thyronine- Affected Metabolic Pathways in Liver of LDL Receptor Deficient Mice. Front Physiol. 2016,7:545.Read this paper

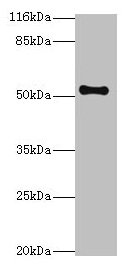
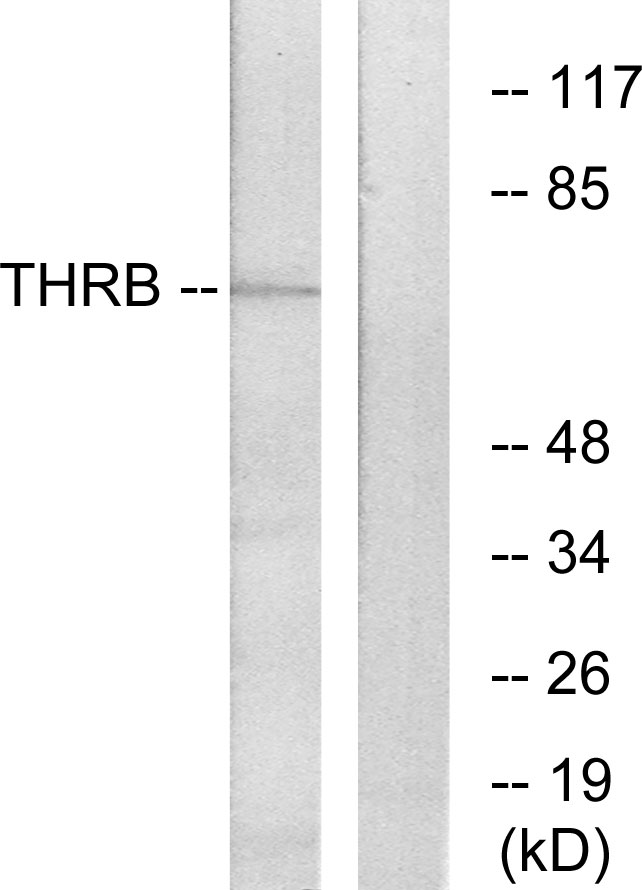


![Western blot of hippocampal lysate showing specific immunolabeling of the ~58k TR-β protein using THRB antibody [2386] (GTX82578).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX82578/Thyroid-Hormone-Receptor-beta-antibody-2386_Western-blot_GTX82578-1_w_23061322_646.webp)
