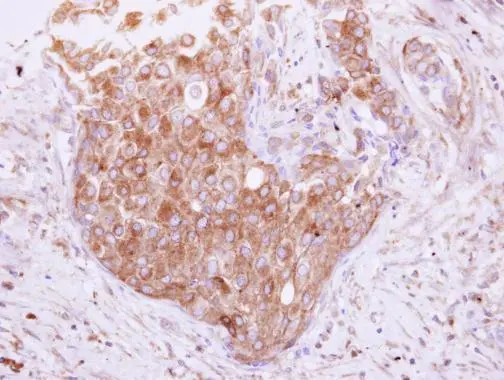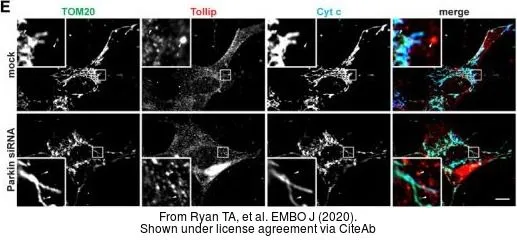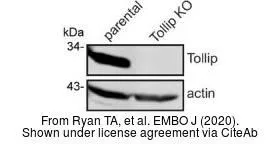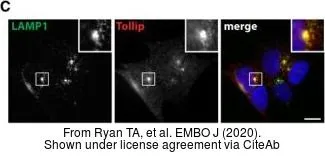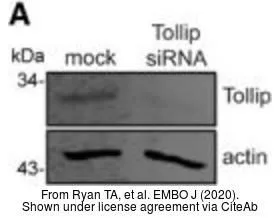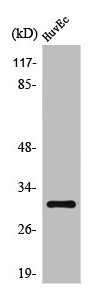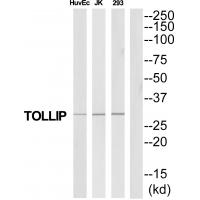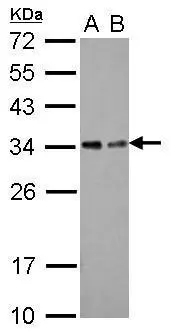
Sample (30 ug of whole cell lysate) A: NT2D1 B: IMR32 12% SDS PAGE GTX116566 diluted at 1:1000
Tollip antibody [N2C3]
GTX116566
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTOLLIP
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTollip antibody [N2C3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.63 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID54472
- Target nameTOLLIP
- Target descriptiontoll interacting protein
- Target synonymsIL-1RAcPIP, toll-interacting protein, adapter protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9H0E2
- Protein NameToll-interacting protein
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a ubiquitin-binding protein that interacts with several Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling cascade components. The encoded protein regulates inflammatory signaling and is involved in interleukin-1 receptor trafficking and in the turnover of IL1R-associated kinase. [supplied by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161