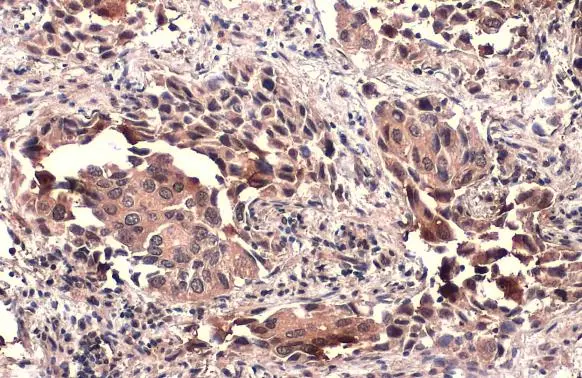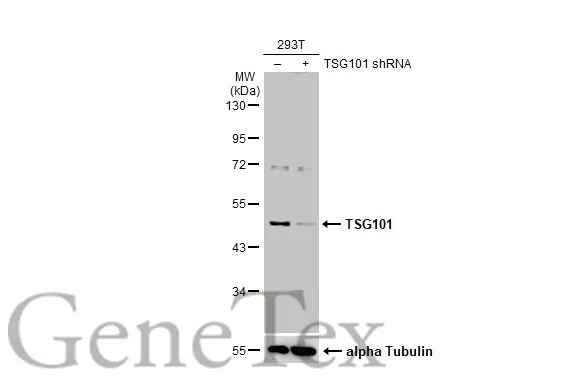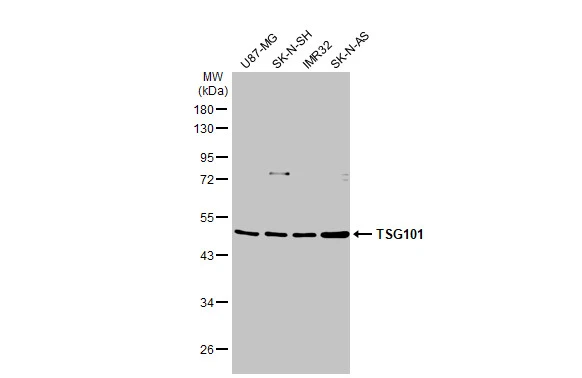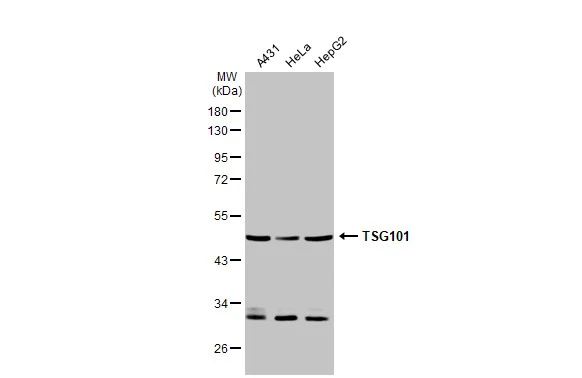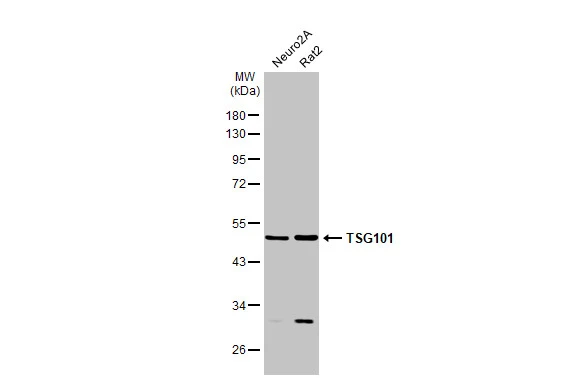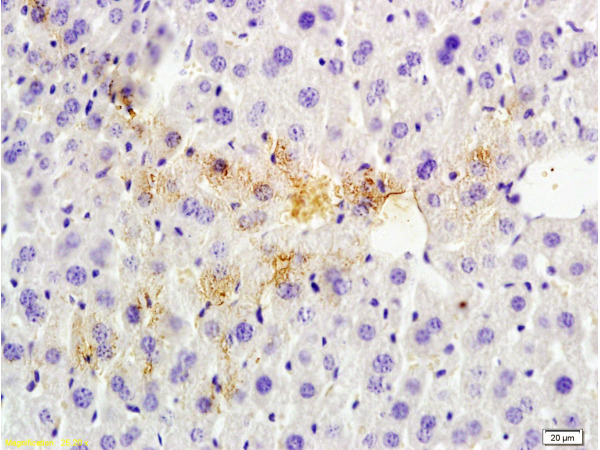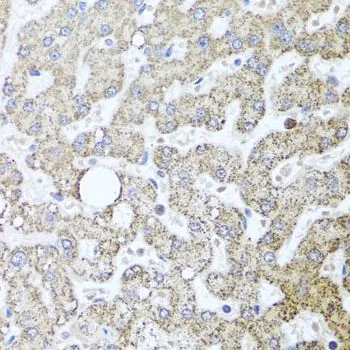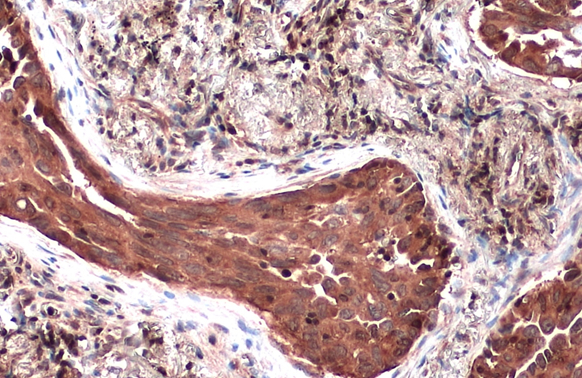
TSG101 antibody detects TSG101 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human lung cancer. TSG101 stained by TSG101 antibody (GTX118736) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
TSG101 antibody
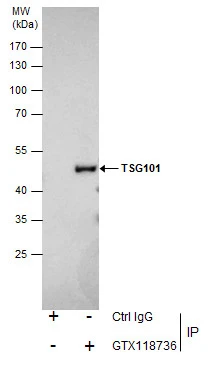
GTX118736
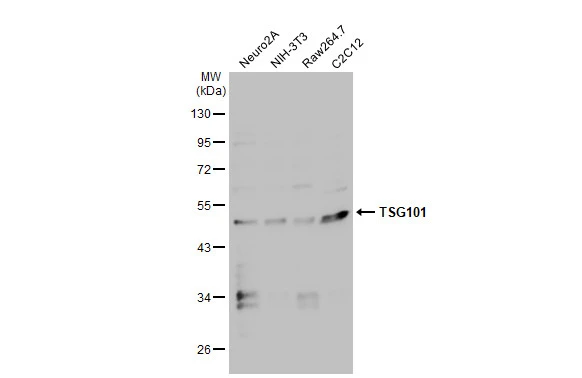
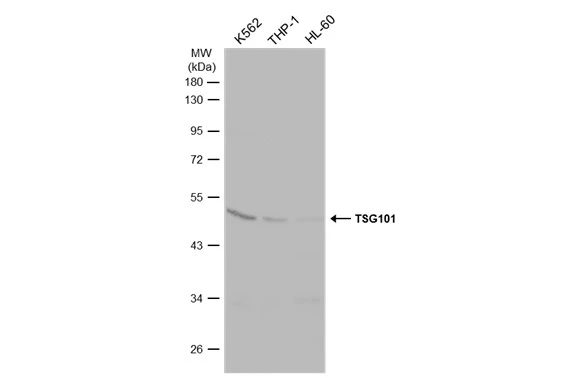
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetTSG101
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTSG101 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
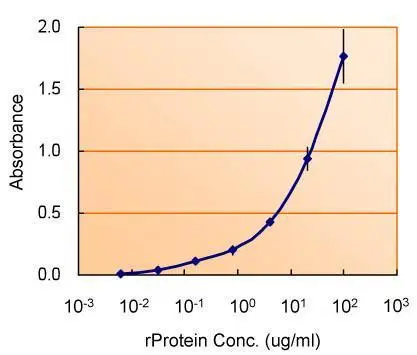
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. ELISA: 1:1000-1:10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.42 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7251
- Target nameTSG101
- Target descriptiontumor susceptibility 101
- Target synonymsTSG10, VPS23, tumor susceptibility gene 101 protein, ESCRT-I complex subunit TSG101, tumor susceptibility gene 10, tumor susceptibility gene 101, tumor susceptibility protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ99816
- Protein NameTumor susceptibility gene 101 protein
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to a group of apparently inactive homologs of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. The gene product contains a coiled-coil domain that interacts with stathmin, a cytosolic phosphoprotein implicated in tumorigenesis. The protein may play a role in cell growth and differentiation and act as a negative growth regulator. In vitro steady-state expression of this tumor susceptibility gene appears to be important for maintenance of genomic stability and cell cycle regulation. Mutations and alternative splicing in this gene occur in high frequency in breast cancer and suggest that defects occur during breast cancer tumorigenesis and/or progression. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161