![Ubiquitin Activating Enzyme E1 [UBA1; UBE1] (human) (rec.) (His) Ubiquitin Activating Enzyme E1 [UBA1; UBE1] (human) (rec.) (His)](https://adipogen.com/pub/media/catalog/product/s/b/sbb-ce0058_finalgel.png)
Ubiquitin Activating Enzyme E1 [UBA1; UBE1] (human) (rec.) (His)
SBB-CE0058
Protein IDP22314
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierSouth Bay Bio
- Product NameUbiquitin Activating Enzyme E1 [UBA1; UBE1] (human) (rec.) (His)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID7317
- Target nameUBA1
- Target descriptionubiquitin like modifier activating enzyme 1
- Target synonymsA1S9, A1S9T, A1ST, AMCX1, CFAP124, GXP1, POC20, SMAX2, UBA1A, UBE1, UBE1X, VEXAS, ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1, A1S9T and BN75 temperature sensitivity complementing, POC20 centriolar protein homolog, UBA1, ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 homolog A, testicular secretory protein Li 63
- Protein IDP22314
- Protein NameUbiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1
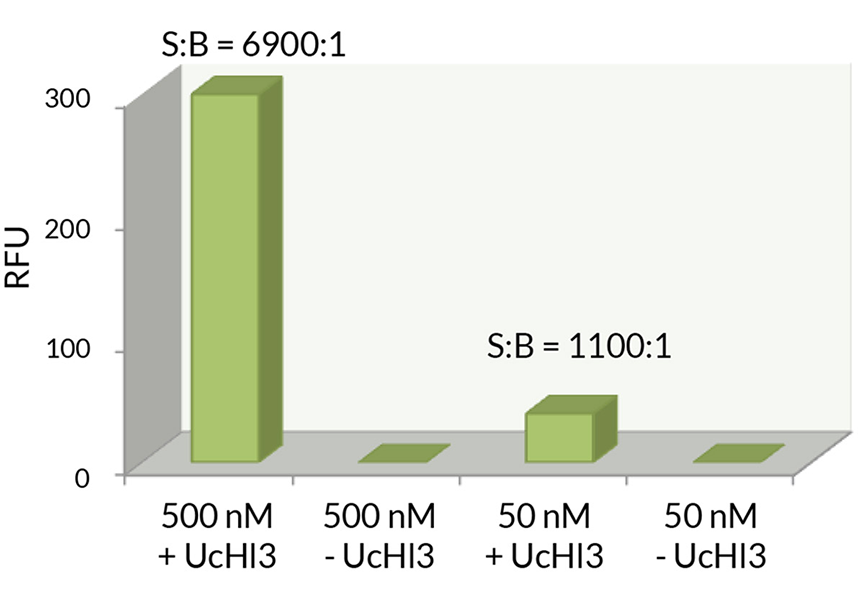
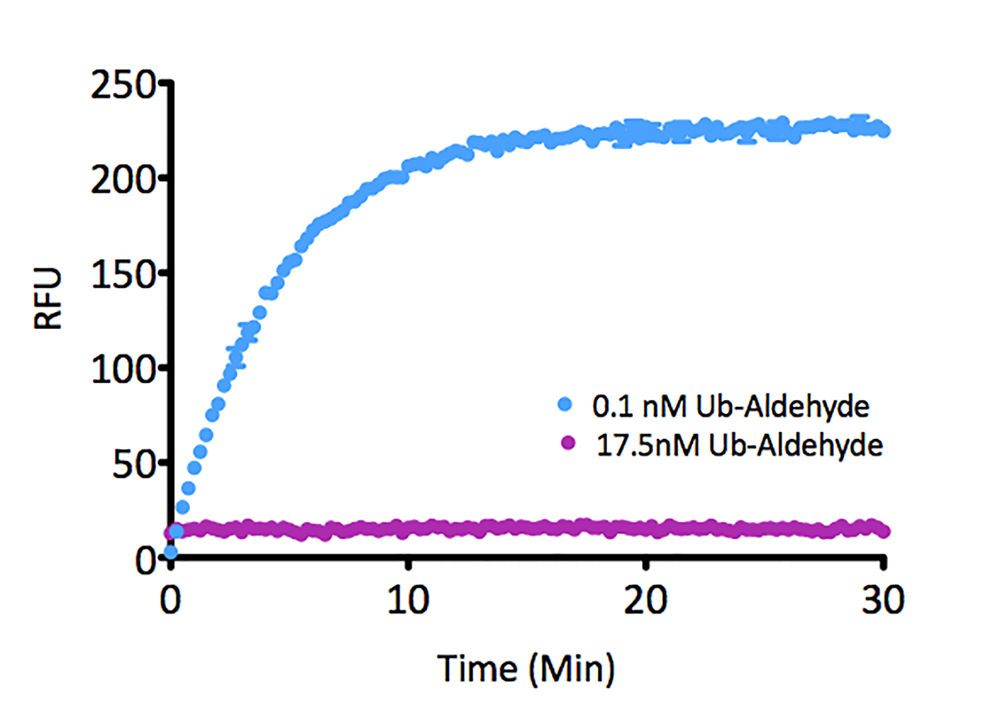
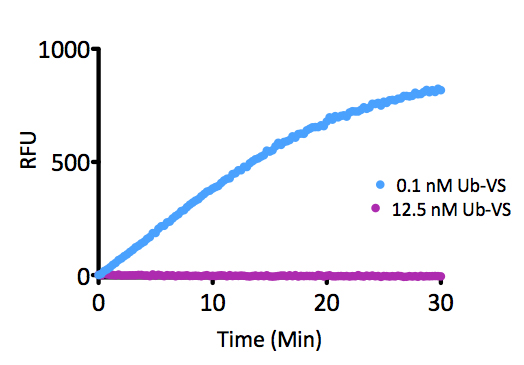
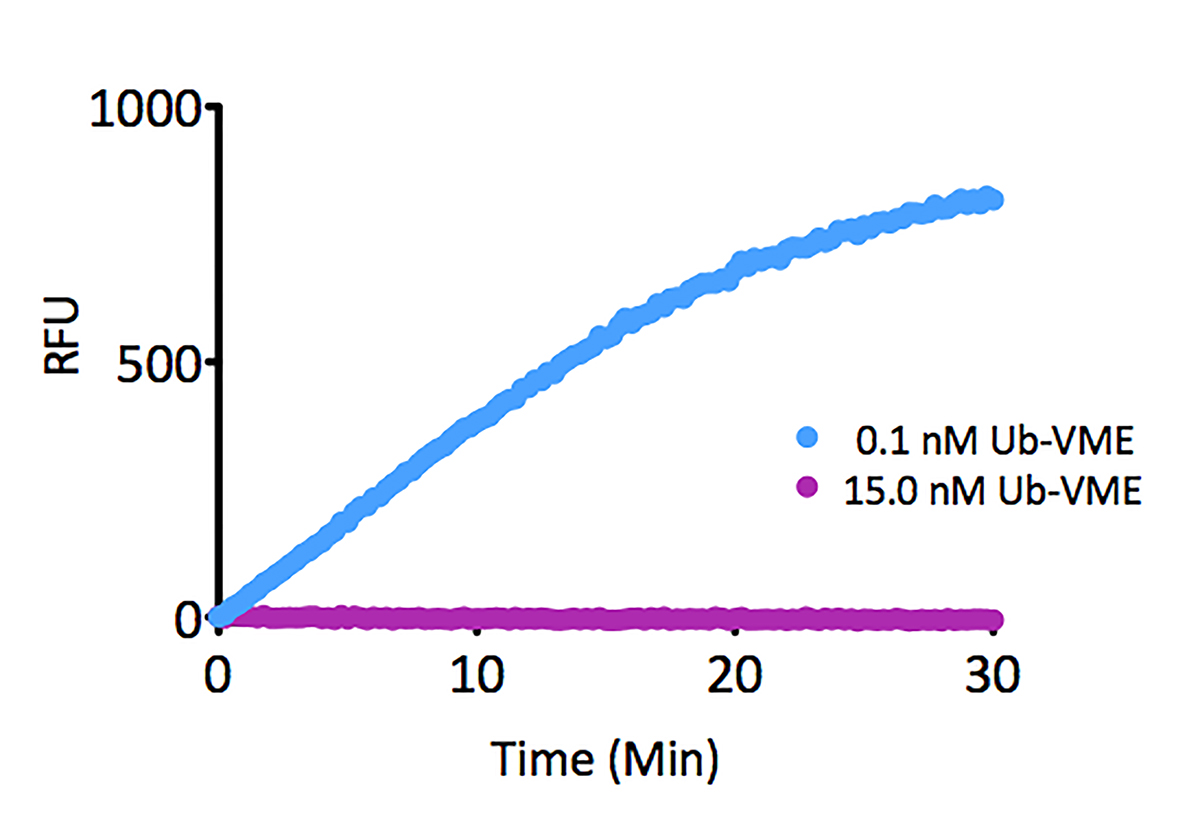
- Scientific DescriptionProtein. Human UBA1 (aa12-1058) is fused at the N-terminus to a His-tag. Source: Sf21 cells. Liquid. In 50mM HEPES pH 7.5, 150mM sodium chloride, 10% glycerol, 2mM TCEP. Purity: >95% (SDS-PAGE). UBA1, the canonical ubiquitin E1 activating enzyme is a 118kDa protein, which forms a homodimer in its active state and catalyzes the first step of the ubiquitin conjugation cascade. It activates ubiquitin in an ATP-dependent mechanism where ATP is hydrolyzed to AMP and PPi, a ubiquitin C-terminal adenylate intermediate is formed, then transferred to the E1s active site cysteine through a thioester bond. This thioester is then transferable to an E2 conjugating enzymes active site cysteine. - UBA1, the canonical ubiquitin E1 activating enzyme is a 118kDa protein, which forms a homodimer in its active state and catalyzes the first step of the ubiquitin conjugation cascade. It activates ubiquitin in an ATP-dependent mechanism where ATP is hydrolyzed to AMP and PPi, a ubiquitin C-terminal adenylate intermediate is formed, then transferred to the E1s active site cysteine through a thioester bond. This thioester is then transferable to an E2 conjugating enzymes active site cysteine.
- Storage Instruction-80°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman