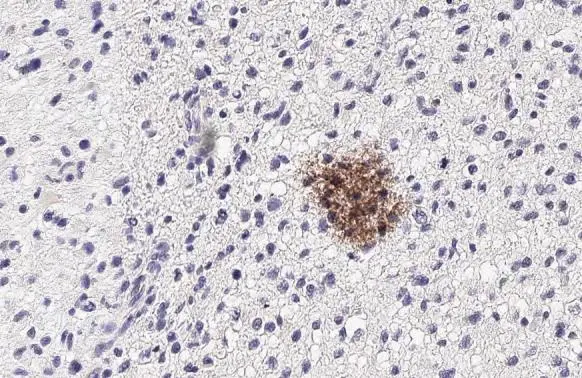
Wnt5a antibody detects secreted Wnt5a protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human glioblastoma. Wnt5a stained by Wnt5a antibody (GTX100618) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
Wnt5a antibody
GTX100618
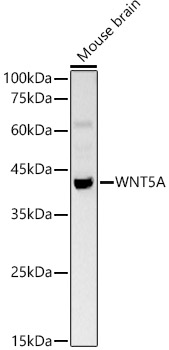
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetWNT5A
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameWnt5a antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7474
- Target nameWNT5A
- Target descriptionWnt family member 5A
- Target synonymshWNT5A, protein Wnt-5a, WNT-5A protein, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 5A
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP41221
- Protein NameProtein Wnt-5a
- Scientific DescriptionThe WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes which encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It encodes a protein which shows 98%, 98% and 87% amino acid identity to the mouse, rat and the xenopus Wnt5A protein, respectively. The experiments performed in Xenopus laevis embryos identified that human frizzled-5 (hFz5) is the receptor for the Wnt5A ligand and the Wnt5A/hFz5 signaling mediates axis induction. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161






![ICC/IF analysis of PC12 cells using GTX83127 WNT5A antibody [6F2]. Green : WNT5A Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83127/GTX83127_20170912_ICCIF_w_23061322_555.webp)