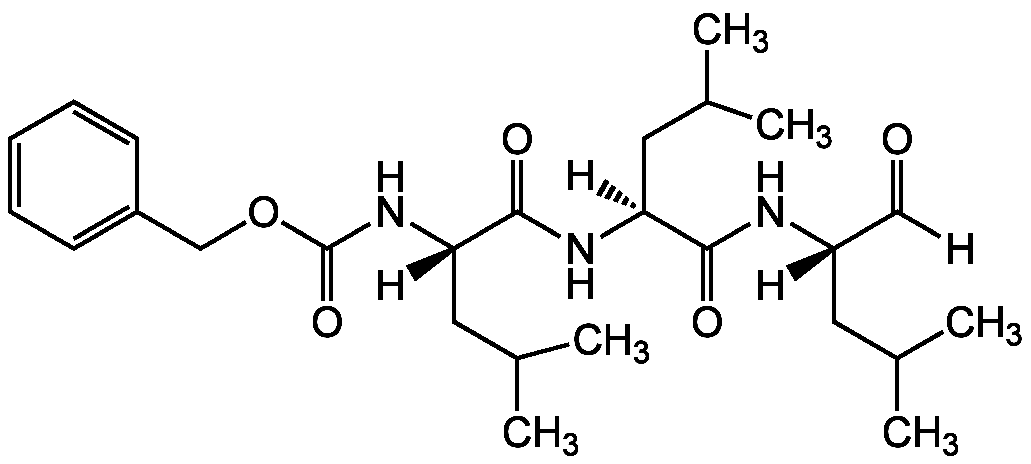
Chemical Structure
Z-Leu-Leu-Leu-CHO [MG-132] [133407-82-6]
AG-CP3-0011
CAS Number133407-82-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>97%
Molecular Weight475.6
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameZ-Leu-Leu-Leu-CHO [MG-132] [133407-82-6]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number133407-82-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>97%
- Molecular FormulaC26H41N3O5
- Molecular Weight475.6
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 133407-82-6. Formula: C26H41N3O5. MW: 475.6. Potent, cell permeable and selective, reversible proteasome inhibitor. Blocks degradation of short-lived proteins and induces a heat shock response. NF-kappaB activation inhibitor through IkappaB degradation. Cell permeable, reversible peptide aldehyde inhibitor. Calpain and cathepsin inhibitor. Has anticancer properties by inducing cell cycle arrest and activating apoptosis in various cancer cell lines. Has adjuvant/chemosensitizer potential. Neurite outgrowth stimulator in PC12 cells. Prevents beta-secretase cleavage. Autophagy activator. - Potent, cell permeable and selective, reversible proteasome inhibitor [2, 7]. Blocks degradation of short-lived proteins and induces a heat shock response [2, 6, 7]. NF-kappaB activation inhibitor through IkappaB degradation [3, 8]. Cell permeable, reversible peptide aldehyde inhibitor. Calpain and cathepsin inhibitor [4, 11]. Has anticancer properties by inducing cell cycle arrest and activating apoptosis in various cancer cell lines [8, 9, 12,13,15]. Has adjuvant/chemosensitizer potential [8]. Neurite outgrowth stimulator in PC12 cells [1]. Prevents beta-secretase cleavage [5, 10]. Autophagy activator [12, 14].
- SMILES[H]C(=O)[C@]([H])(CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@]([H])(CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@]([H])(CC(C)C)NC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200



![MG-132 [133407-82-6]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/5F/CgoaEWayHaSEUb5sAAAAAC5oh1w831.png)