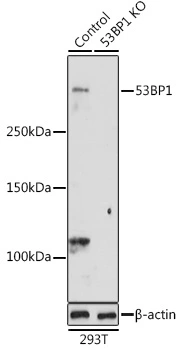
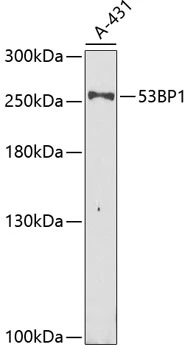
WB analysis of extracts from normal (control) and 53BP1 knockout (KO) 293T cells using GTX64370 53BP1 antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25microg per lane
53BP1 antibody
GTX64370
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTP53BP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Name53BP1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:200. IHC-P: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7158
- Target nameTP53BP1
- Target descriptiontumor protein p53 binding protein 1
- Target synonyms53BP1, TDRD30, p202, p53BP1, TP53-binding protein 1, p53-binding protein 1, tumor protein 53-binding protein, 1, tumor suppressor p53-binding protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ12888
- Protein NameTP53-binding protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a protein that functions in the DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice, promoting non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathways, and limiting homologous recombination. This protein plays multiple roles in the DNA damage response, including promoting checkpoint signaling following DNA damage, acting as a scaffold for recruitment of DNA damage response proteins to damaged chromatin, and promoting NHEJ pathways by limiting end resection following a double-strand break. These roles are also important during V(D)J recombination, class switch recombination and at unprotected telomeres. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Li G, Chen S, Zhang Y, et al. Matrix stiffness regulates α-TAT1-mediated acetylation of α-tubulin and promotes silica-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via DNA damage. J Cell Sci. 2021,134(2):pii: jcs243394. doi: 10.1242/jcs.243394.Read this paper

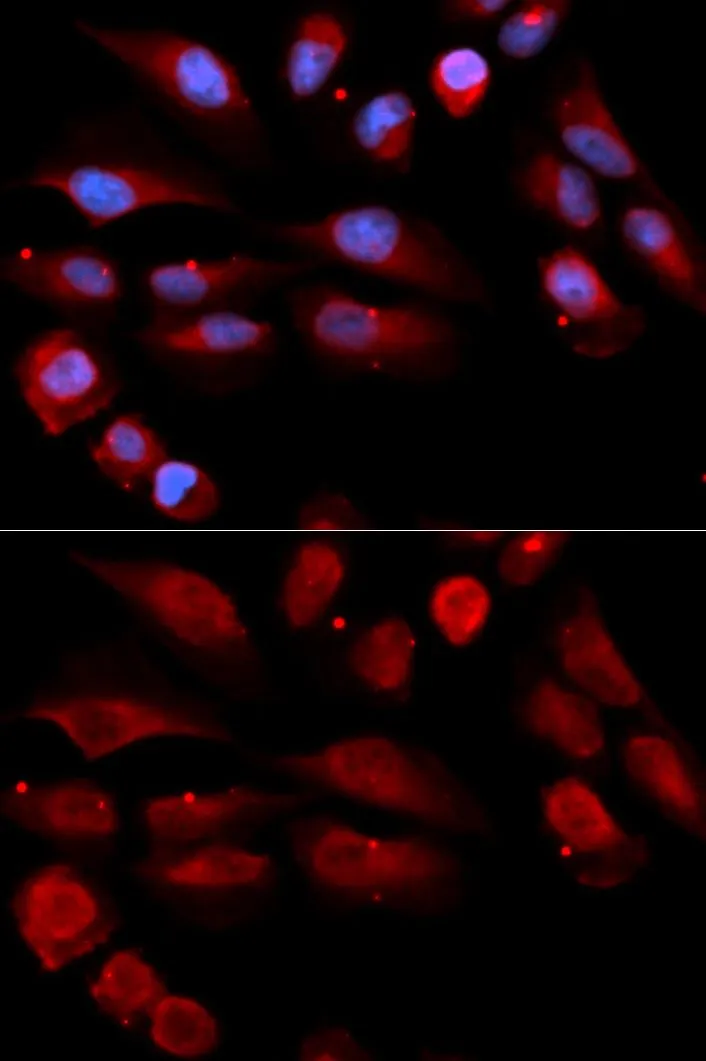
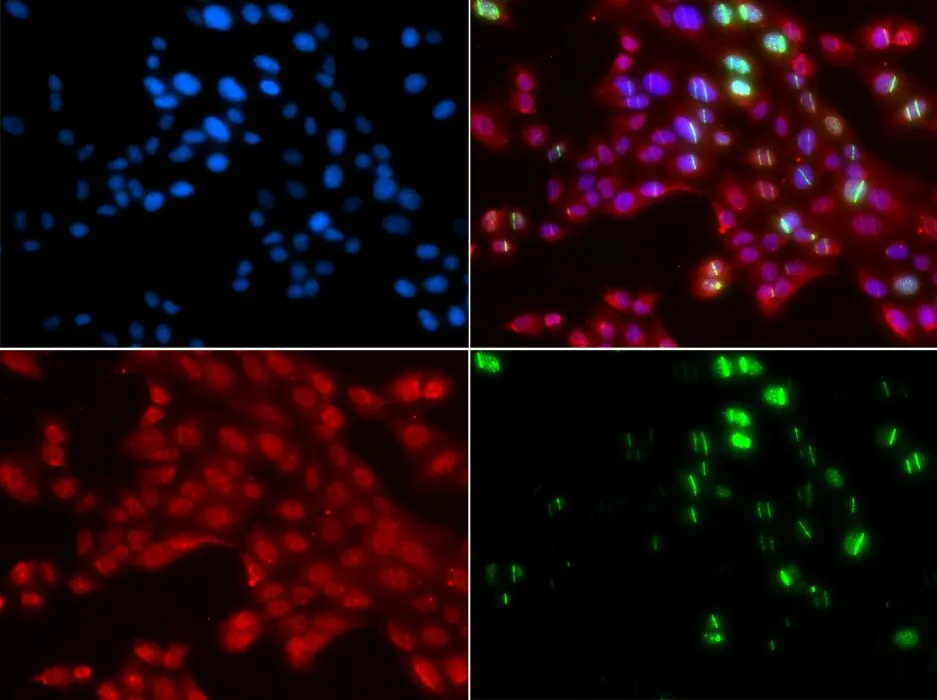
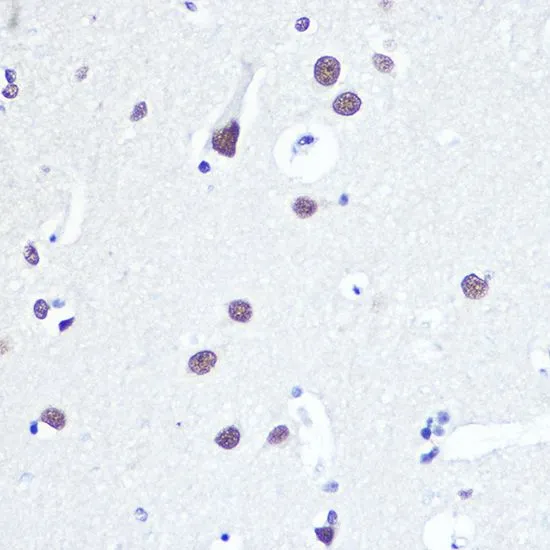
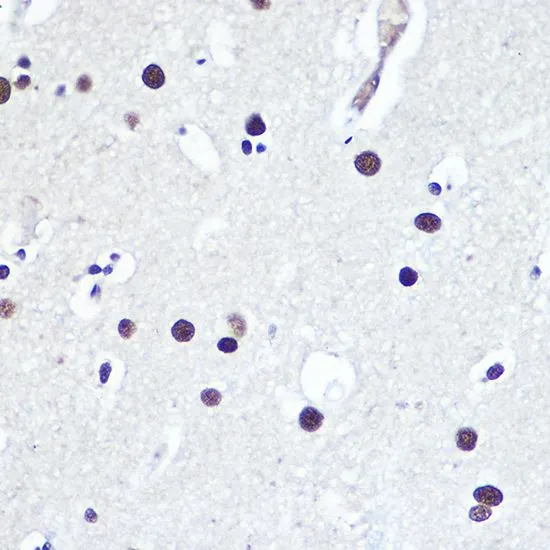
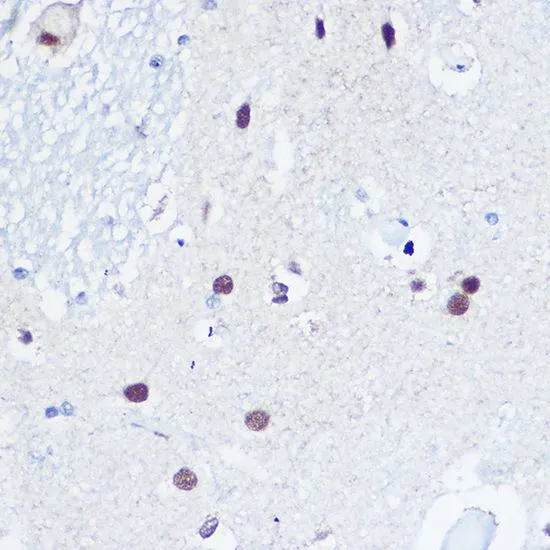
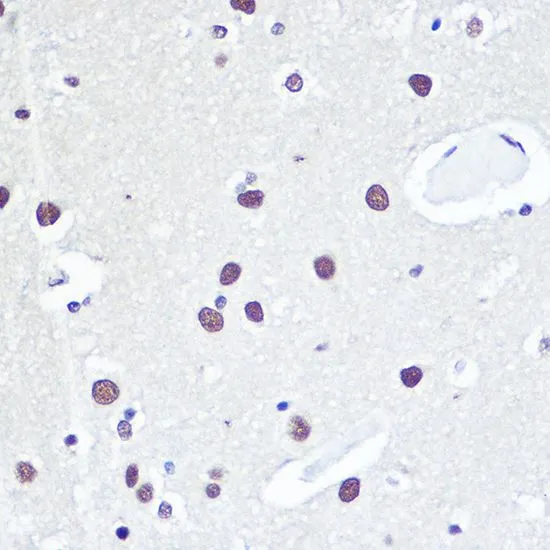
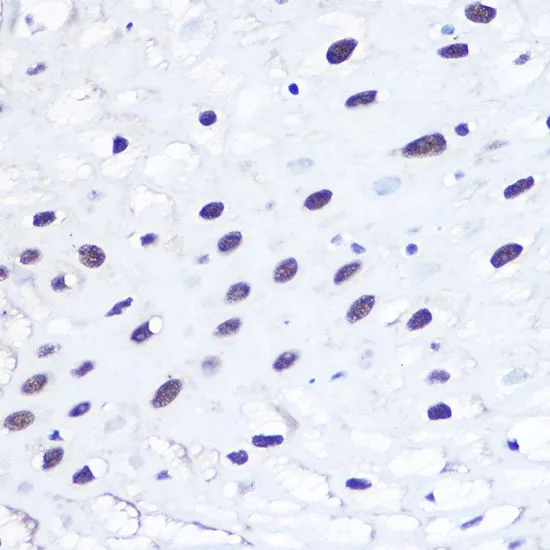
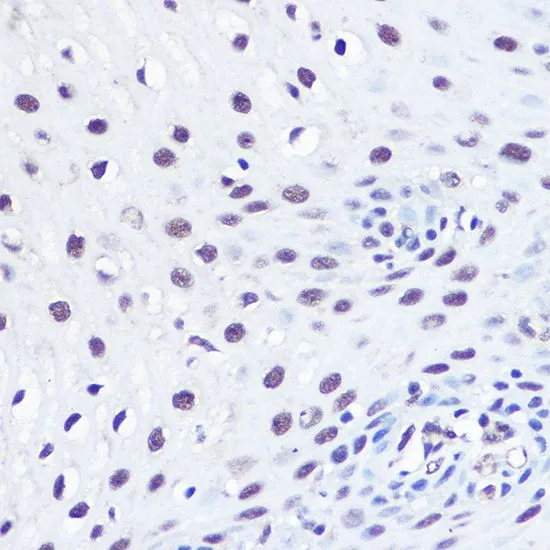

![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60762 53BP1 antibody [6B3E10]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60762/GTX60762_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_284.webp)
