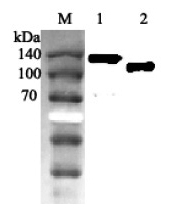
![Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced. Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_43824_20200327_WB_M_kidney_w_23060100_326.webp)
Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.
ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term
GTX101395
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Monkey, Mouse, Rat
TargetACE2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID59272
- Target nameACE2
- Target descriptionangiotensin converting enzyme 2
- Target synonymsACEH, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, ACE-related carboxypeptidase, angiotensin I converting enzyme (peptidyl-dipeptidase A) 2, angiotensin I converting enzyme 2, angiotensin-converting enzyme homolog, angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase, metalloprotease MPROT15, peptidyl-dipeptidase A
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9BYF1
- Protein NameAngiotensin-converting enzyme 2
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to the angiotensin-converting enzyme family of dipeptidyl carboxydipeptidases and has considerable homology to human angiotensin 1 converting enzyme. This secreted protein catalyzes the cleavage of angiotensin I into angiotensin 1-9, and angiotensin II into the vasodilator angiotensin 1-7. The organ- and cell-specific expression of this gene suggests that it may play a role in the regulation of cardiovascular and renal function, as well as fertility. In addition, the encoded protein is a functional receptor for the spike glycoprotein of the human coronaviruses SARS and HCoV-NL63. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Monkey, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Escalera A, Laporte M, Turner S, et al. The impact of S2 mutations on Omicron SARS-CoV-2 cell surface expression and fusogenicity. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024,13(1):2297553. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2297553Read this paper
- Chen YR, Jiang WP, Deng JS, et al. Anisomeles indica Extracts and Their Constituents Suppress the Protein Expression of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 In Vivo and In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2023,24(20). doi: 10.3390/ijms242015062Read this paper
- Resnick JD, Wilson JL, Anaya E, et al. Growth media affects susceptibility of air-lifted human nasal epithelial cell cultures to SARS-CoV2, but not Influenza A, virus infection. bioRxiv. 2023,:pii: 2023.07.31.551381. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.31.551381.Read this paper
- Sun TK, Huang WC, Sun YW, et al. Schizophyllum commune Reduces Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Receptors ACE2 and TMPRSS2. Int J Mol Sci. 2022,23(23). doi: 10.3390/ijms232314766Read this paper
- Isobe A, Arai Y, Kuroda D, et al. ACE2 N-glycosylation modulates interactions with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in a site-specific manner. Commun Biol. 2022,5(1):1188. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-04170-6Read this paper
- Chien LH, Deng JS, Jiang WP, et al. Study on the potential of Sanghuangporus sanghuang and its components as COVID-19 spike protein receptor binding domain inhibitors. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022,153:113434. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113434Read this paper
- Wang WJ, Chen Y, Su WC, et al. Peimine inhibits variants of SARS-CoV-2 cell entry via blocking the interaction between viral spike protein and ACE2. J Food Biochem. 2022,46(10):e14354. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14354Read this paper
- Nguyen HT, Kawahara M, Vuong CK, et al. SARS-CoV-2 M Protein Facilitates Malignant Transformation of Breast Cancer Cells. Front Oncol. 2022,12:923467. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.923467Read this paper
- Yeh H, Vo DNK, Lin ZH, et al. GMI, a protein from Ganoderma microsporum, induces ACE2 degradation to alleviate infection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-pseudotyped virus. Phytomedicine. 2022,103:154215. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154215Read this paper
- Lin EC, Hong CH. IL-33 Enhances ACE2 Expression on Epidermal Keratinocytes in Atopic Dermatitis: A Plausible Issue for SARS-CoV-2 Transmission in Inflamed Atopic Skin. Biomedicines. 2022,10(5). doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051183Read this paper

![Untreated (–) and treated (+) Vero E6 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Untreated (–) and treated (+) Vero E6 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_44041_20200904_WB_Monkey_treatment_Tunicamycin_w_23060100_956.webp)
![ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cell membrane by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: Vero E6 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cell membrane by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: Vero E6 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_43993_20200806_ICC_IF_Monkey_w_23060100_968.webp)
![Indirect ELISA analysis performed by coating plate with recombinant Human ACE2 (ECD) protein , mouse IgG Fc tag protein (GTX135683-pro) (15.63-1000 ng/mL). Coated protein probed with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) (0.1 μg/mL). Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) (1:10000) detected bound primary antibody. Indirect ELISA analysis performed by coating plate with recombinant Human ACE2 (ECD) protein , mouse IgG Fc tag protein (GTX135683-pro) (15.63-1000 ng/mL). Coated protein probed with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) (0.1 μg/mL). Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) (1:10000) detected bound primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_43887_20200626_ELISA_Indirect_w_23060100_656.webp)
![ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: Caco-2 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: Caco-2 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_44041_20220325_ICC_IF_w_23060100_500.webp)
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) HepG2 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) HepG2 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_44006_20200731_WB_shRNA_watermark_w_23060100_857.webp)
![ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat lung. ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:2000. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat lung. ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:2000. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_43842_20200313_IHC-P_R_w_23060100_682.webp)
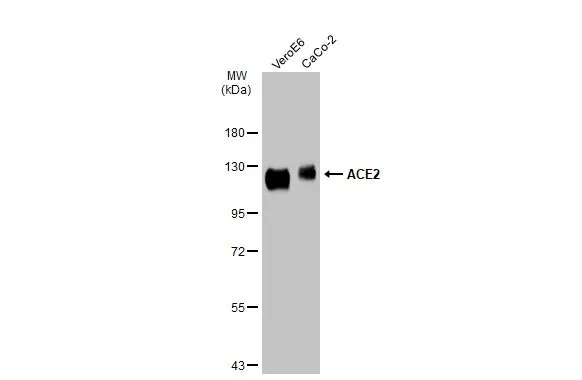
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) Caco-2 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) Caco-2 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_44041_20201113_WB_shRNA_watermark_w_23060100_338.webp)
![Functional ELISA analysis of immobilized recombinant SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Spike RBD protein, His tag (active) (GTX01546-pro) (coated at 2 μg/mL) binding to soluble recombinant Human ACE2 (ECD) protein , mouse IgG Fc tag (GTX135683-pro) (4.5-10000 ng/mL). Bound protein was detected by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) (0.5 μg/mL) and Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) (1:10000) detected bound primary antibody. Functional ELISA analysis of immobilized recombinant SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Spike RBD protein, His tag (active) (GTX01546-pro) (coated at 2 μg/mL) binding to soluble recombinant Human ACE2 (ECD) protein , mouse IgG Fc tag (GTX135683-pro) (4.5-10000 ng/mL). Bound protein was detected by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) (0.5 μg/mL) and Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) (1:10000) detected bound primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_43887_20200709_ELISA_PAIR_Function_w_23060100_555.webp)
![ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse duodenum. ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:1000. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects ACE2 protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse duodenum. ACE2 stained by ACE2 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX101395) diluted at 1:1000. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101395/GTX101395_43887_20200522_IHC-P_M_w_23060100_333.webp)