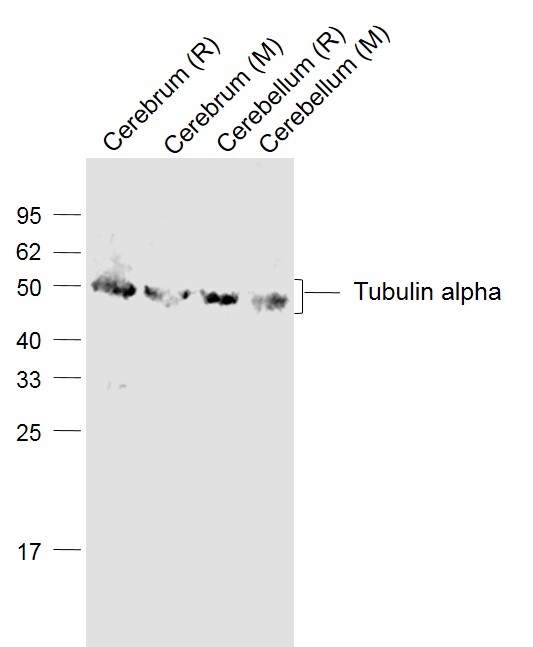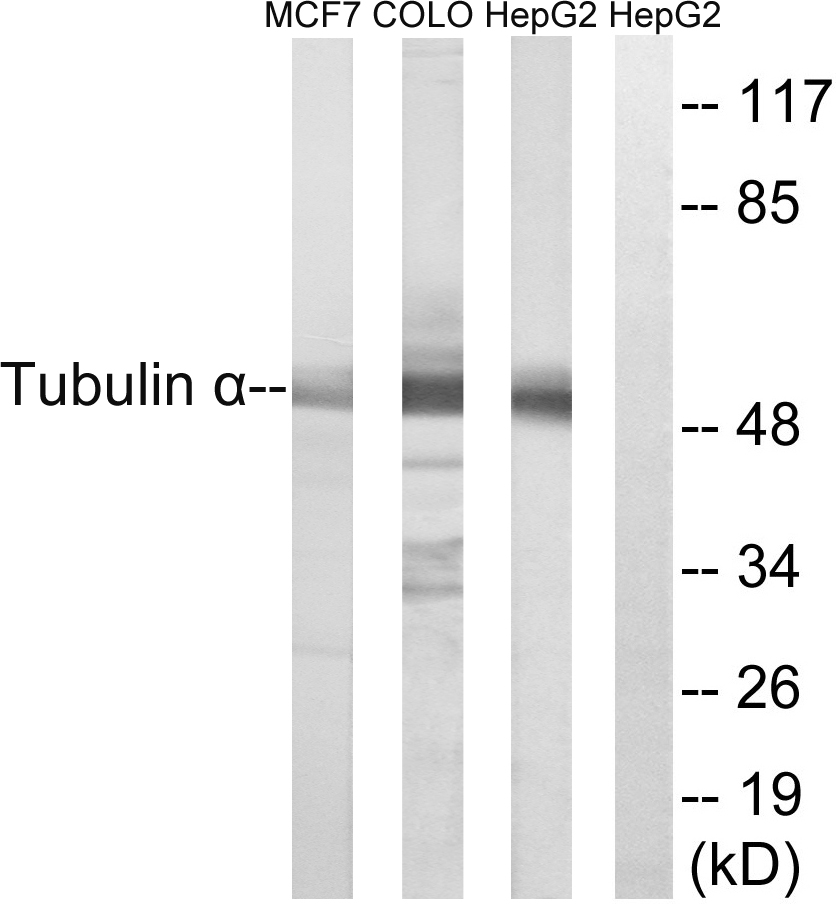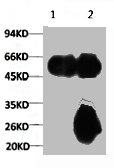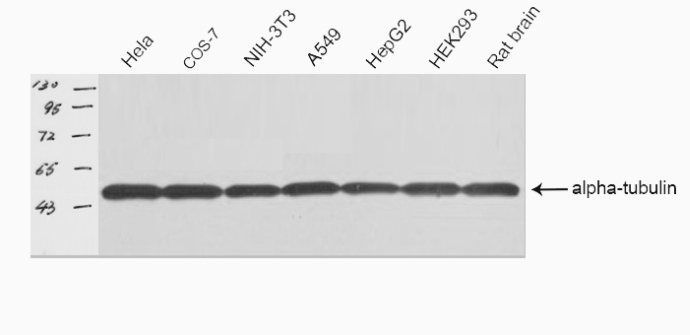
Western blot analysis of Tubulin alpha expression in NIH-3T3 whole cell lysates,The lane on the left is treated with the antigen-specific peptide.
alpha Tubulin antibody
GTX52379
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetTUBA1A
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namealpha Tubulin antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB 1:500-1:2000, IHC 1:50-1:200, IF/ICC 1:100-1:500
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7846
- Target nameTUBA1A
- Target descriptiontubulin alpha 1a
- Target synonymsB-ALPHA-1, LIS3, TUBA3, tubulin alpha-1A chain, hum-a-tub1, hum-a-tub2, tubulin B-alpha-1, tubulin alpha-3 chain, tubulin, alpha, brain-specific
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionMicrotubules of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton perform essential and diverse functions and are composed of a heterodimer of alpha and beta tubulins. The genes encoding these microtubule constituents belong to the tubulin superfamily, which is composed of six distinct families. Genes from the alpha, beta and gamma tubulin families are found in all eukaryotes. The alpha and beta tubulins represent the major components of microtubules, while gamma tubulin plays a critical role in the nucleation of microtubule assembly. There are multiple alpha and beta tubulin genes, which are highly conserved among species. This gene encodes alpha tubulin and is highly similar to the mouse and rat Tuba1 genes. Northern blotting studies have shown that the gene expression is predominantly found in morphologically differentiated neurologic cells. This gene is one of three alpha-tubulin genes in a cluster on chromosome 12q. Mutations in this gene cause lissencephaly type 3 (LIS3) - a neurological condition cha
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Cheng CF, Cheng JK, Chen CY, et al. Nerve growth factor-induced synapse-like structures in contralateral sensory ganglia contribute to chronic mirror-image pain. Pain. 2015,156(11):2295-2309. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000280Read this paper