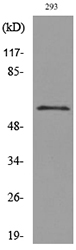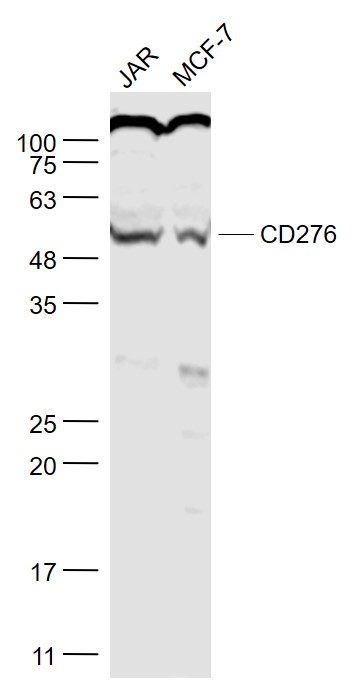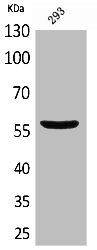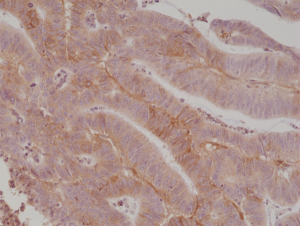
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human colon cancer tissue section using anti-CD276 (B7-H3) rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM335) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-CD276 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM335)
REV-31-1223-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD276
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD276 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM335)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM335
- Gene ID80381
- Target nameCD276
- Target descriptionCD276 molecule
- Target synonyms4Ig-B7-H3, B7-H3, B7H3, B7RP-2, CD276 antigen, B7 homolog 3, costimulatory molecule
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ5ZPR3
- Protein NameCD276 antigen
- Scientific DescriptionCD276 (B7-H3) is a member of the B7/CD28 superfamily of costimulatory molecules serving as an accessory modulator of T cell response. B7 family molecules, which are expressed on antigen-presenting cells and display extracellular regions containing immunoglobulin (Ig) variable (V)- and constant (C)-like domains, are known to modulate T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated T cell activation by providing co-signals that are either stimulatory or inhibitory. B7-H3 provides a stimulatory signal to T cells. However, recent studies suggest a negative regulatory role for B7-H3 in T cell responses. B7-H3 inhibited T cell proliferation mediated by antibody to T cell receptor or allogeneic antigen-presenting cells. B7-H3 is a negative regulator that preferentially affects T(H)1 responses. B7-H3 may play an important role in muscle-immune interactions, providing further evidence of the active role of muscle cells in local immunoregulatory processes. Recently, B7-H3 expression has also been found in a variety of different human cancers, including prostate cancer, clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer (CRC) and urothelial cell carcinoma. B7-H3 was expressed in some human cancers and correlated with poor outcome of cancer patients. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the cytoplasmic domain of human CD276 (B7-H3). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. CD276 (B7-H3) is a member of the B7/CD28 superfamily of costimulatory molecules serving as an accessory modulator of T cell response. B7 family molecules, which are expressed on antigen-presenting cells and display extracellular regions containing immunoglobulin (Ig) variable (V)- and constant (C)-like domains, are known to modulate T cell receptor (TCR)-mediated T cell activation by providing co-signals that are either stimulatory or inhibitory. B7-H3 provides a stimulatory signal to T cells. However, recent studies suggest a negative regulatory role for B7-H3 in T cell responses. B7-H3 inhibited T cell proliferation mediated by antibody to T cell receptor or allogeneic antigen-presenting cells. B7-H3 is a negative regulator that preferentially affects T(H)1 responses. B7-H3 may play an important role in muscle-immune interactions, providing further evidence of the active role of muscle cells in local immunoregulatory processes. Recently, B7-H3 expression has also been found in a variety of different human cancers, including prostate cancer, clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), pancreatic cancer, gastric cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer (CRC) and urothelial cell carcinoma. B7-H3 was expressed in some human cancers and correlated with poor outcome of cancer patients.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161