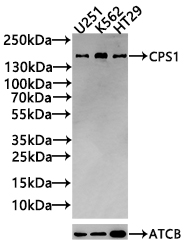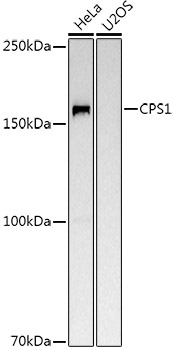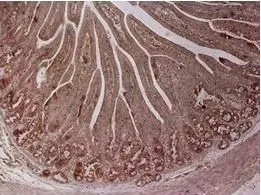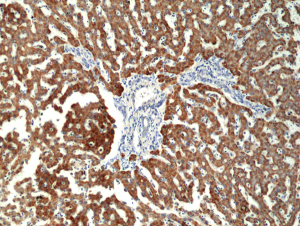
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human liver tissue section using anti-CPS1 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM395) at a 1:100 dilution.
anti-CPS1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM395)
REV-31-1281-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCPS1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CPS1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM395)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM395
- Gene ID1373
- Target nameCPS1
- Target descriptioncarbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1
- Target synonymsCPSASE1, GATD6, PHN, carbamoyl-phosphate synthase [ammonia], mitochondrial, carbamoyl-phosphate synthase (ammonia), carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1, mitochondrial, carbamoylphosphate synthetase I
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP31327
- Protein NameCarbamoyl-phosphate synthase [ammonia], mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionCarbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS1 or CPSI) is a ligase enzyme located in the mitochondria involved in the production of urea. It transfers an ammonia molecule from glutamine or glutamate to a molecule of bicarbonate that has been phosphorylated by a molecule of ATP. The resulting carbamate is then phosphorylated with another molecule of ATP. The resulting molecule of carbamoyl phosphate leaves the enzyme. This reaction is the first committed step of the urea cycle, which is important in the removal of excess urea from cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency (CPS1D), susceptibility to persistent pulmonary hypertension and susceptibility to venoocclusive disease after bone marrow transplantation. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CPS1. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS1 or CPSI) is a ligase enzyme located in the mitochondria involved in the production of urea. It transfers an ammonia molecule from glutamine or glutamate to a molecule of bicarbonate that has been phosphorylated by a molecule of ATP. The resulting carbamate is then phosphorylated with another molecule of ATP. The resulting molecule of carbamoyl phosphate leaves the enzyme. This reaction is the first committed step of the urea cycle, which is important in the removal of excess urea from cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency (CPS1D), susceptibility to persistent pulmonary hypertension and susceptibility to venoocclusive disease after bone marrow transplantation.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161