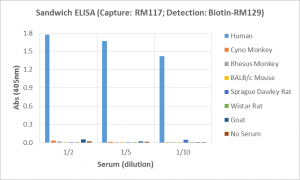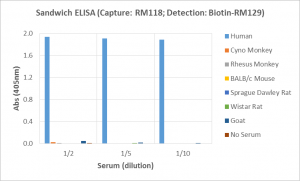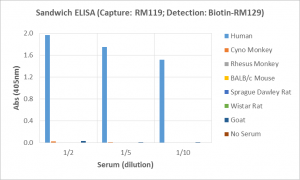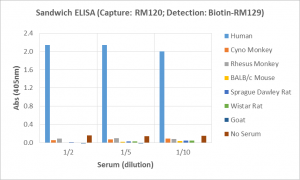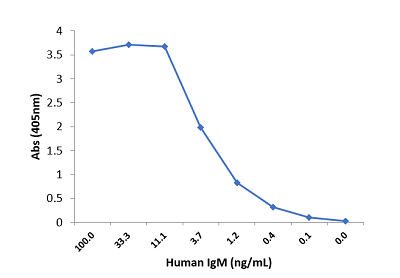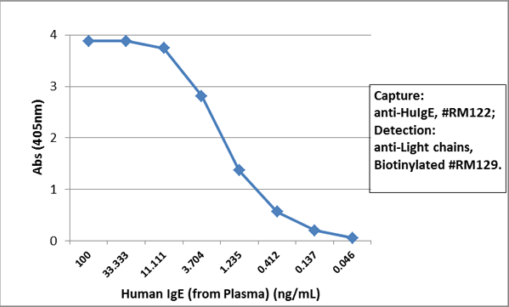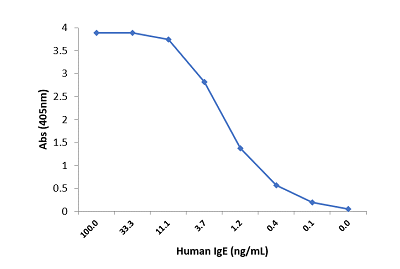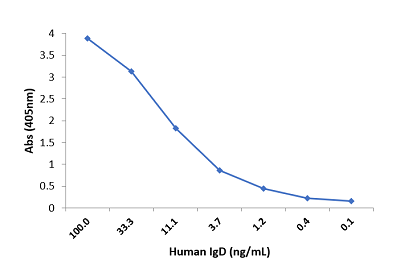
Immunohistochemistry of Human Lymphoid Tissue using Anti-Human IgD antibody RM123.
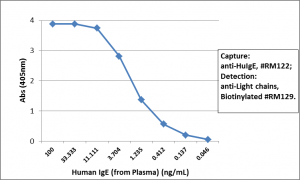
anti-IgE (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM122) (Biotin)
REV-31-1024-02
ApplicationsELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-IgE (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM122) (Biotin)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM122
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateBiotin
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01854
- Protein NameImmunoglobulin heavy constant epsilon
- Scientific DescriptionImmunoglobulin E (IgE) is an antibody isotype that has only been found in mammals. IgE is synthesized by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (epsilon chain) and two light chains, with the epsilon chain containing 4 Ig-like constant domains (Cepsilon1-Cepsilon4). IgEs main function is immunity to parasites such as helminths or certain protozoan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum. IgE may have evolved as a last line of defense to protect against venoms. IgE also has an essential role in type I hypersensitivity, which manifests in various allergic diseases, such as allergic asthma, most types of sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, food allergies and atopic dermatitis. IgE also plays a pivotal role in responses to allergens, such as: anaphylactic reactions to drugs, bee stings and antigen preparations used in desensitization immunotherapy. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgE immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human IgE. No cross reactivity with human IgG, IgM, IgD, or IgA. Applications: ELISA. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is an antibody isotype that has only been found in mammals. IgE is synthesized by plasma cells. Monomers of IgE consist of two heavy chains (epsilon chain) and two light chains, with the epsilon chain containing 4 Ig-like constant domains (Cepsilon1-Cepsilon4). IgEs main function is immunity to parasites such as helminths or certain protozoan parasites such as Plasmodium falciparum. IgE may have evolved as a last line of defense to protect against venoms. IgE also has an essential role in type I hypersensitivity, which manifests in various allergic diseases, such as allergic asthma, most types of sinusitis, allergic rhinitis, food allergies and atopic dermatitis. IgE also plays a pivotal role in responses to allergens, such as: anaphylactic reactions to drugs, bee stings and antigen preparations used in desensitization immunotherapy. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgE immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161