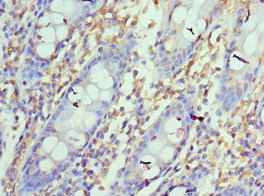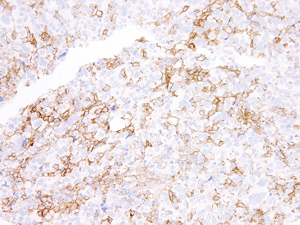
PD-1 receptor-induced CD4 T cell activation and proliferation by PD-1 (mouse), mAb (blocking) (1H10) (AG-20B-0075).Method: Magnetic bead affinity purified CD4+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice are stimulated in vitro with PD-1 (mouse), mAb (b
anti-PD-L1 (human), mAb (AG-IHC411)
AG-20B-6022
ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD274
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-PD-L1 (human), mAb (AG-IHC411)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDAG-IHC411
- Gene ID29126
- Target nameCD274
- Target descriptionCD274 molecule
- Target synonymsADMIO5, B7-H, B7H1, PD-L1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, PDL1, hPD-L1, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1, B7 homolog 1, CD274 antigen, PDCD1 ligand 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9NZQ7
- Protein NameProgrammed cell death 1 ligand 1
- Scientific DescriptionMonoclonal Antibody. Recognizes human PD-L1 (CD274). Applications: ELISA, IHC. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Clone: AG-IHC411. Liquid. In Tris Buffer, pH 7.4, containing 1% BSA and <0.1% sodium azide. Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1, B7-H1 or CD274) is a member of the growing B7 family of immune proteins that provide signals for both stimulating and inhibiting T cell activation. PD-L1 is a transmembrane protein involved in suppressing the immune system and rendering tumor cells resistant to CD8+ T cell-mediated lysis through binding of the Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) receptor. PD-L1 is widely expressed in several organs such as heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung, and in lower amounts in thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. Overexpression of PD-L1 may allow cancer cells to evade the actions of the host immune system. In renal cell carcinoma, upregulation of PD-L1 has been linked to increased tumor aggressiveness and risk of death, and, in ovarian cancer, higher expression of this protein has lead to significantly poorer prognosis. PD-L1 has also been linked to systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous melanoma. When considered in adjunct with CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density, expression levels of PD-L1 may be a useful predictor of multiple cancer types, including stage III non-small cell lung cancer, hormone receptor negative breast cancer and sentinel lymph node melanoma. This antibody is intended to qualitatively identify by light microscopy the presence of associated antigens in sections of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections using IHC test methods. It has been optimized and validated using the BOND-MAX fully automated IHC&ISH stainer (see Protocol). - Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1, B7-H1 or CD274) is a member of the growing B7 family of immune proteins that provide signals for both stimulating and inhibiting T cell activation. PD-L1 is a transmembrane protein involved in suppressing the immune system and rendering tumor cells resistant to CD8+ T cell-mediated lysis through binding of the Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) receptor. PD-L1 is widely expressed in several organs such as heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung, and in lower amounts in thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. Overexpression of PD-L1 may allow cancer cells to evade the actions of the host immune system. In renal cell carcinoma, upregulation of PD-L1 has been linked to increased tumor aggressiveness and risk of death, and, in ovarian cancer, higher expression of this protein has lead to significantly poorer prognosis. PD-L1 has also been linked to systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous melanoma. When considered in adjunct with CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density, expression levels of PD-L1 may be a useful predictor of multiple cancer types, including stage III non-small cell lung cancer, hormone receptor negative breast cancer and sentinel lymph node melanoma. This antibody is intended to qualitatively identify by light microscopy the presence of associated antigens in sections of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections using IHC test methods. It has been optimized and validated using the BOND-MAX fully automated IHC&ISH stainer (see Protocol).
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161