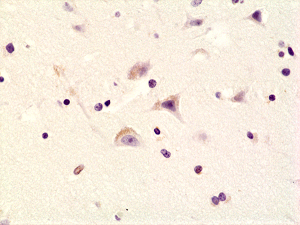
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human brain tissue sections using Anti-Phospho-AMPA Receptor (GluR 1) (Ser845) rabbit monoclonal antibody (clone RM296) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-Phospho-AMPA Receptor (Ser845) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM296)
REV-31-1179-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetGRIA1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Phospho-AMPA Receptor (Ser845) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM296)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM296
- Gene ID2890
- Target nameGRIA1
- Target descriptionglutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 1
- Target synonymsGLUH1, GLUR1, GLURA, GluA1, HBGR1, MRD67, MRT76, glutamate receptor 1, AMPA 1, AMPA receptor subunit GluA1, AMPA-selective glutamate receptor 1, gluR-1, gluR-A, gluR-K1, glutamate receptor, ionotropic, AMPA 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP42261
- Protein NameGlutamate receptor 1
- Scientific DescriptionAMPA receptors (AMPARs) are heterotetrameric complexes composed of subunits GluR1-4, each of them conferring specific properties on the active receptor, including trafficking motifs, which is related to synaptic plasticity. These glutamate receptors are responsible for the fast, immediate postsynaptic response to glutamate release. Therefore, the receptor-channel complex, predominantly permeable for sodium and potassium ions, activates fast and shows rapid desensitization. AMPA receptors are abundant and widely distributed in the central nervous system. GluR1 (Glutamate Receptor 1) is an ionotropic glutamate receptor. L-glutamate acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter at many synapses in the central nervous system. Binding of the excitatory neurotransmitter, L-glutamate, induces a conformation change that leads to the opening of the cation channel and converts the chemical signal to an electrical impulse. Then, the receptor desensitizes rapidly and enters a transiet inactive state characterized by the presence of a bound agonist. In the presence of CACNG4, CACNG7, or CACNG8, GluR1 shows resensitization which is characterized by a delayed accumulation of current flux upon continued application of glutamate. Phosphorylation of GluR1 is critical for long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) expression and the retention of memories. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Glutamate Receptor 1, AMPA Receptor (GluR1) only when phosphorylated at Ser845. There is no cross-reactivity to GluR1 that is not phosphorylated at Ser845. This antibody may also react to mouse or rat Phospho-AMPA Receptor (GluR1) (Ser845) as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. AMPA receptors (AMPARs) are heterotetrameric complexes composed of subunits GluR1-4, each of them conferring specific properties on the active receptor, including trafficking motifs, which is related to synaptic plasticity. These glutamate receptors are responsible for the fast, immediate postsynaptic response to glutamate release. Therefore, the receptor-channel complex, predominantly permeable for sodium and potassium ions, activates fast and shows rapid desensitization. AMPA receptors are abundant and widely distributed in the central nervous system. GluR1 (Glutamate Receptor 1) is an ionotropic glutamate receptor. L-glutamate acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter at many synapses in the central nervous system. Binding of the excitatory neurotransmitter, L-glutamate, induces a conformation change that leads to the opening of the cation channel and converts the chemical signal to an electrical impulse. Then, the receptor desensitizes rapidly and enters a transiet inactive state characterized by the presence of a bound agonist. In the presence of CACNG4, CACNG7, or CACNG8, GluR1 shows resensitization which is characterized by a delayed accumulation of current flux upon continued application of glutamate. Phosphorylation of GluR1 is critical for long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) expression and the retention of memories.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161








![GluR1 antibody detects GluR1 protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Frozen-sectioned mouse mouse cerebellum. Green: GluR1 stained by GluR1 antibody (GTX132945) diluted at 1:250. Red: NF-H, stained by NF-H antibody [GT114] (GTX634289) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 10 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX132945/GTX132945_43166_20180530_IHC-Fr_M_2_w_23060523_599.webp)