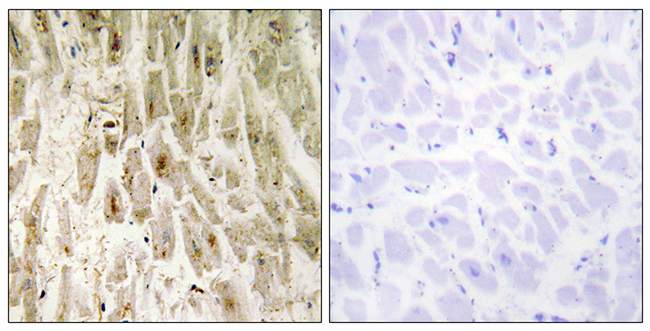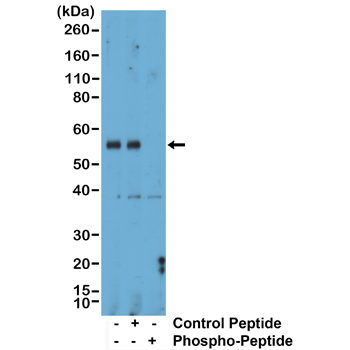
Western Blot of mouse liver tissue lysate, using Anti-Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/465)/Smad5 (Ser463/465)/Smad9 (Ser465/467) rabbit monoclonal antibody (clone RM487) at a 1:1000 dilution. The phospho-specificity of RM487 was verified by peptide blocking using a control nonphospho-peptide or phosphor-peptide targeting residue Ser463/465 of Smad1 and Smad5 and residue Ser465/467 of Smad9.
anti-Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/465) / Smad5 (Ser463/465) / Smad9 (Ser465/467), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM487)
REV-31-1379-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetSMAD1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/465) / Smad5 (Ser463/465) / Smad9 (Ser465/467), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM487)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM487
- Gene ID4086
- Target nameSMAD1
- Target descriptionSMAD family member 1
- Target synonymsBSP-1, BSP1, JV4-1, JV41, MADH1, MADR1, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1, MAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1, Mad-related protein 1, SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 1, TGF-beta signaling protein 1, mothers against DPP homolog 1, transforming growth factor-beta signaling protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO15198
- Protein NameMothers against decapentaplegic homolog 9
- Scientific DescriptionMembers of the Smad family of signal transduction molecules are components of a critical intracellular pathway that transmits TGF-beta signals from the cell surface into the nucleus. Three distinct classes of Smads have been defined: the receptor-regulated Smads (R-Smads), which include Smad1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9; the common-mediator Smad (co-Smad), Smad4; and the antagonistic or inhibitory Smads (I-Smads), Smad6 and 7. Binding of the TGF-beta superfamily of ligands that includes Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-beta) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) to its cognate receptor allows phosphorylation of Smad 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9 (R-Smad, Receptor Smad). This signals for heterotrimerization with Smad4 (co-Smad, co-mediator Smad) and translocation of the complex to the nucleus. Inhibitory or antagonistic Smad (I-Smad) that includes Smad 6 and 7, interact with activated R-Smads and attenuate the signaling pathway. Smad4 acts as a tumor suppressor protein by transcriptionally regulating its target genes such as Cyclin D1 (downregulation) and collagen (upregulation) that inhibit cell proliferation. Dephosphorylation regulates nuclear export and nucleocytoplasmic dynamics of Smads. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to Smad1 and Smad5 when phosphorylated at Ser463/465 and Smad9 (Smad8) when phosphorylated at Ser465/467. There is no cross-reactivity to Smad1, Smad5, or Smad9 that are not phosphorylated. This antibody reacts to human, mouse or rat Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/465)/Smad5 (Ser463/465)/Smad9 (Ser465/467). Source: Rabbit. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: A phospho-peptide corresponding to human Phospho-Smad1 (Ser463/465)/Smad5 (Ser463/465)/Smad9 (Ser465/467). Applications: WB. Members of the Smad family of signal transduction molecules are components of a critical intracellular pathway that transmits TGF-beta signals from the cell surface into the nucleus. Three distinct classes of Smads have been defined: the receptor-regulated Smads (R-Smads), which include Smad1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9; the common-mediator Smad (co-Smad), Smad4; and the antagonistic or inhibitory Smads (I-Smads), Smad6 and 7. Binding of the TGF-beta superfamily of ligands that includes Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-beta) and bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) to its cognate receptor allows phosphorylation of Smad 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 9 (R-Smad, Receptor Smad). This signals for heterotrimerization with Smad4 (co-Smad, co-mediator Smad) and translocation of the complex to the nucleus. Inhibitory or antagonistic Smad (I-Smad) that includes Smad 6 and 7, interact with activated R-Smads and attenuate the signaling pathway. Smad4 acts as a tumor suppressor protein by transcriptionally regulating its target genes such as Cyclin D1 (downregulation) and collagen (upregulation) that inhibit cell proliferation. Dephosphorylation regulates nuclear export and nucleocytoplasmic dynamics of Smads.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161