![Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Apolipoprotein E protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HepG2 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Apolipoprotein E stained by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Apolipoprotein E protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HepG2 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Apolipoprotein E stained by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_43006_20171220_ICC_IF_w_23053123_454.webp)
Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Apolipoprotein E protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HepG2 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Apolipoprotein E stained by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.
Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term
GTX100053
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetAPOE
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameApolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:20000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. ELISA: 1:1000-1:10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.66 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID348
- Target nameAPOE
- Target descriptionapolipoprotein E
- Target synonymsAD2, APO-E, ApoE4, LDLCQ5, LPG, apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein E3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP02649
- Protein NameApolipoprotein E
- Scientific DescriptionChylomicron remnants and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) remnants are rapidly removed from the circulation by receptor-mediated endocytosis in the liver. Apolipoprotein E, a main apoprotein of the chylomicron, binds to a specific receptor on liver cells and peripheral cells. ApoE is essential for the normal catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein constituents. The APOE gene is mapped to chromosome 19 in a cluster with APOC1 and APOC2. Defects in apolipoprotein E result in familial dysbetalipoproteinemia, or type III hyperlipoproteinemia (HLP III), in which increased plasma cholesterol and triglycerides are the consequence of impaired clearance of chylomicron and VLDL remnants. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

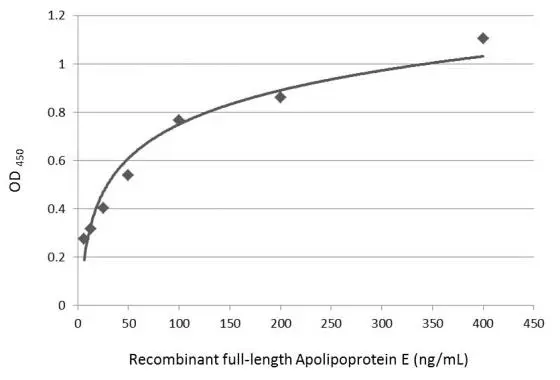
![Sandwich ELISA detection of recombinant full-length human apolipoprotein E using Apolipoprotein E antibody [GT1627] (GTX635891) as capture antibody at concentration of 5 μg/mL and Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) as detection antibody at concentration of 1 μg/mL. Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) was diluted at 1:10000 and used to detect the primary antibody. Sandwich ELISA detection of recombinant full-length human apolipoprotein E using Apolipoprotein E antibody [GT1627] (GTX635891) as capture antibody at concentration of 5 μg/mL and Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) as detection antibody at concentration of 1 μg/mL. Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) was diluted at 1:10000 and used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_42963_20200122_ELISA_PAIR_2_w_23053123_276.webp)
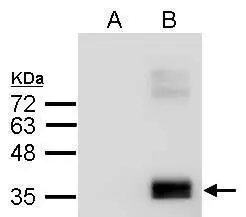
![Human plasma (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:10000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Human plasma (30 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:10000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_42963_20171027_WB_H_plasma_w_23053123_852.webp)
![Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Apolipoprotein E protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: THP-1 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: Apolipoprotein E protein stained by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Apolipoprotein E protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: THP-1 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: Apolipoprotein E protein stained by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_39233_IFA_w_23053123_506.webp)
![Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term immunoprecipitates Apolipoprotein E protein in IP experiments. IP Sample: HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract A : 30 μg whole cell lysate/extract of Apolipoprotein E protein expressing HepG2 cells B : Control with 3 μg of pre-immune rabbit IgG C : Immunoprecipitation of Apolipoprotein E by 3 μg of Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) 10% SDS-PAGE The immunoprecipitated Apolipoprotein E protein was detected by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:1000. EasyBlot anti-rabbit IgG (HRP) (GTX221666-01) was used as a secondary reagent. Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term immunoprecipitates Apolipoprotein E protein in IP experiments. IP Sample: HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract A : 30 μg whole cell lysate/extract of Apolipoprotein E protein expressing HepG2 cells B : Control with 3 μg of pre-immune rabbit IgG C : Immunoprecipitation of Apolipoprotein E by 3 μg of Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) 10% SDS-PAGE The immunoprecipitated Apolipoprotein E protein was detected by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:1000. EasyBlot anti-rabbit IgG (HRP) (GTX221666-01) was used as a secondary reagent.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_39233_IP_w_23053123_873.webp)
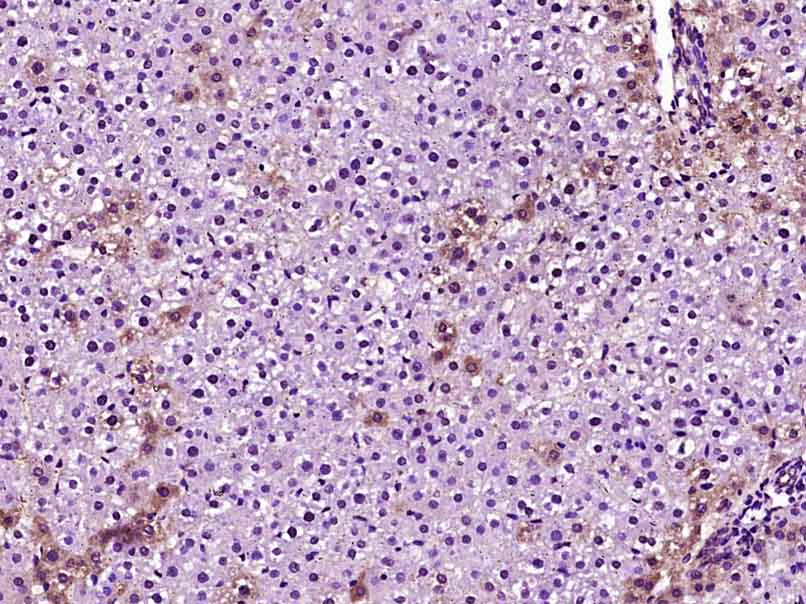
![Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects secreted Apolipoprotein E protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human ovarian cancer. Apolipoprotein E stained by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects secreted Apolipoprotein E protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human ovarian cancer. Apolipoprotein E stained by Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_42963_20190517_IHC-P_w_23053123_424.webp)
![Sandwich ELISA detection of recombinant full-length human apolipoprotein E using Apolipoprotein E antibody [GT27711] (GTX635889) as capture antibody at concentration of 5 μg/mL and Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) as detection antibody at concentration of 1 μg/mL. Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) was diluted at 1:10000 and used to detect the primary antibody. Sandwich ELISA detection of recombinant full-length human apolipoprotein E using Apolipoprotein E antibody [GT27711] (GTX635889) as capture antibody at concentration of 5 μg/mL and Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) as detection antibody at concentration of 1 μg/mL. Rabbit IgG antibody (HRP) (GTX213110-01) was diluted at 1:10000 and used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_42963_20200122_ELISA_PAIR_w_23053123_688.webp)
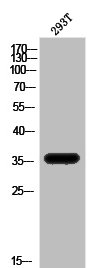
![Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects APOE protein by western blot analysis. A. 30 μg HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract 12% SDS-PAGE Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) dilution: 1:1000 The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term detects APOE protein by western blot analysis. A. 30 μg HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract 12% SDS-PAGE Apolipoprotein E antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX100053) dilution: 1:1000 The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100053/GTX100053_39233_WB_w_23053123_616.webp)






![Apolipoprotein E (R136S Mutant) antibody detects Apolipoprotein E (R136S Mutant) protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HepG2 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Apolipoprotein E (R136S Mutant) stained by Apolipoprotein E (R136S Mutant) antibody (GTX135410) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX135410/GTX135410_43999_20220121_ICC_IF_w_23060620_209.webp)