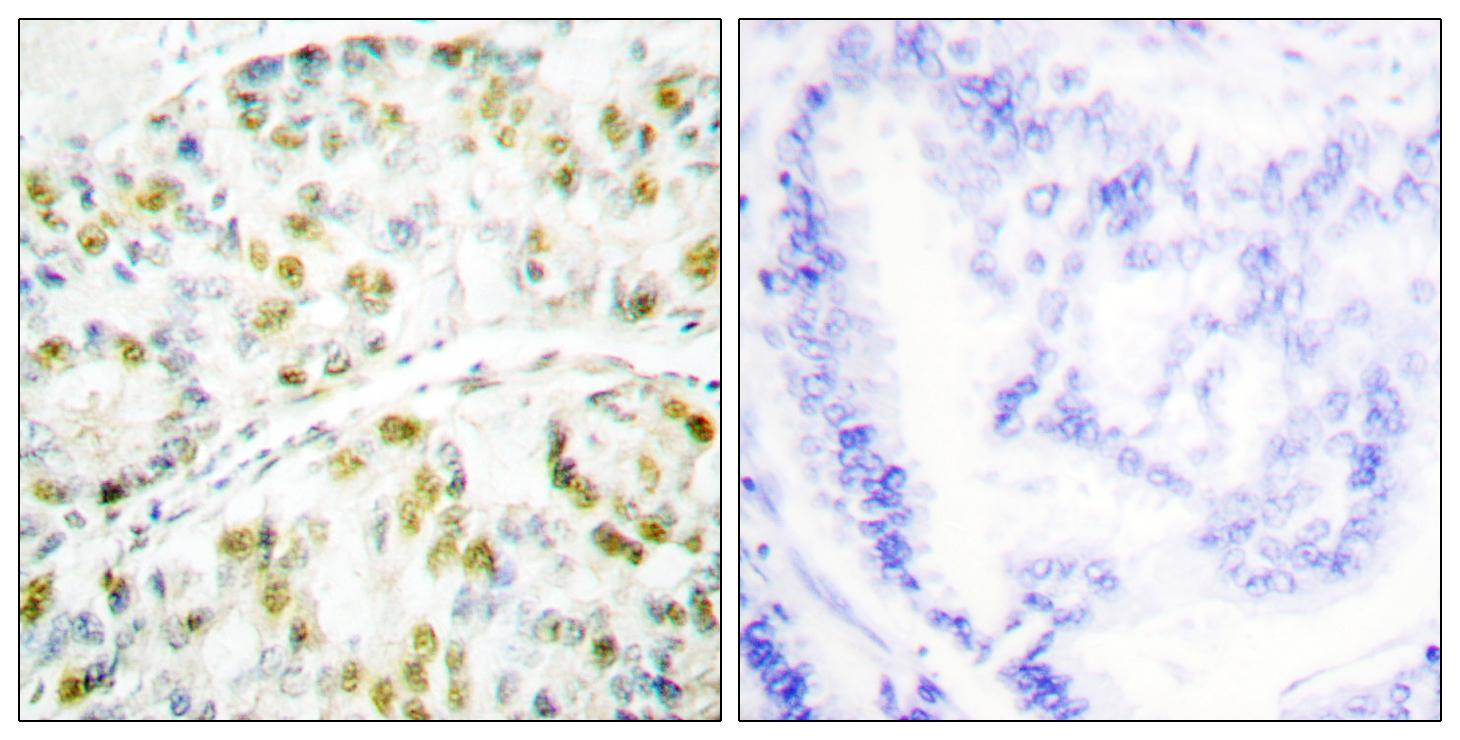
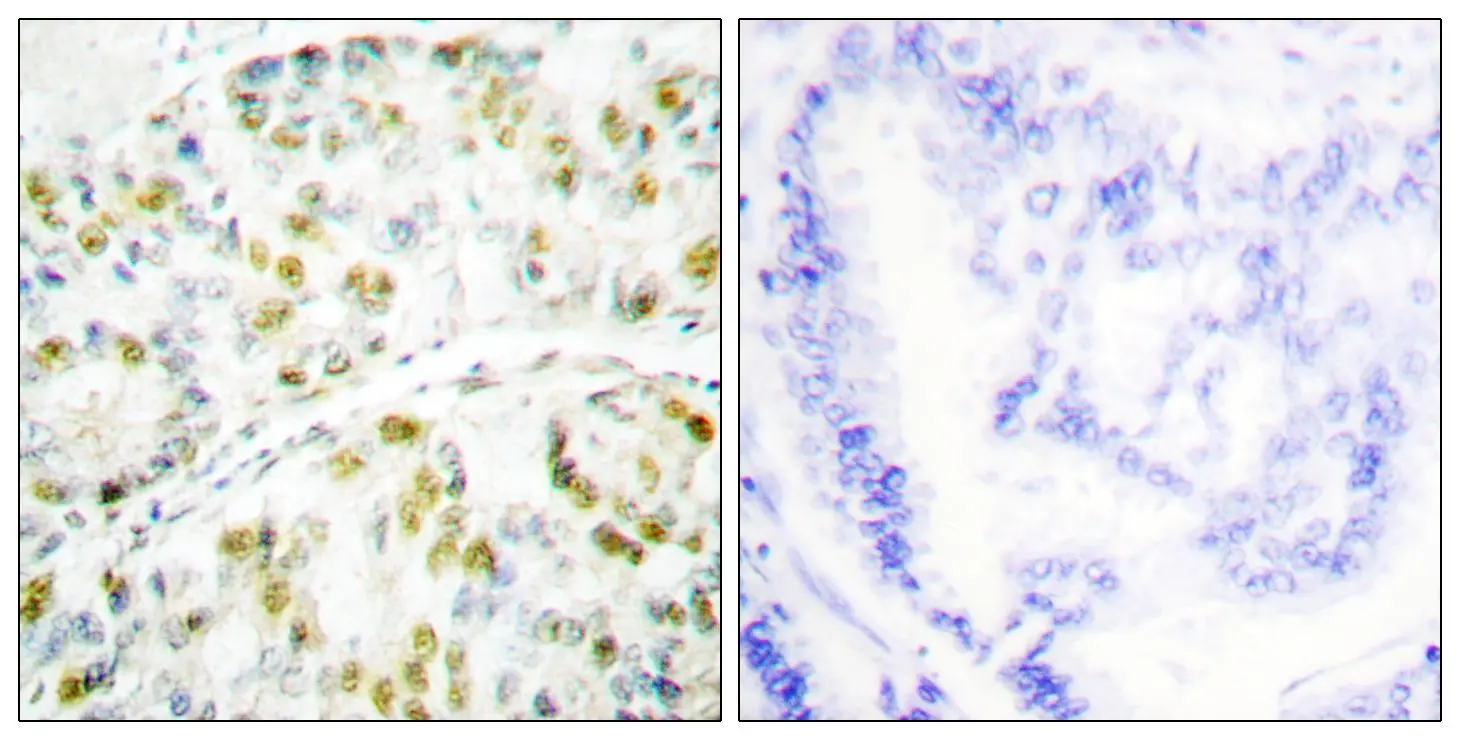
![IHC-P analysis of ovarian cancer tissue (left) and lung cancer tissue (right) using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5]. IHC-P analysis of ovarian cancer tissue (left) and lung cancer tissue (right) using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX80399/GTX80399_20170912_IHC-P_w_23061322_586.webp)
IHC-P analysis of ovarian cancer tissue (left) and lung cancer tissue (right) using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5].
Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5]
GTX80399
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetATXN1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameAtaxin 1 antibody [2F5]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1/500 - 1/2000. ICC/IF: 1/200 - 1/1000. IHC-P: 1/200 - 1/1000. FCM: 1/200 - 1/400. ELISA: 1/10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID2F5
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6310
- Target nameATXN1
- Target descriptionataxin 1
- Target synonymsATX1, D6S504E, SCA1, ataxin-1, alternative ataxin1, spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 protein
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP54253
- Protein NameAtaxin-1
- Scientific DescriptionThe autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxias (ADCA) are a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by progressive degeneration of the cerebellum, brain stem and spinal cord. Clinically, ADCA has been divided into three groups: ADCA types I-III. ADCAI is genetically heterogeneous, with five genetic loci, designated spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6, being assigned to five different chromosomes. ADCAII, which always presents with retinal degeneration (SCA7), and ADCAIII often referred to as the pure cerebellar syndrome (SCA5), are most likely homogeneous disorders. Several SCA genes have been cloned and shown to contain CAG repeats in their coding regions. ADCA is caused by the expansion of the CAG repeats, producing an elongated polyglutamine tract in the corresponding protein. The expanded repeats are variable in size and unstable, usually increasing in size when transmitted to successive generations. The function of the ataxins is not known. This loc
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![ICC/IF analysis of NTERA-2 cells using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5]. Green : Ataxin 1 Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye Red: Actin filaments ICC/IF analysis of NTERA-2 cells using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5]. Green : Ataxin 1 Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye Red: Actin filaments](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX80399/GTX80399_20170912_ICCIF_w_23061322_740.webp)
![WB analysis of HEK293 (1) and ATXN1(AA: 645-815)-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5]. WB analysis of HEK293 (1) and ATXN1(AA: 645-815)-hIgGFc transfected HEK293 (2) cell lysate using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX80399/GTX80399_20170912_WB_w_23061322_895.webp)
![FACS analysis of Jurkat cells using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5]. Green : Ataxin 1 Purple : negative control FACS analysis of Jurkat cells using GTX80399 Ataxin 1 antibody [2F5]. Green : Ataxin 1 Purple : negative control](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX80399/GTX80399_20170912_FACS_w_23061322_219.webp)