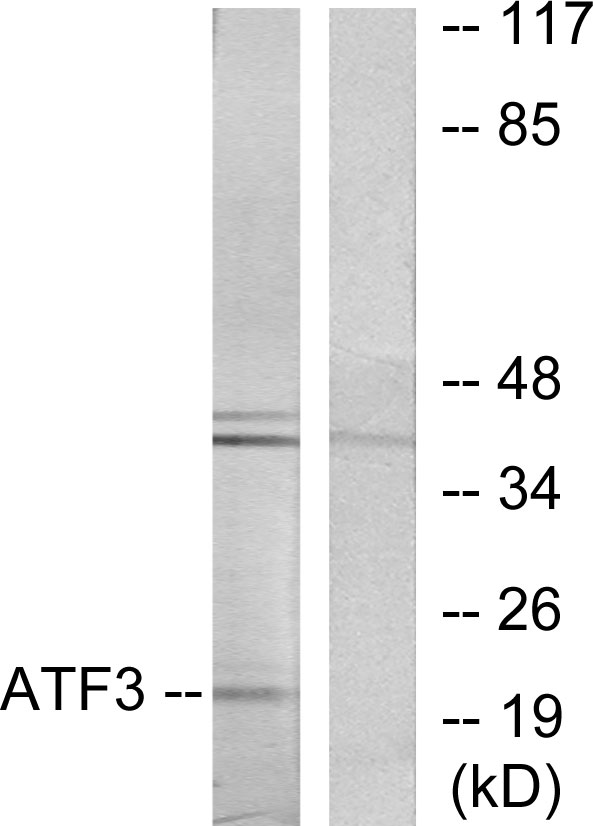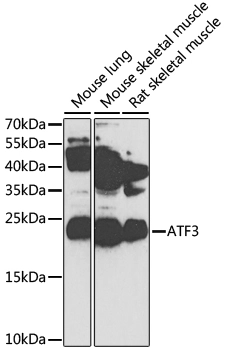
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX30069 ATF3 antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane
ATF3 antibody
GTX30069
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetATF3
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameATF3 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID467
- Target nameATF3
- Target descriptionactivating transcription factor 3
- Target synonymscyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-3, cAMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP18847
- Protein NameCyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-3
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the mammalian activation transcription factor/cAMP responsive element-binding (CREB) protein family of transcription factors. This gene is induced by a variety of signals, including many of those encountered by cancer cells, and is involved in the complex process of cellular stress response. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. It is possible that alternative splicing of this gene may be physiologically important in the regulation of target genes. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Benefits of Valsartan and Amlodipine in Lipolysis through PU.1 Inhibition in Fructose-Induced Adiposity.Read this paper
- Transcriptional factor ATF3 promotes liver fibrosis via activating hepatic stellate cells. Shi Z et al., 2020 Dec 14, Cell Death DisRead this paper