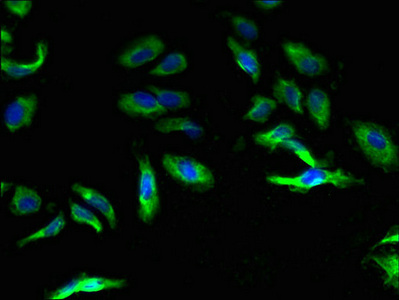
![IHC-Fr analysis of mouse stomach tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. Green : Primary antibody Blue : DAPI Antigen retireval : sodium citrate buffer for 45 minutes at 4oC, immersing in sodium citrate buffer for 10 minutes at 100oC Fixation : 4% formalin Permeabilization : 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS IHC-Fr analysis of mouse stomach tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. Green : Primary antibody Blue : DAPI Antigen retireval : sodium citrate buffer for 45 minutes at 4oC, immersing in sodium citrate buffer for 10 minutes at 100oC Fixation : 4% formalin Permeabilization : 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX19347/GTX19347_1005_IHC-Fr_w_23060620_610.webp)
IHC-Fr analysis of mouse stomach tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. Green : Primary antibody Blue : DAPI Antigen retireval : sodium citrate buffer for 45 minutes at 4oC, immersing in sodium citrate buffer for 10 minutes at 100oC Fixation : 4% formalin Permeabilization : 0.3% Triton X-100 in PBS
Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]
GTX19347
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Rat
TargetCASR
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCalcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 2 microg/ml. IHC-Fr: 2 microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID5C10, ADD
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID846
- Target nameCASR
- Target descriptioncalcium sensing receptor
- Target synonymsCAR, EIG8, FHH, FIH, GPRC2A, HHC, HHC1, HYPOC1, NSHPT, PCAR1, hCasR, extracellular calcium-sensing receptor, parathyroid Ca(2+)-sensing receptor 1, parathyroid cell calcium-sensing receptor 1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP41180
- Protein NameExtracellular calcium-sensing receptor
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a plasma membrane G protein-coupled receptor that senses small changes in circulating calcium concentration. The encoded protein couples this information to intracellular signaling pathways that modify parathyroid hormone secretion or renal cation handling, and thus this protein plays an essential role in maintaining mineral ion homeostasis. Mutations in this gene are a cause of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism, and autosomal dominant hypocalcemia. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017]
- ReactivityBovine, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Differential parathyroid and kidney Ca(2+)-sensing receptor activation in autosomal dominant hypocalcemia 1. van Megen WH et al., 2022 Apr, EBioMedicineRead this paper
- Activation of the calcium sensing receptor increases claudin-14 expression via a PLC -p38-Sp1 pathway.Read this paper
- Thick ascending limb claudins are altered to increase calciuria and magnesiuria in metabolic acidosis. Oh IH et al., 2021 Mar 1, Am J Physiol Renal PhysiolRead this paper
- Activation of the calcium sensing receptor attenuates TRPV6-dependent intestinal calcium absorption. Lee JJ et al., 2019 Apr 23, JCI InsightRead this paper
- Novel Ca2+-dependent mechanisms regulate spontaneous release at excitatory synapses onto CA1 pyramidal cells. Babiec WE et al., 2018 Feb 1, J NeurophysiolRead this paper

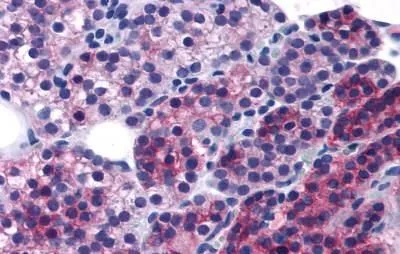
![IHC-P analysis of human kidney tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:100 IHC-P analysis of human kidney tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:100](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX19347/GTX19347_1067_IHC-P_w_23060620_681.webp)
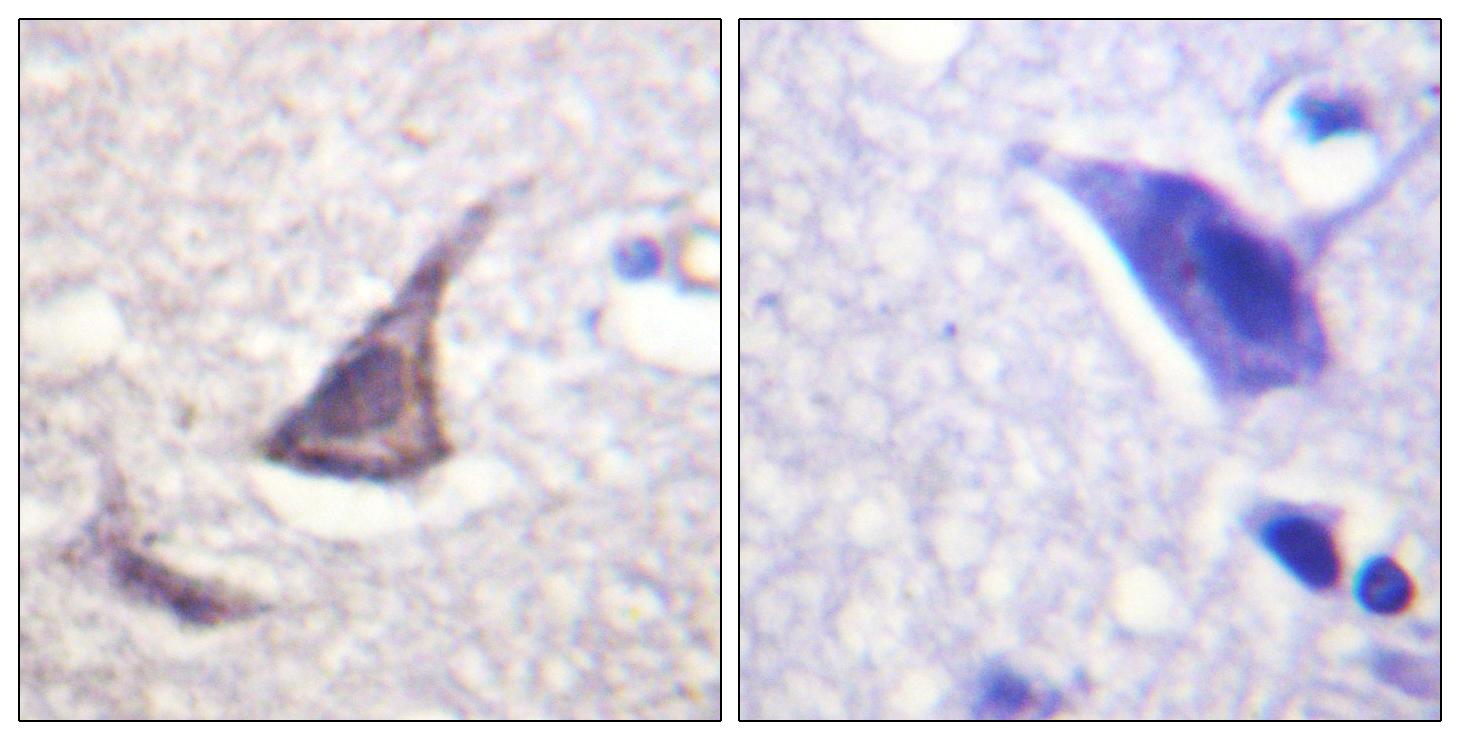
![IHC-P analysis of human brain tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:100 IHC-P analysis of human brain tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. Left : Primary antibody Right : Negative control without primary antibody Antigen retrieval : heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes Dilution : 1:100](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX19347/GTX19347_1066_IHC-P_w_23060620_320.webp)
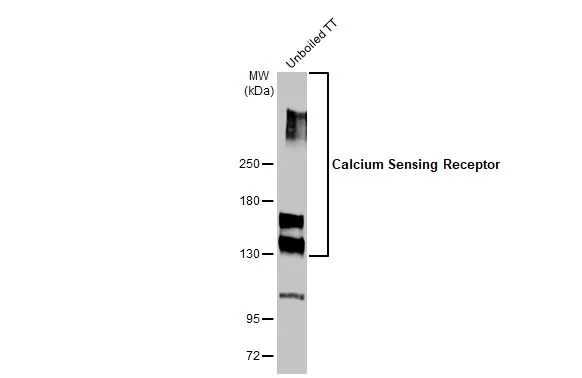
![WB analysis of HEK7-2 cell extract using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. WB analysis of HEK7-2 cell extract using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX19347/GTX19347_2134_WB_w_23060620_362.webp)
![IHC-Fr analysis of bovine corneal epithelium (CE) limbus tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD]. IHC-Fr analysis of bovine corneal epithelium (CE) limbus tissue using GTX19347 Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [5C10, ADD].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX19347/GTX19347_952_IHC-Fr_w_23060620_575.webp)



![Rat tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Calcium Sensing Receptor antibody [HL2357] (GTX638563) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX638563/GTX638563_T-45033_20230512_WB_R_kidney_23051702_619.webp)