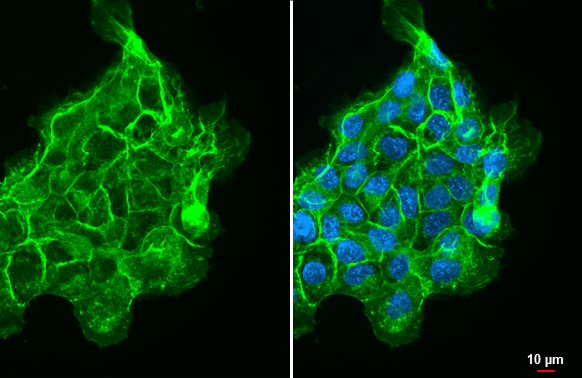
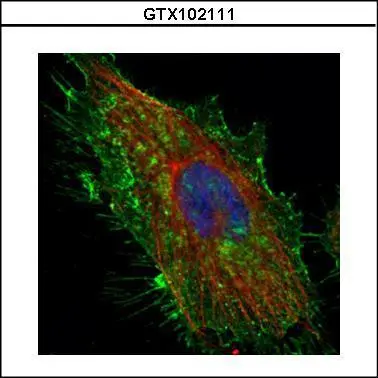
CD44 antibody detects CD44 protein at cell membrane by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: A431 cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: CD44 stained by CD44 antibody (GTX102111) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
CD44 antibody
GTX102111
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Rabbit, Rat
TargetCD44
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD44 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:20000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID960
- Target nameCD44
- Target descriptionCD44 molecule (IN blood group)
- Target synonymsCDW44, CSPG8, ECM-III, ECMR-III, H-CAM, HCELL, HUTCH-1, HUTCH-I, Hermes-1, LHR, MC56, MDU2, MDU3, MIC4, Pgp1, CD44 antigen, CD44 molecule (Indian blood group), GP90 lymphocyte homing/adhesion receptor, Hermes antigen, In(Lu) related-p80, Indian blood group antigen, cell surface glycoprotein CD44, chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 8, epican, extracellular matrix receptor III, hematopoietic cell E- and L-selectin ligand, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, homing cell adhesion molecule, homing function and Indian blood group system, hyaluronate receptor, phagocyte glycoprotein 1, phagocytic glycoprotein 1, soluble CD44
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP16070
- Protein NameCD44 antigen
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This protein participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. Transcripts for this gene undergo complex alternative splicing that results in many functionally distinct isoforms, however, the full length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. Alternative splicing is the basis for the structural and functional diversity of this protein, and may be related to tumor metastasis. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Rabbit, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

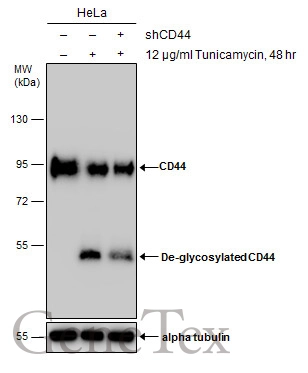
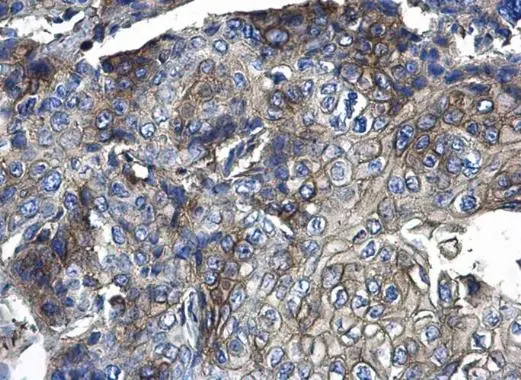
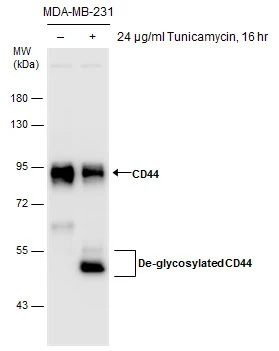
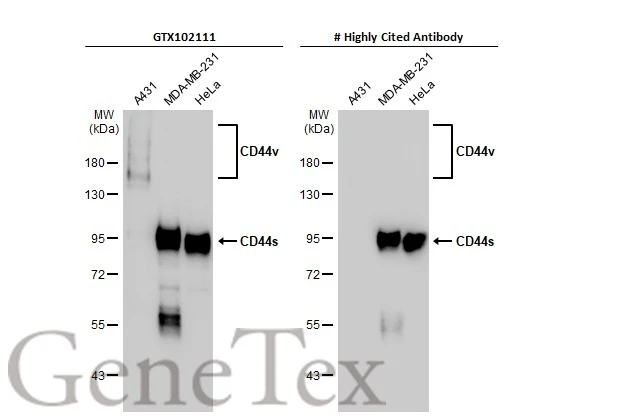
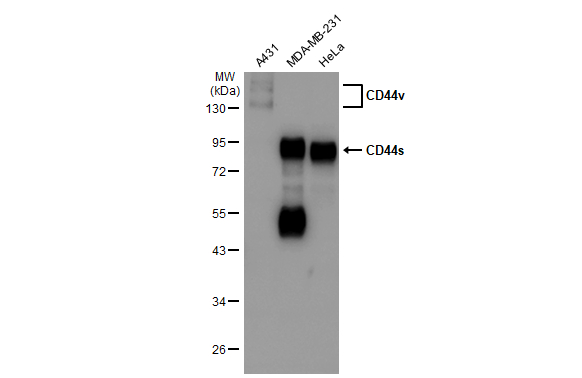
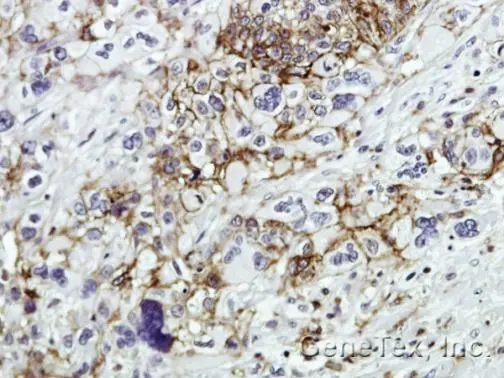
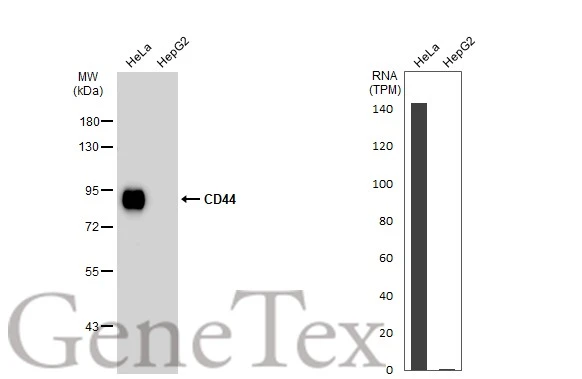







![WB analysis of MOLT-4 (lane 1) and HeLa (lane 2) cell lysates (non-reducing) using GTX29524 CD44 antibody [MEM-263].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX29524/GTX29524_20191025_AP_001_229_w_23060722_294.webp)