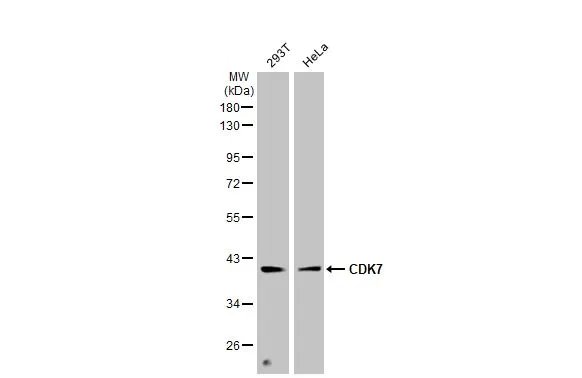
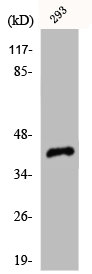
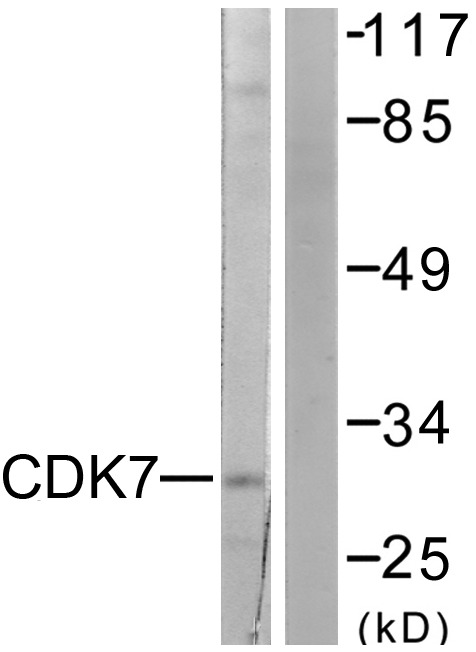
CDK7 Antibody, HRP conjugated
CSB-PA005075LB01HU
ApplicationsELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCDK7
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NameCDK7 Antibody, HRP conjugated
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateHRP
- Gene ID1022
- Target nameCDK7
- Target descriptioncyclin dependent kinase 7
- Target synonymsCAK, CAK1, CDKN7, HCAK, MO15, STK1, p39MO15, cyclin-dependent kinase 7, 39 KDa protein kinase, CDK-activating kinase 1, TFIIH basal transcription factor complex kinase subunit, cell division protein kinase 7, cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (MO15 homolog, Xenopus laevis, cdk-activating kinase), homolog of Xenopus MO15 Cdk-activating kinase, kinase subunit of CAK, serine/threonine kinase stk1, serine/threonine protein kinase 1, serine/threonine protein kinase MO15
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP50613
- Protein NameCyclin-dependent kinase 7
- Scientific DescriptionSerine/threonine kinase involved in cell cycle control and in RNA polymerase II-mediated RNA transcription. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are activated by the binding to a cyclin and mediate the progression through the cell cycle. Each different complex controls a specific transition between 2 subsequent phases in the cell cycle. Required for both activation and complex formation of CDK1/cyclin-B during G2-M transition, and for activation of CDK2/cyclins during G1-S transition (but not complex formation). CDK7 is the catalytic subunit of the CDK-activating kinase (CAK) complex. Phosphorylates SPT5/SUPT5H, SF1/NR5A1, POLR2A, p53/TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6 and CDK11B/CDK11. CAK activates the cyclin-associated kinases CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 by threonine phosphorylation, thus regulating cell cycle progression. CAK complexed to the core-TFIIH basal transcription factor activates RNA polymerase II by serine phosphorylation of the repetitive C-terminal domain (CTD) of its large subunit (POLR2A), allowing its escape from the promoter and elongation of the transcripts. Phosphorylation of POLR2A in complex with DNA promotes transcription initiation by triggering dissociation from DNA. Its expression and activity are constant throughout the cell cycle. Upon DNA damage, triggers p53/TP53 activation by phosphorylation, but is inactivated in turn by p53/TP53; this feedback loop may lead to an arrest of the cell cycle and of the transcription, helping in cell recovery, or to apoptosis. Required for DNA-bound peptides-mediated transcription and cellular growth inhibition.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161