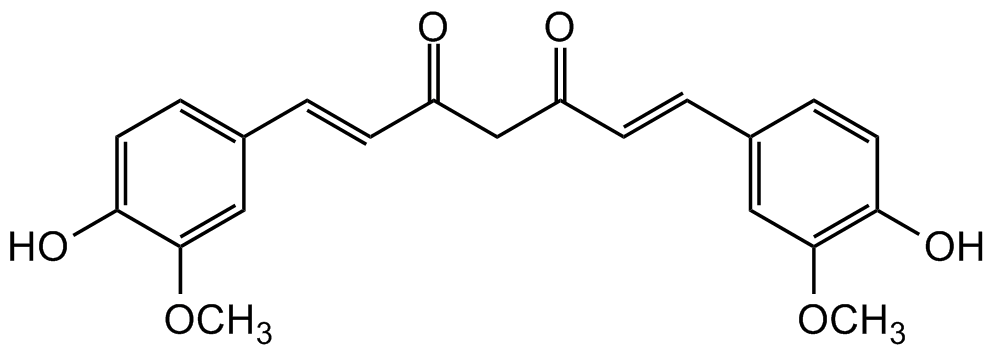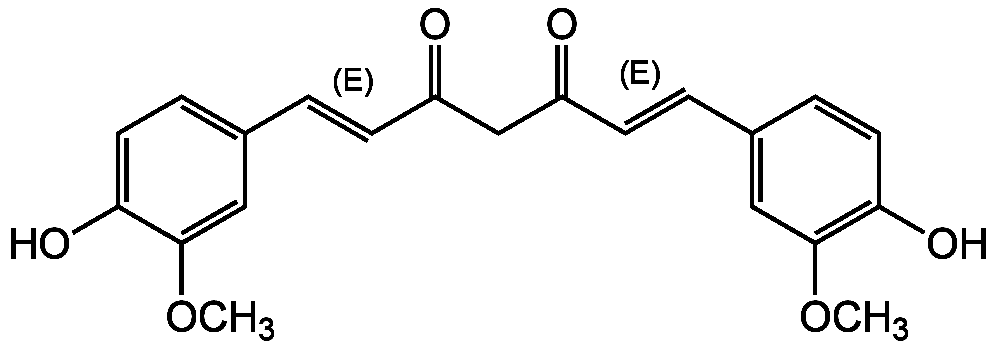
Chemical Structure
Curcumin (high purity) [458-37-7]
AG-CN2-0059
CAS Number458-37-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight368.4
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCurcumin (high purity) [458-37-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number458-37-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC21H20O6
- Molecular Weight368.4
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 458-37-7. Formula: C21H20O6. MW: 368.4. Synthetic. Originally isolated from turmeric (Curcuma longa). Anti-cancer compound. Interferes with multiple cell signaling pathways, including cell cycle (cyclin D1 and cyclin E), apoptosis (activation of caspases and down-regulation of anti-apoptotic gene products), proliferation (HER-2, EGFR and AP-1), survival (PI3K/AKT pathway), invasion (MMP-9 and adhesion molecules), angiogenesis (VEGF), metastasis (CXCR-4) and inflammation (NF-kappaB, TNF, IL-6, IL-1, COX-2 and 5-LOX). Anti-angiogenic. Anti-metastatic. Anti-invasive. Chemopreventive. Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway modulator. Downregulates Shh and Gli1. Antioxidant. Anti-inflammatory. Potent inhibitor of NF-kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), lipooxygenase (LOX), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOSII). Downregulates the expression of various proinflammatory cytokines including TNF, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12 and chemokines. Potent immunomodulator. Modulates several key transcription factors. Down-regulate transcription factors NF-kappaB, AP-1 and Egr-1. Down-regulates the expression of COX-2, LOX, NOS, MMP-9, uPA, TNF, chemokines, cell surface adhesion molecules and cyclin D1. Down-regulate growth factor receptors (such as EGFR and HER2) and inhibits the activity of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, protein tyrosine kinases and protein serine/threonine kinases. Neuroprotective. Anti-amyloid activity. Cardioprotective. p300/CBP-HAT inhibitor. Regulates lipid metabolism and downregulates obesity. Activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) and Nrf2 cell-signaling pathways. Antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal. Epigenetic agent. Interacts with histone deacetylases (HDACs), histone acetyltransferases (HATs), DNA methyltransferase I and microRNAs. Inducer of autophagy in lung adenocarcinoma cells. - Curcumin is the major yellow pigment in turmeric and curry and has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, antidiabetic, antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, chemopreventive and antitumor activities. It interferes with multiple cell signaling pathways, including cell cycle (cyclin D1 and cyclin E), apoptosis (activation of caspases and down-regulation of anti-apoptotic gene products), proliferation (HER-2, EGFR and AP-1), survival (PI3K/AKT pathway), invasion (MMP-9 and adhesion molecules), angiogenesis (VEGF), metastasis (CXCR-4), tumorigenesis and development (Shh, Gli), metabolism (PPARgamma, Nrf2), epigenetics (HDACs, HATs, DNA methyltransferase I and microRNAs) and inflammation (NLRP3, TLR4, NF-kappaB, TNF, IL-6, IL-1, COX-2 and 5-LOX). Anti-angiogenic. Anti-metastatic. Anti-invasive. Chemopreventive. Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway modulator. Downregulates Shh and Gli1. Anti-inflammatory. Potent inhibitor of NF-kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), lipooxygenase (LOX), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS; NOSII). Downregulates the expression of various proinflammatory cytokines including TNF, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12 and chemokines. Inhibits TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling. Modulates several key transcription factors. Down-regulate transcription factors NF-kappaB, AP-1 and Egr-1. Down-regulates the expression of COX-2, LOX, NOS, MMP-9, uPA, TNF, chemokines, cell surface adhesion molecules and cyclin D1. Down-regulate growth factor receptors (such as EGFR and HER2) and inhibits the activity of c-Jun N-terminal kinase, protein tyrosine kinases and protein serine/threonine kinases. Neuroprotective. Anti-amyloid activity. Cardioprotective. p300/CBP-HAT inhibitor. Regulates lipid metabolism and downregulates obesity. Activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma) and Nrf2 cell-signaling pathways. Epigenetic agent. Interacts with histone deacetylases (HDACs), histone acetyltransferases (HATs), DNA methyltransferase I and microRNAs. Proteasome modulator/inhibitor.
- SMILESCOC1=CC(\C=C\C(=O)CC(=O)\C=C\C2=CC(OC)=C(O)C=C2)=CC=C1O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Curcumin [458-37-7]](https://bpsbioscience.com/media/catalog/product/2/7/27104_structure.png)