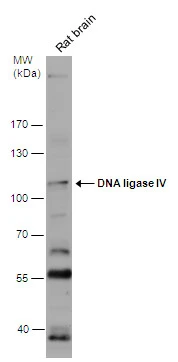
Sample(30 μg of whole cell lysate) A:MOLT4(GTX27912) 7.5% SDS PAGE GTX100100 diluted at 1:1000
DNA ligase IV antibody [N2C2], Internal
GTX100100
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetLIG4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameDNA ligase IV antibody [N2C2], Internal
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.65 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3981
- Target nameLIG4
- Target descriptionDNA ligase 4
- Target synonymsLIG4S, DNA ligase 4, DNA joinase, DNA ligase IV, DNA repair enzyme, ligase IV, DNA, ATP-dependent, polydeoxyribonucleotide synthase [ATP] 4, polynucleotide ligase, sealase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP49917
- Protein NameDNA ligase 4
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a DNA ligase that joins single-strand breaks in a double-stranded polydeoxynucleotide in an ATP-dependent reaction. This protein is essential for V(D)J recombination and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair through nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ). This protein forms a complex with the X-ray repair cross complementing protein 4 (XRCC4), and further interacts with the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). Both XRCC4 and DNA-PK are known to be required for NHEJ. The crystal structure of the complex formed by this protein and XRCC4 has been resolved. Defects in this gene are the cause of LIG4 syndrome. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

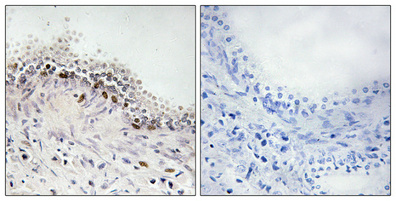
![DNA ligase IV antibody [N2C2], Internal detects DNA ligase IV protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse testis. DNA ligase IV stained by DNA ligase IV antibody [N2C2], Internal (GTX100100) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min DNA ligase IV antibody [N2C2], Internal detects DNA ligase IV protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse testis. DNA ligase IV stained by DNA ligase IV antibody [N2C2], Internal (GTX100100) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX100100/GTX100100_39820_20220401_IHC-P_M_w_23053123_430.webp)