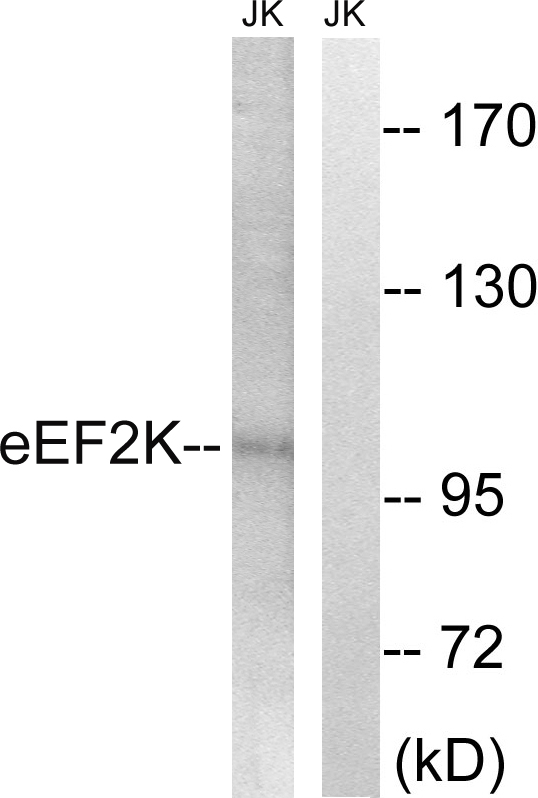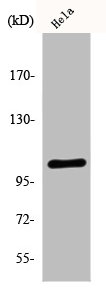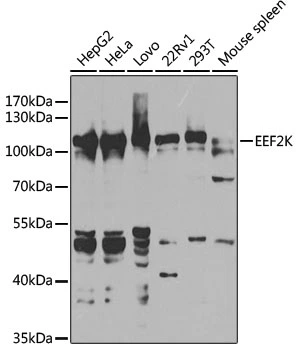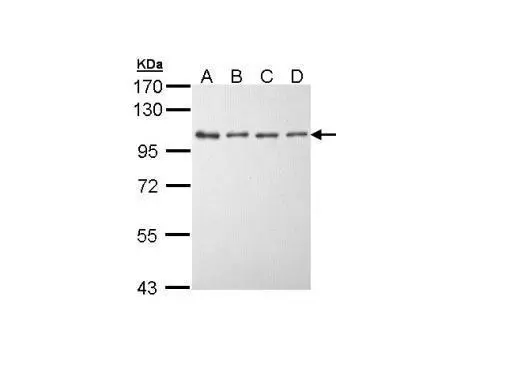
Sample (30 ug of whole cell lysate) A: A431 (GTX27909) B: H1299 C: Hela D: Hep G2 (GTX27900) 7.5% SDS PAGE GTX111496 diluted at 1:5000
eEF2K antibody [N1N3]
GTX111496
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetEEF2K
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameeEF2K antibody [N1N3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID29904
- Target nameEEF2K
- Target descriptioneukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase
- Target synonymsCaMKIII, HSU93850, eEF-2K, eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase, alternative protein EEF2K, calcium/calmodulin-dependent eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase, calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III, eEF-2 kinase, elongation factor-2 kinase, eukaroytic elongation factor 2 kinase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO00418
- Protein NameEukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a highly conserved protein kinase in the calmodulin-mediated signaling pathway that links activation of cell surface receptors to cell division. This kinase is involved in the regulation of protein synthesis. It phosphorylates eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (EEF2) and thus inhibits the EEF2 function. The activity of this kinase is increased in many cancers and may be a valid target for anti-cancer treatment. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161