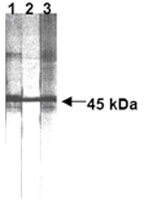
Western blot analysis of human Fas expression in human Fas transfected cells
Lane 1: anti-human Fas (ZB4)
Lane 2: anti-human Fas (UB2)
Lane 3: anti-human Fas (CH11).
Fas antibody [ZB4]
GTX13549
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, Neutralisation/Blocking, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetFAS
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameFas antibody [ZB4]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteFACS: Use at a concentration of 5 - 20 microg/ml. FuncS: Use at a concentration of 500 ng/ml to block the apoptotic activity other anti-CD95 antibodies. IHC: Use at an assay dependent dilution. WB: Use at a concentration of 5 microg/ml. Predicted molecular weight: 44 kDa. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, Neutralisation/Blocking, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDZB4
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID355
- Target nameFAS
- Target descriptionFas cell surface death receptor
- Target synonymsALPS1A, APO-1, APT1, CD95, FAS1, FASTM, TNFRSF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6, APO-1 cell surface antigen, CD95 antigen, FASLG receptor, Fas (TNF receptor superfamily, member 6), Fas AMA, TNF receptor superfamily member 6, apoptosis antigen 1, apoptosis signaling receptor FAS, apoptosis-mediating surface antigen FAS, mutant tumor necrosis receptor superfamily member 6, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 6
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP25445
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. This receptor contains a death domain. It has been shown to play a central role in the physiological regulation of programmed cell death, and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various malignancies and diseases of the immune system. The interaction of this receptor with its ligand allows the formation of a death-inducing signaling complex that includes Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD), caspase 8, and caspase 10. The autoproteolytic processing of the caspases in the complex triggers a downstream caspase cascade, and leads to apoptosis. This receptor has been also shown to activate NF-kappaB, MAPK3/ERK1, and MAPK8/JNK, and is found to be involved in transducing the proliferating signals in normal diploid fibroblast and T cells. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described, some of which are candidates for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). The isoforms lacking the transmembrane domain may negatively regulate the apoptosis mediated by the full length isoform. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2011]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Zhang X, Tang J, Kou X, et al. Proteomic analysis of MSC-derived apoptotic vesicles identifies Fas inheritance to ameliorate haemophilia a via activating platelet functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022,11(7):e12240. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12240Read this paper
- Kawasaki N, Yamashita-Kashima Y, Fujimura T, et al. Resistance to obinutuzumab-induced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity caused by abnormal Fas signaling is overcome by combination therapies. Mol Biol Rep. 2022,49(6):4421-4433. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07280-wRead this paper
- Tan X, Feng H, Guo Z, et al. Rabbit antithymocyte globulin induces human lymphocyte activation, proliferation, and apoptosis in the absence of complement: an experimental study. Transpl Int. 2021,34(5):930-941. doi: 10.1111/tri.13864Read this paper
- Dou R, Hong Z, Tan X, et al. Fas/FasL interaction mediates imbalanced cytokine/cytotoxicity responses of iNKT cells against Jurkat cells. Mol Immunol. 2018,99:145-153. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.05.011Read this paper
- Yang T, Shi R, Chang L, et al. Huachansu suppresses human bladder cancer cell growth through the Fas/Fasl and TNF- alpha/TNFR1 pathway in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2015,34(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s13046-015-0134-9Read this paper
- Lin KH, Hsiao G, Shih CM, et al. Mechanisms of resveratrol-induced platelet apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2009,83(3):575-85. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp139Read this paper
- Dabrowska A, Kim N, Aldovini A. Tat-induced FOXO3a is a key mediator of apoptosis in HIV-1-infected human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2008,181(12):8460-77.Read this paper



![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Fas antibody [GT1169] (GTX09129) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX09129/GTX09129_40000000061_20200306_WB_w_23053123_690.webp)
![WB analysis of human FAS (AA: 87-278) recombinant protein using GTX60557 Fas antibody [4F8H6].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60557/GTX60557_20170912_WB_1_w_23061123_994.webp)
![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60559 Fas antibody [4F8D6].
Black : Control antigen 100ng
Purple : Antigen 10ng
Blue : Antigen 50ng
Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60559/GTX60559_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_134.webp)
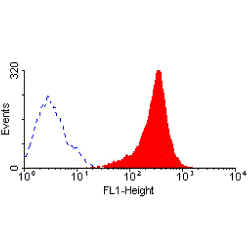
![FACS analysis of HUT78 cells using GTX75107 Fas antibody [LOB 3/17] (FITC).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX75107/GTX75107_3656_FACS_w_23061322_433.webp)
![FACS analysis of human peripheral blood using GTX78359 Fas antibody [LT95] (FITC).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX78359/GTX78359_20191025_AP_006_301_w_23061322_925.webp)