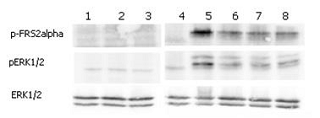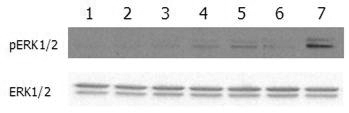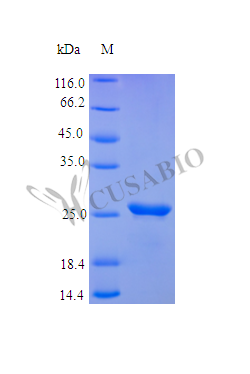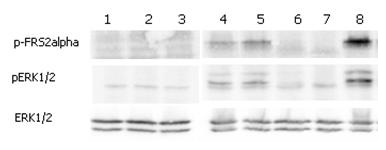
ERK and FRS2alpha phosphorylation induced by FGF-21 in Klotho expressing cells. Klotho expressing HEK 293EBNA cells were serum starved for 16hr and then stimulated with hFGF-23-His, FGF-23-Fc (Prod. No. AG-40A-0109), mCD137-Fc (Fc control) and FGF
FGF-23 (human):Fc (human) (rec.)
AG-40A-0109
Protein IDQ9GZV9
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameFGF-23 (human):Fc (human) (rec.)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Gene ID8074
- Target nameFGF23
- Target descriptionfibroblast growth factor 23
- Target synonymsADHR, FGFN, HFTC2, HPDR2, HYPF, PHPTC, fibroblast growth factor 23, phosphatonin, tumor-derived hypophosphatemia inducing factor
- Protein IDQ9GZV9
- Protein NameFibroblast growth factor 23
- Scientific DescriptionFGF-23 (Fibroblast growth factor 23) is a regulator of phosphate homeostasis. It upregulates EGR1 expression in the presence of KLBy. Acts directly on the parathyroid to decrease PTH secretion. Regulates the vitamin-D metabolism. Negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation and matrix mineralization. Defects in FGF-23 are the cause of autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets (ADHR) and of hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC). - Protein. Signal peptide and human FGF-23 (aa 1-251) are fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1. Source: HEK 293 cells. Endotoxin content: 90% (SDS-PAGE). FGF-23 (Fibroblast growth factor 23) is a regulator of phosphate homeostasis. It upregulates EGR1 expression in the presence of KLBy. Acts directly on the parathyroid to decrease PTH secretion. Regulates the vitamin-D metabolism. Negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation and matrix mineralization. Defects in FGF-23 are the cause of autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets (ADHR) and of hyperphosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis (HFTC).
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman