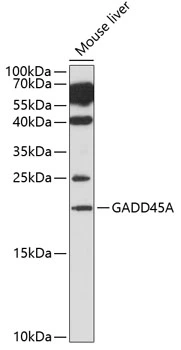
WB analysis of mouse liver tissue lysate using GTX54090 GADD45A antibody. The signal was developed with ECL plus-Enhanced. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane
GADD45A antibody
GTX54090
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetGADD45A
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameGADD45A antibody
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1647
- Target nameGADD45A
- Target descriptiongrowth arrest and DNA damage inducible alpha
- Target synonymsDDIT1, GADD45, growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD45 alpha, DDIT-1, DNA damage-inducible transcript 1 protein, DNA damage-inducible transcript-1, growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible 45 alpha
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP24522
- Protein NameGrowth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein GADD45 alpha
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of a group of genes whose transcript levels are increased following stressful growth arrest conditions and treatment with DNA-damaging agents. The protein encoded by this gene responds to environmental stresses by mediating activation of the p38/JNK pathway via MTK1/MEKK4 kinase. The DNA damage-induced transcription of this gene is mediated by both p53-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
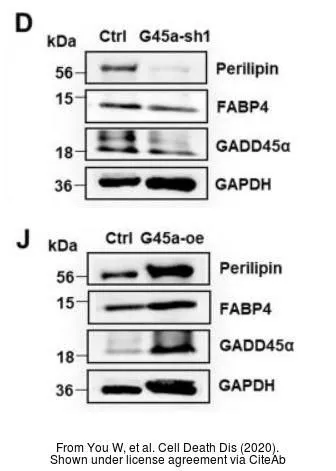
- GADD45alpha drives brown adipose tissue formation through upregulating PPARgamma in mice. You W et al., 2020 Jul 27, Cell Death DisRead this paper
- Protein inhibitor of activated STAT1 Ser503 phosphorylation-mediated Elk-1 SUMOylation promotes neuronal survival in APP/PS1 mice. Liu SY et al., 2019 Jun, Br J PharmacolRead this paper