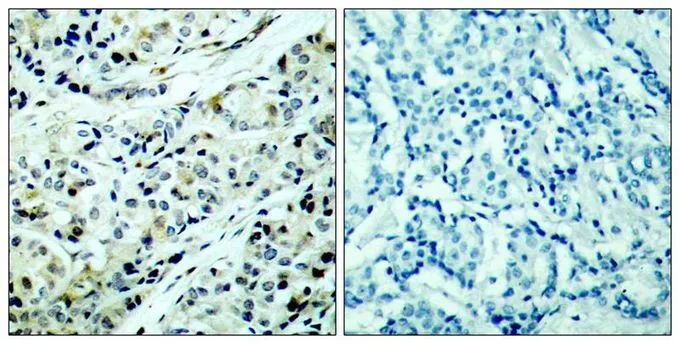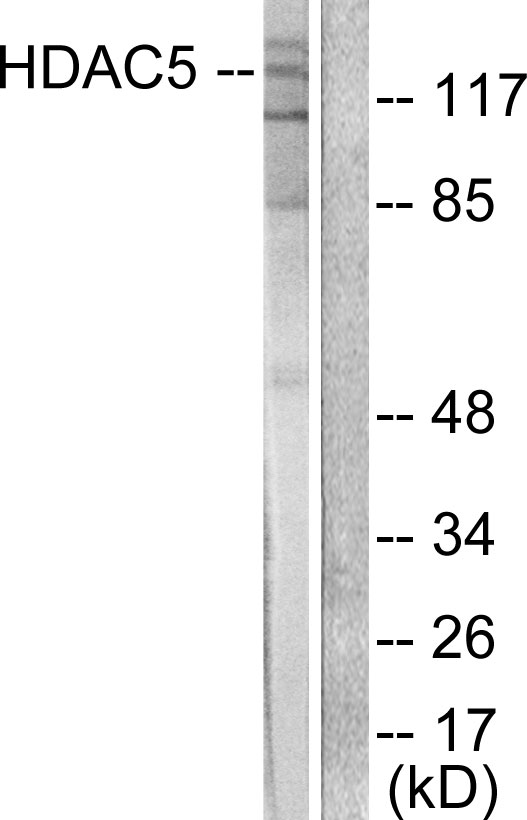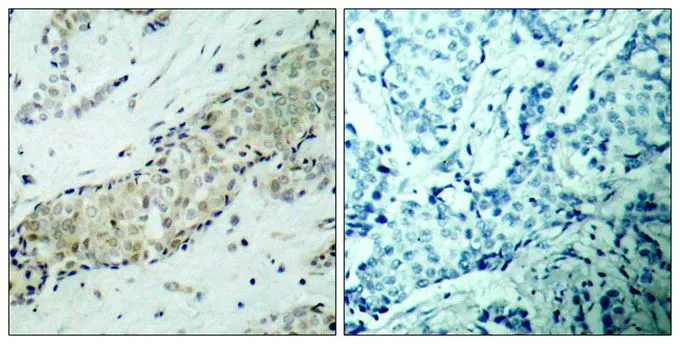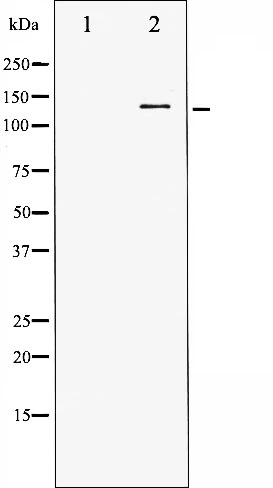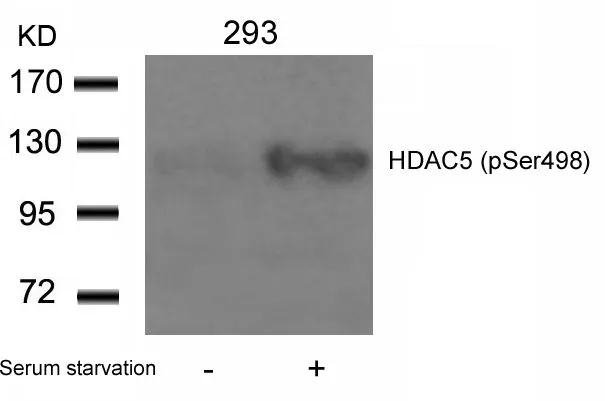
WB analysis of extracts from 293 cells untreated or treated with serum starvation using GTX50238 HDAC5 (phospho Ser498) antibody.
HDAC5 (phospho Ser498) antibody
GTX50238
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetHDAC5
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHDAC5 (phospho Ser498) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:50-1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID10014
- Target nameHDAC5
- Target descriptionhistone deacetylase 5
- Target synonymsHD5, NY-CO-9, histone deacetylase 5, antigen NY-CO-9
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UQL6
- Protein NameHistone deacetylase 5
- Scientific DescriptionHistones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the class II histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. It coimmunoprecipitates only with HDAC3 family member and might form multicomplex proteins. It also interacts with myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) proteins, resulting in repression of MEF2-dependent genes. This gene is thought to be associated with colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- The myokine meteorin-like (metrnl) improves glucose tolerance in both skeletal muscle cells and mice by targeting AMPKalpha2. Lee JO et al., 2020 May, FEBS JRead this paper