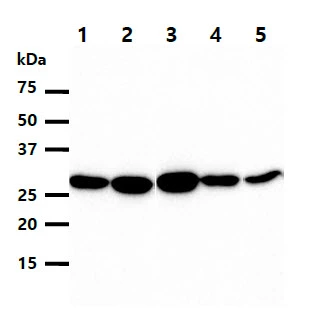
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] (GTX633693) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] (GTX633693) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX633693/GTX633693_42639_20230519_WB_multiple_B_23053001_417.webp)
Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] (GTX633693) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664]
GTX633693
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetHMOX1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHeme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDGT664
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3162
- Target nameHMOX1
- Target descriptionheme oxygenase 1
- Target synonymsHMOX1D, HO-1, HSP32, bK286B10, heme oxygenase 1, heat shock protein, 32-kD, heme oxygenase (decycling) 1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP09601
- Protein NameHeme oxygenase 1
- Scientific DescriptionHeme oxygenase, an essential enzyme in heme catabolism, cleaves heme to form biliverdin, which is subsequently converted to bilirubin by biliverdin reductase, and carbon monoxide, a putative neurotransmitter. Heme oxygenase activity is induced by its substrate heme and by various nonheme substances. Heme oxygenase occurs as 2 isozymes, an inducible heme oxygenase-1 and a constitutive heme oxygenase-2. HMOX1 and HMOX2 belong to the heme oxygenase family. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Luo K, Stocker R, Britton WJ, et al. Haem oxygenase limits Mycobacterium marinum infection-induced detrimental ferrostatin-sensitive cell death in zebrafish. FEBS J. 2022,289(3):671-681. doi: 10.1111/febs.16209Read this paper
- Hseu YC, Vudhya Gowrisankar Y, Wang LW, et al. The in vitro and in vivo depigmenting activity of pterostilbene through induction of autophagy in melanocytes and inhibition of UVA-irradiated α-MSH in keratinocytes via Nrf2-mediated antioxidant pathways. Redox Biol. 2021,44:102007. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102007Read this paper

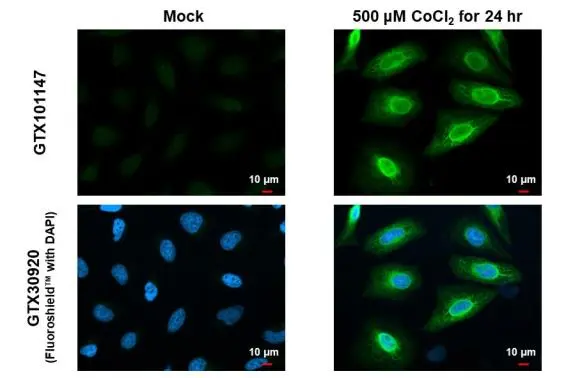
![Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] detects Heme Oxygenase 1 protein at endoplasmic reticulum by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: Mock and treated HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Heme Oxygenase 1 stained by Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] (GTX633693) diluted at 1:2000. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. Scale bar= 10μm. Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] detects Heme Oxygenase 1 protein at endoplasmic reticulum by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: Mock and treated HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Heme Oxygenase 1 stained by Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] (GTX633693) diluted at 1:2000. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. Scale bar= 10μm.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX633693/GTX633693_42639_20180718_ICC_IF_CoCl2_w_23061202_831.webp)
![Untreated (–) and treated (+) HeLa whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] (GTX633693) diluted at 1:1000. Untreated (–) and treated (+) HeLa whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT664] (GTX633693) diluted at 1:1000.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX633693/GTX633693_42639_20161020_WB_CoCl2_w_23061202_607.webp)

![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT1334] (GTX633676) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX633676/GTX633676_42590_20230519_WB_multiple_B_23053001_657.webp)
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [GT17811] (GTX633677) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX633677/GTX633677_42590_20230519_WB_multiple_B_23053001_670.webp)
![Wild-type (WT) and HMOX1 knockout (KO) HeLa cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Heme Oxygenase 1 antibody [HL1780] (GTX637432) diluted at 1:2000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX637432/GTX637432_T-44802_20221209_WB_KO_watermark_22121123_519.webp)