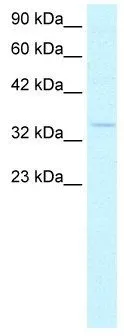
WB analysis of human lung tissue using GTX42614 HEY1 antibody at 1.0μg/ml.
HEY1 antibody, C-term
GTX42614
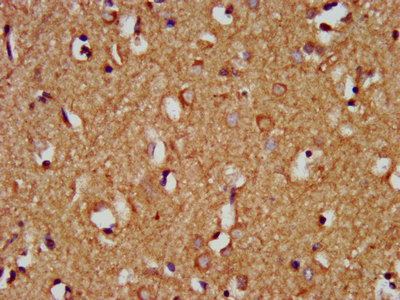
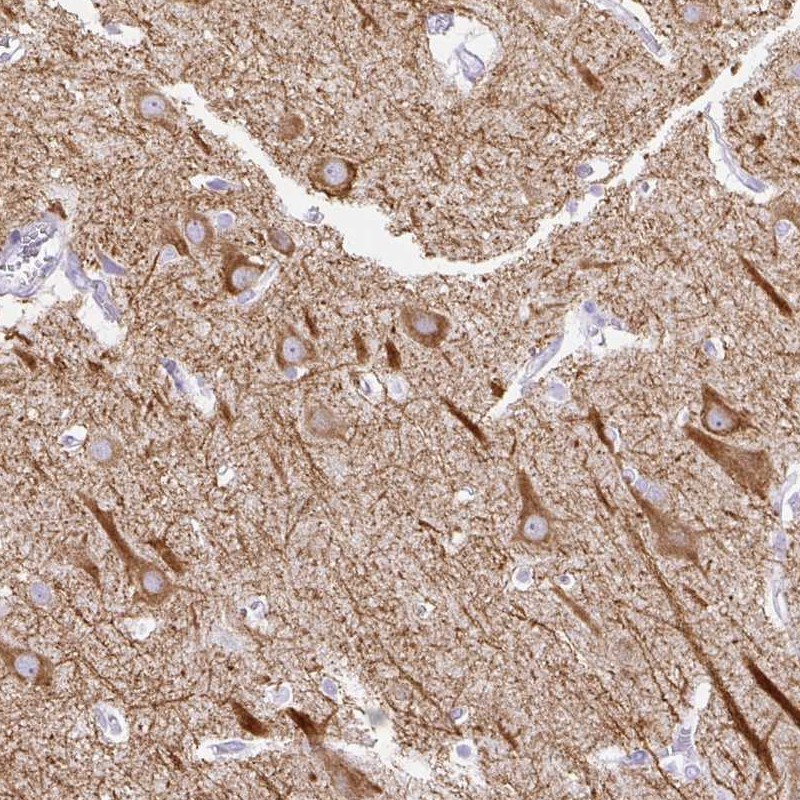
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetHEY1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHEY1 antibody, C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.2-2.5 ug/ml. IHC-P: 2-10 ug/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.5-1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID23462
- Target nameHEY1
- Target descriptionhes related family bHLH transcription factor with YRPW motif 1
- Target synonymsBHLHb31, CHF2, HERP2, HESR1, HRT-1, NERP2, OAF1, hHRT1, hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1, HES-related repressor protein 1, HES-related repressor protein 2, basic helix-loop-helix protein OAF1, cardiovascular helix-loop-helix factor 2, class B basic helix-loop-helix protein 31, hairy and enhancer of split-related protein 1, hairy-related transcription factor 1, hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9Y5J3
- Protein NameHairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a nuclear protein belonging to the hairy and enhancer of split-related (HESR) family of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)-type transcriptional repressors. Expression of this gene is induced by the Notch and c-Jun signal transduction pathways. Two similar and redundant genes in mouse are required for embryonic cardiovascular development, and are also implicated in neurogenesis and somitogenesis. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Converting melanoma-associated fibroblasts into a tumor-suppressive phenotype by increasing intracellular Notch1 pathway activity. Shao H et al., 2021, PLoS OneRead this paper
- Notch1 Pathway Activity Determines the Regulatory Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Melanoma Growth and Invasion. Shao H et al., 2015, PLoS OneRead this paper
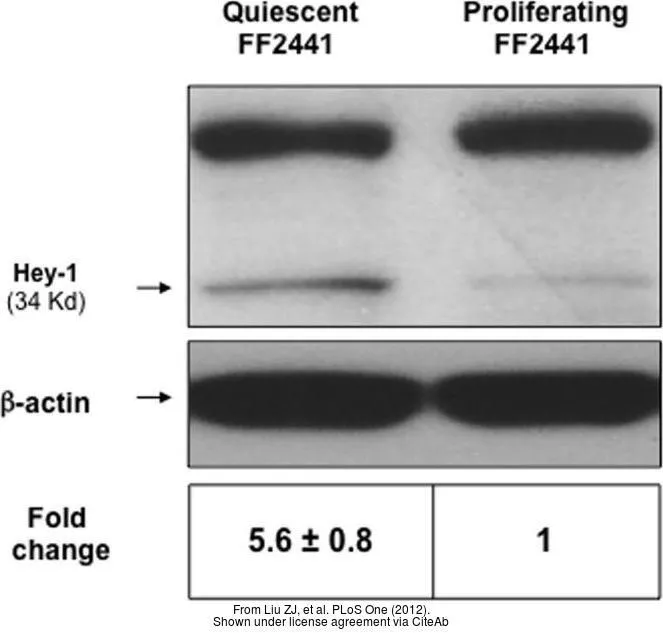
- Inhibition of fibroblast growth by Notch1 signaling is mediated by induction of Wnt11-dependent WISP-1. Liu ZJ et al., 2012, PLoS OneRead this paper
- Activation of Notch1 signaling in stromal fibroblasts inhibits melanoma growth by upregulating WISP-1. Shao H et al., 2011 Oct 20, OncogeneRead this paper



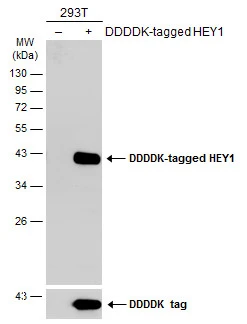
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with HEY1 antibody [HL2367] (GTX638573) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX638573/GTX638573_T-45033_20230512_WB_B_23051702_918.webp)